Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: General population-based cardiovascular (CV) risk estimators are known to underestimate CV risk in RA. High-sensitivity cardiac troponin T (hs-cTnT), typically measured during a work-up for acute coronary syndrome, is present in RA patients without known CVD. Moreover, hs-cTnT is associated with future CV events, independent of the 2019 ACC/AHA estimated 10-year atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) risk in RA suggesting its potential application as a screening marker for CV risk. However, the optimal subgroup of RA patients to screen with hs-cTnT remains unclear. The objective of this study was to determine the prevalence of hs-cTnT among RA patients not at high CV risk, and to identify clinical and biomarker factors associated with a detectable hs-cTnT to inform screening in the clinic.
Methods: We studied RA patients from a single-center observational cohort. The earliest blood sample was selected, and patients on lipid-lowering therapy were excluded. We measured the primary outcome, hs-cTnT, as well as inflammatory markers relevant to RA: high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hsCRP), IL-6, soluble tumor necrosis factor receptor 2 (sTNFR2), and lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 (Lp-PLA2). Estimated 10-year ASCVD risk was calculated, and patients with high ASCVD risk (10-year risk of >20%) were excluded. We determined the cross-sectional univariable associations between demographics, RA clinical factors, and inflammatory markers with detectable hs-cTnT ( >6ng/L). Variables from the univariable analysis with p< 0.10 were included in a multivariable logistic regression with ASCVD risk to identify factors independently associated with detectable hs-cTnT. The cohort was also categorized by population-based guidelines for low (< 5%), borderline (5-7.5%) or intermediate (7.5-20%) ASCVD risk and stratified by sex.
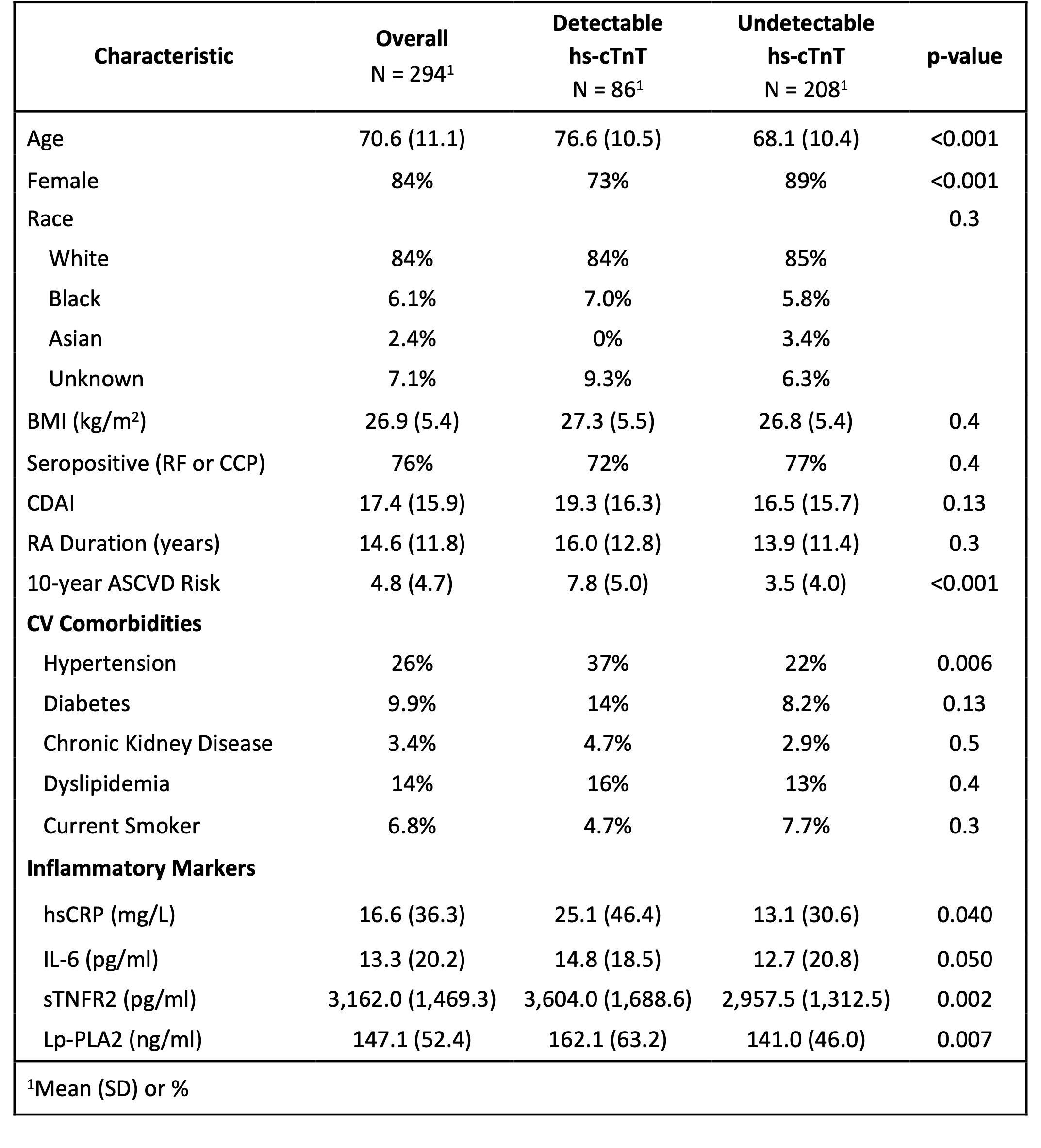
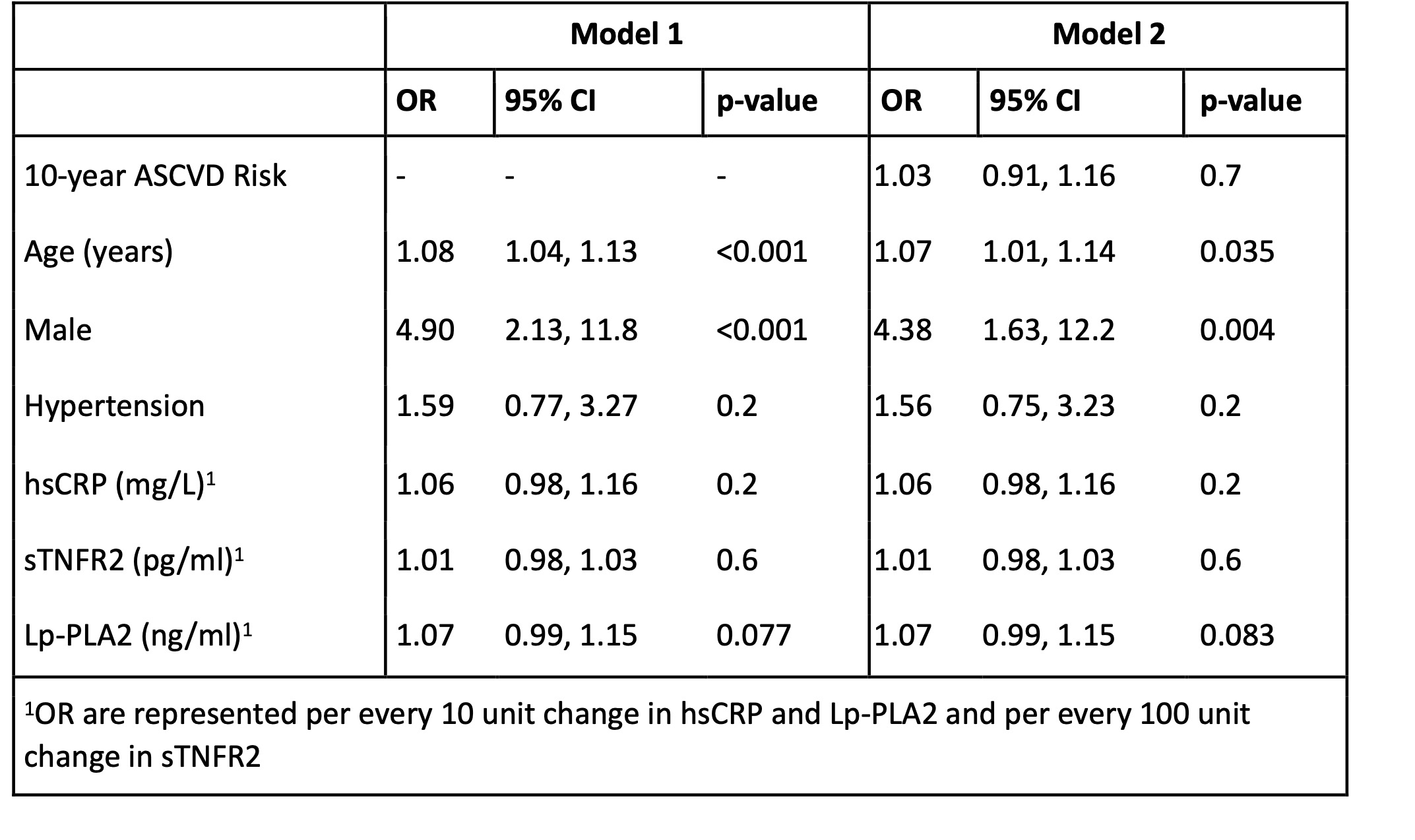
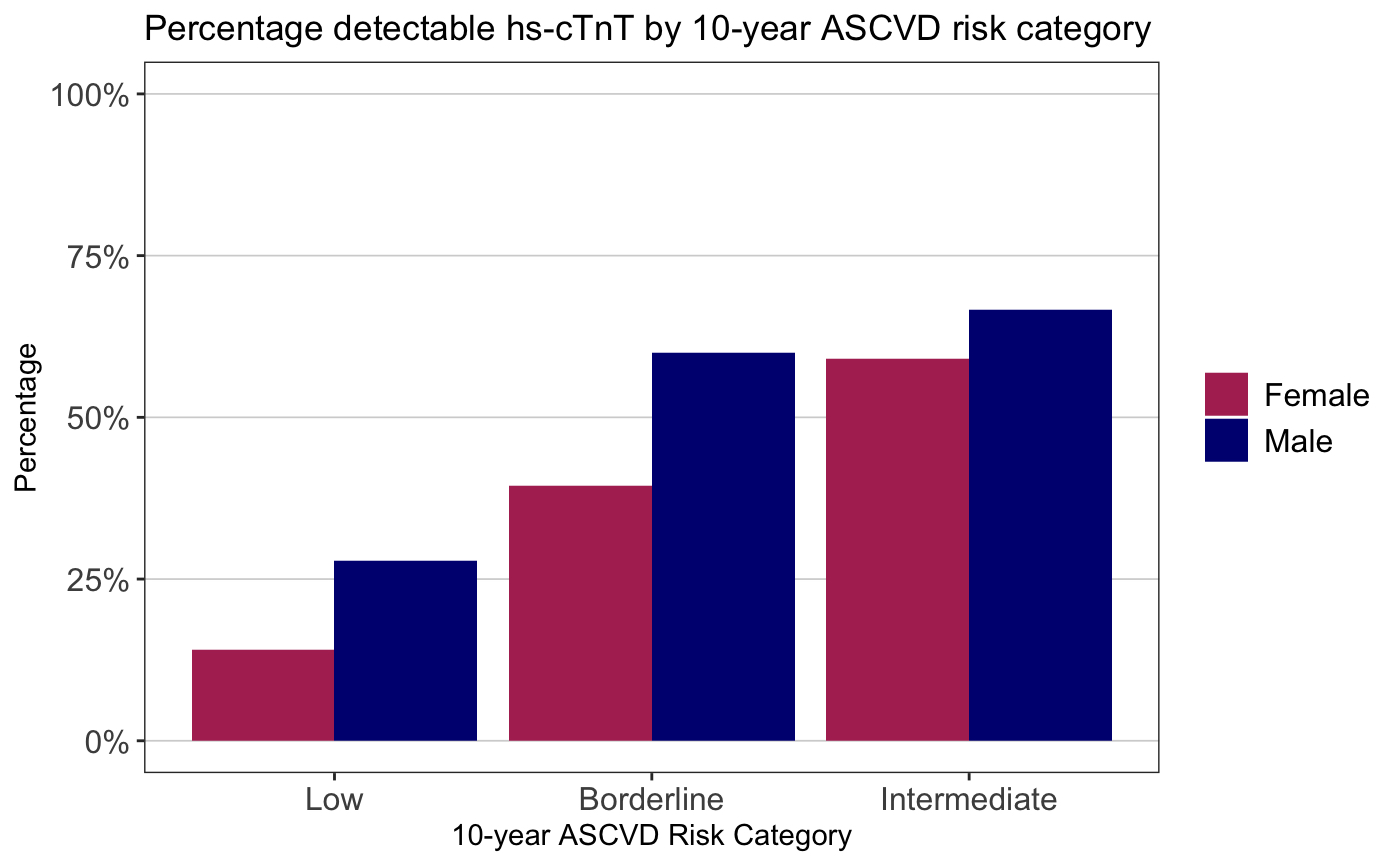
Results: We studied 294 RA patients with mean age 70.6; 84% were female, 76% were seropositive, mean RA duration was 14.6 years, 58% were on methotrexate, 52% were taking a biologic DMARD, mean Clinical Disease Activity Index (CDAI) was 17.4 (moderate severity), and mean ASCVD risk was 4.8% (low risk). 30% had a detectable hs-cTnT (Table 1). ASCVD risk was associated with detectable hs-cTnT (OR 1.22 (95% CI 1.15-1.29). In addition to ASCVD risk, age and sex were associated with detectable hs-cTnT (Table 2). Lp-PLA2 was the inflammatory marker most strongly associated with detectable hs-cTnT in multivariable analysis. 15% of RA patients with low ASCVD risk and 44% with borderline ASCVD risk had a detectable hs-cTnT; 27% of males and 14% of females with low ASCVD risk had detectable hs-cTnT (Figure 1).
Conclusion: Approximately 30% of RA patients with low-intermediate ASCVD risk based on population-based CV guidelines had a detectable hs-cTnT, an independent risk factor for future CV events. While age and sex are components of ASCVD risk, additionally accounting for these factors in RA may help identify patients with low/borderline ASCVD risk in whom to measure hs-cTnT. Lp-PLA2, a clinically available biomarker associated with unstable plaque, may also aid in identifying individuals with elevated CV risk not identified with population-based ASCVD risk estimators.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Usiskin I, Jeffway M, Liu F, Shadick N, Weinblatt M, Weber B, Liao K. Clinical Characteristics and Biomarkers Associated with Detectable High-Sensitivity Cardiac Troponin in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/clinical-characteristics-and-biomarkers-associated-with-detectable-high-sensitivity-cardiac-troponin-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/clinical-characteristics-and-biomarkers-associated-with-detectable-high-sensitivity-cardiac-troponin-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/