Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 1:00PM-3:00PM
Background/Purpose: Musculoskeletal ultrasound (US) has been reported to predict radiographic progression in rheumatoid arthritis (RA). The aim of the study was to test the predictive value of composite disease activity indices (DAI) based on solely clinical as well as clinical and US (USDAI) information to predict radiographic progression in RA.
Methods: Data from the Swiss Clinical Quality Management (SCQM) database were extracted from patients with RA;
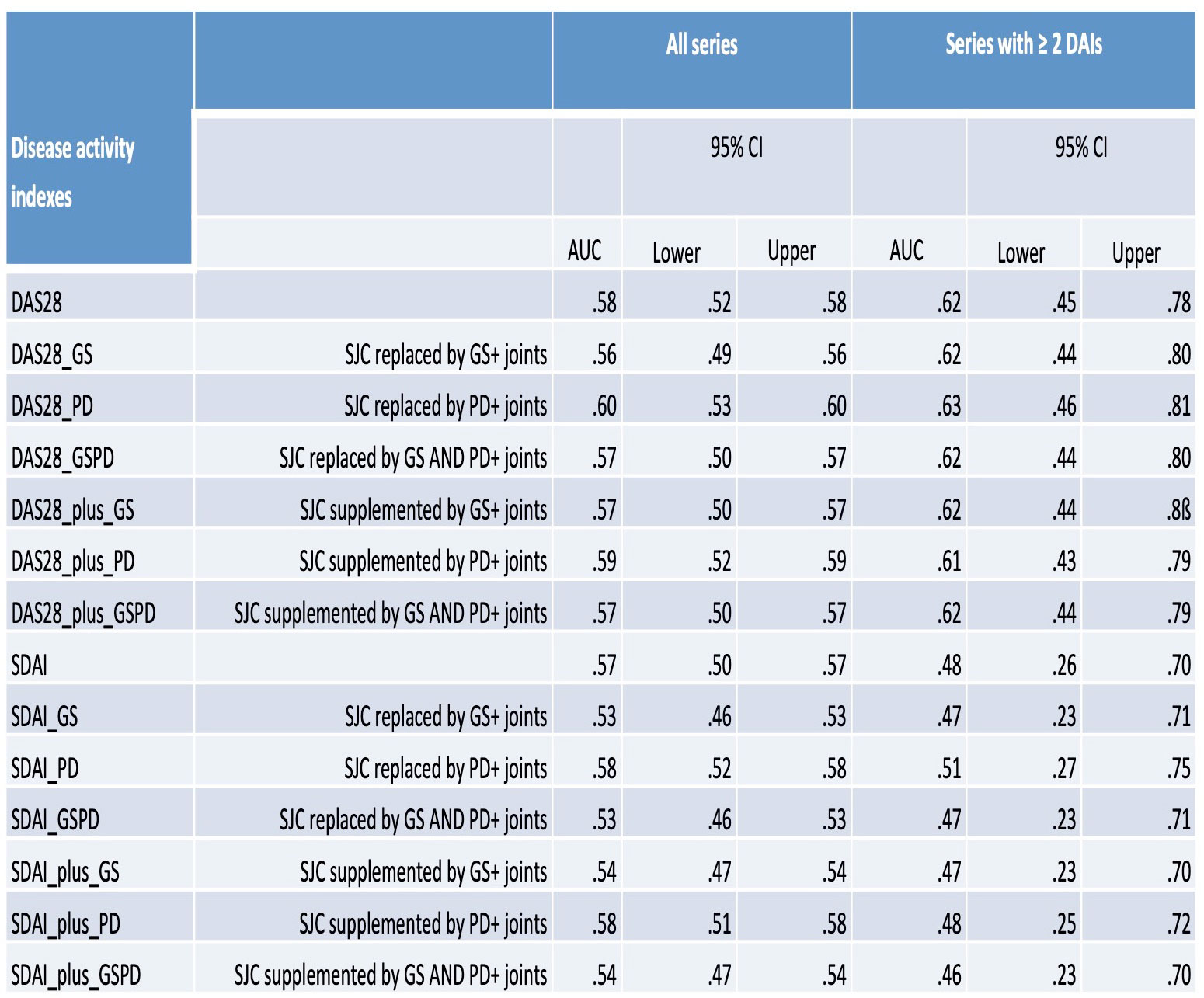
USDAIs were created based on previous publications (1) (Table 1). In summary, the disease activity score in 28 joints (DAS28) and the simplified disease activity index (SDAI) were modified by supplementing or replacing the clinical swollen JC with joints showing signs of power Doppler (PD) and/or grey scale (GS) synovitis. Series with two standard x-rays of the hands (difference ≥ 183 days) and ≥1 visit with clinical and US data in between were analyzed. Progression was defined as an increase of ≥6.27 points of the Ratingen-Rau x-ray score.
Receiver operating curve (ROC) analyses were used to assess predictive ability of every DAI for radiographic progression.
As a subanalysis, ROCs using the median DAIs of series with ≥2 DAIs between two x-rays were run. Clinical DAS28/SDAIs were compared to their respective USDAI counterpart with the highest area under the curves (AUC).
References:
1. Mandl P et al., Arthritis Care Res 2013
Results: We included 649 series in 475 patients. Progression was observed in 84/649 (12.9%) series. Mean difference between the x-rays was 27.6±18.0 months. Mean age was 56.3±12.7 years, 474/649 (73%) series were from female patients. There was no significant difference between the AUC of the ROC of SDAI vs. SDAI_PD (p=0.19) nor between DAS28 vs. DAS28_PD: (p=0.17) (Figure 1A, Table 1). Similarly, when analyzing only series with ≥2 DAIs (143 series) we observed no difference between the AUC of the ROC of SDAI vs. SDAI-PD (p=0.28) nor between that of DAS28 vs. DAS28_PD (p=0.23) (Figure 1B, Table 1).
Conclusion: The predictability of radiographic progression by disease activity measures was generally limited. The composite USDAIs containing sonographic JC were not superior for predicting radiographic progression compared to their clinical counterparts although there was a trend for higher predictive value for indices containing PD.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Gessl I, Deimel T, Studenic P, Tamborrini G, Zufferey P, Aletaha D, Moeller B, Mandl P. Clinical and Ultrasound-based Composite Disease Activity Indices and Radiographic Progression in Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/clinical-and-ultrasound-based-composite-disease-activity-indices-and-radiographic-progression-in-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/clinical-and-ultrasound-based-composite-disease-activity-indices-and-radiographic-progression-in-rheumatoid-arthritis/