Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: SLE is an autoimmune disorder characterized by autoantibody-mediated tissue damage. Antibodies against C1q (anti-C1q) can identify patients with LN and rising titers predict renal flares and correlate with SLE disease activity. Despite the reported clinical significance of anti-C1q for SLE and the development of anti-C1q commercial kits, their performance characteristics in routine patient evaluation remain poorly defined. In this cross-sectional study, we aimed to compare the performance of three commercial ELISA-based anti-C1q kits for SLE diagnosis and disease activity.
Methods: An unselected cohort of 107 patients with suspicion of a systemic autoimmune disease (i.e., with autoimmune workup requested by a physician from February-October 2021), and 102 controls from the Mayo Clinic biobank were included and underwent anti-C1q testing with three kits (Buhlmann [Kit 1], Orgentec [Kit 2], Werfen [Kit 3]). Patients in the unselected cohort were classified as having SLE (meeting 2019 EULAR/ACR Classification Criteria) or a mimicker condition as per physician diagnoses. For patients with SLE, disease activity was assessed using SLEDAI and they were subclassified based on the presence of LN (history and/or active). Each anti-C1q kit was assessed for diagnostic performance of the following comparisons: SLE vs non-SLE, SLE vs mimickers, history of LN vs non-renal SLE, active LN vs non-active LN. Sensitivity, specificity, positive and negative likelihood ratios were calculated, and receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves were generated. The degree of association between anti-C1q and SLEDAI/complement levels was assessed using the Spearman correlation coefficient (rho). Between kit agreement was evaluated using Fleiss Ƙ.
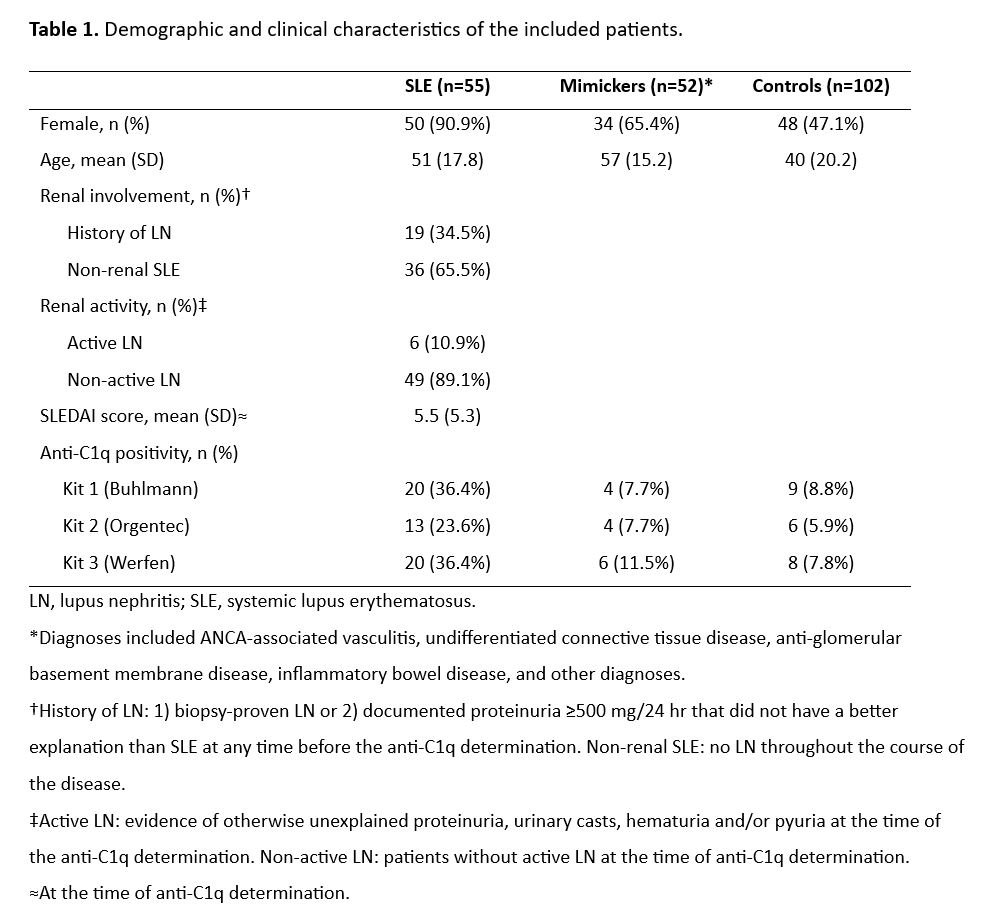
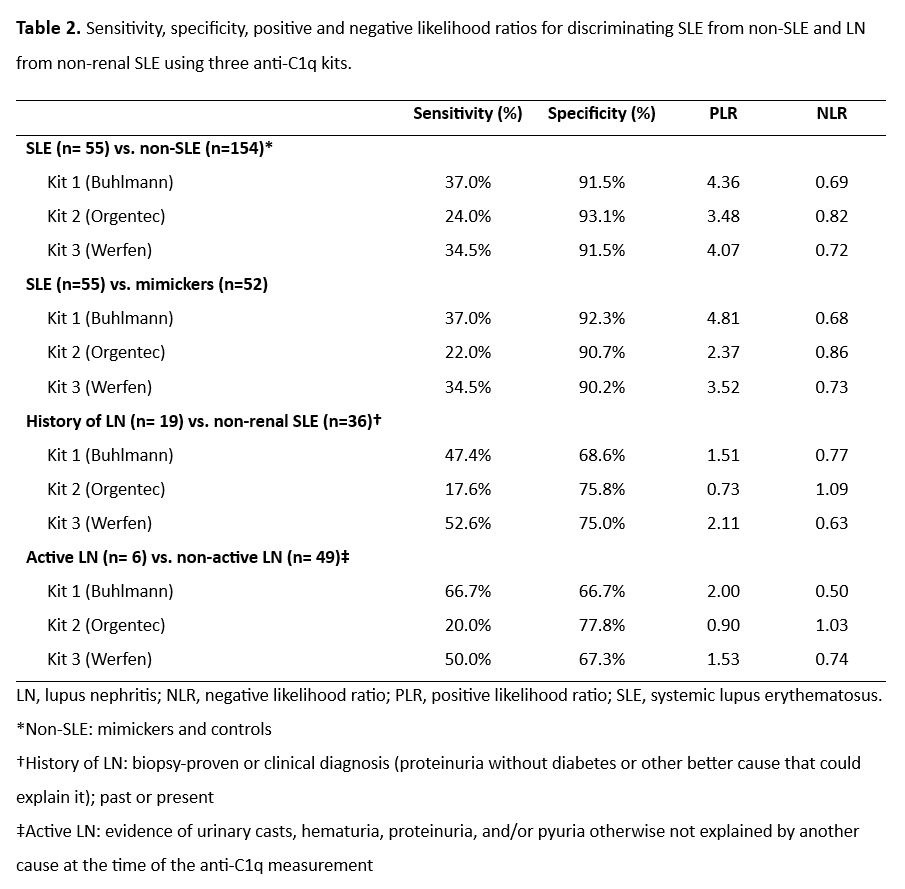
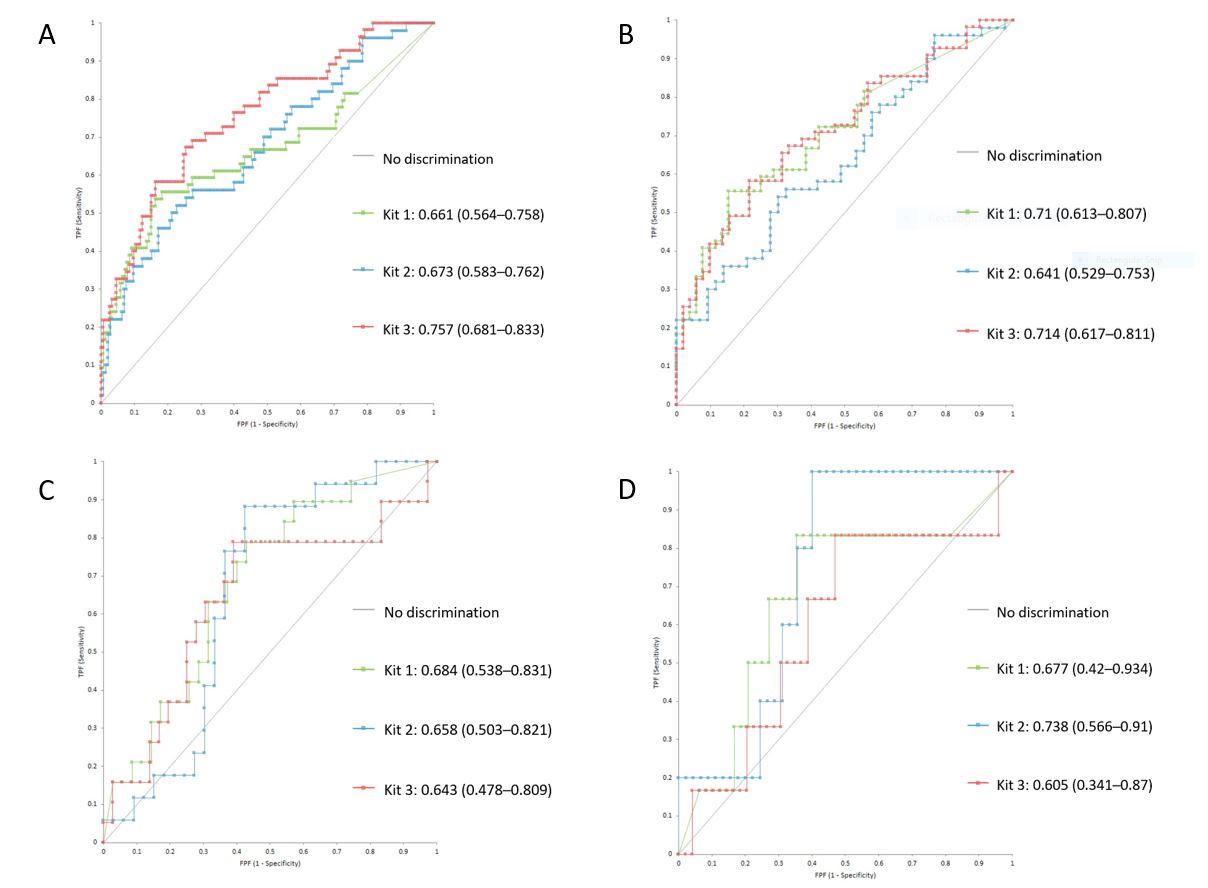
Results: A total of 209 patients were analyzed, 107 from the unselected cohort (55 SLE and 52 mimickers) and 102 from the control biobank. Table 1 contains the characteristics of the study groups. Overall, the three kits displayed low sensitivity and high specificity for all the comparisons (Table 2). Kit 3 had the best performance in discriminating patients with SLE from non-SLE (area under the curve [AUC]=0.76, 95% CI 0.7–0.84), whereas for the SLE vs mimicker comparison Kit 1 (AUC=0.71, 95% CI 0.61–0.81) and Kit 3 (AUC=0.71, 95% CI 0.62–0.82) exhibited adequate discrimination (Figure 1). Among patients with SLE, all kits exhibited poor discrimination of patients with history of LN vs non-renal SLE (AUC= 0.68, 0.66, 0.64; respectively), but Kit 2 displayed good discrimination for patients with active LN from non-active LN (AUC= 0.74, 95% CI 0.57–0.91). A positive correlation was observed between anti-C1q and SLEDAI scores (rho=0.4, 0.4, 0.5) whereas a negative correlation was found between anti-C1q and complement C3 (rho=-0.6, -0.5, -0.6) and C4 (rho=-0.4, -0.5, -0.4) for kits 1, 2, and 3, respectively. Agreement for SLE between the three kits was moderate (Ƙ=0.42).
Conclusion: Anti-C1q can identify patients with SLE and correlate with global and renal disease activity, highlighting their potential to function as follow-up markers in SLE. Agreement with commercial anti-C1q kits is variable. Further studies are required to validate anti-C1q kits for routine patient evaluation.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Gonzalez-Trevino M, Hetrick M, Sanchez-Rodriguez A, Duarte-Garcia A, Tebo A. Clinical Utility and Performance of Anti-C1q Antibodies for Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Comparative Analysis of Three Different Assays [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/clinical-utility-and-performance-of-anti-c1q-antibodies-for-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-comparative-analysis-of-three-different-assays/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/clinical-utility-and-performance-of-anti-c1q-antibodies-for-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-comparative-analysis-of-three-different-assays/