Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 19, 2024
Title: Abstracts: Muscle Biology, Myositis & Myopathies – Basic & Clinical Science II
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 11:00AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Anti-melanoma differentiation-associated gene 5 (MDA5)-positive dermatomyositis (DM) is frequently associated with rapidly progressive interstitial lung disease (RP-ILD), leading to poor prognosis. Initial combinational therapy with glucocorticoids, calcineurin inhibitors, and cyclophosphamide has improved outcomes, but some patients remain refractory. This study aimed to identify the epitopes of MDA5 and elucidate the clinical implications of autoantibodies targeting these sites.
Methods: We explored candidate epitopes by screening T7 phage libraries displaying random 7-35 peptides of MDA5 and performing enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISA) with MDA5 fragments using sera from 16 Japanese anti-MDA5-positive DM-ILD patients. Anti-MDA5 positivity was confirmed by immunoprecipitation. MDA5 protein was divided into 100 amino acid segments expressed by E. Coli, overlapping by 50 amino acids, which were used for ELISA to validate the candidate epitopes. Then, we classified 30 anti-MDA5-positive DM-ILD patients who received initial combinational therapy into resistant or non-resistant groups. Resistance was defined as disease exacerbation within 6 months from initial therapy, resulting in death or the need for additional therapy including plasmapheresis. The antibody titers to candidate epitopes were compared between the two groups using the Wilcoxon signed-rank test. Antibody titers were indexed using a positive control sample, and the optimal cutoff value was determined to predict resistance.
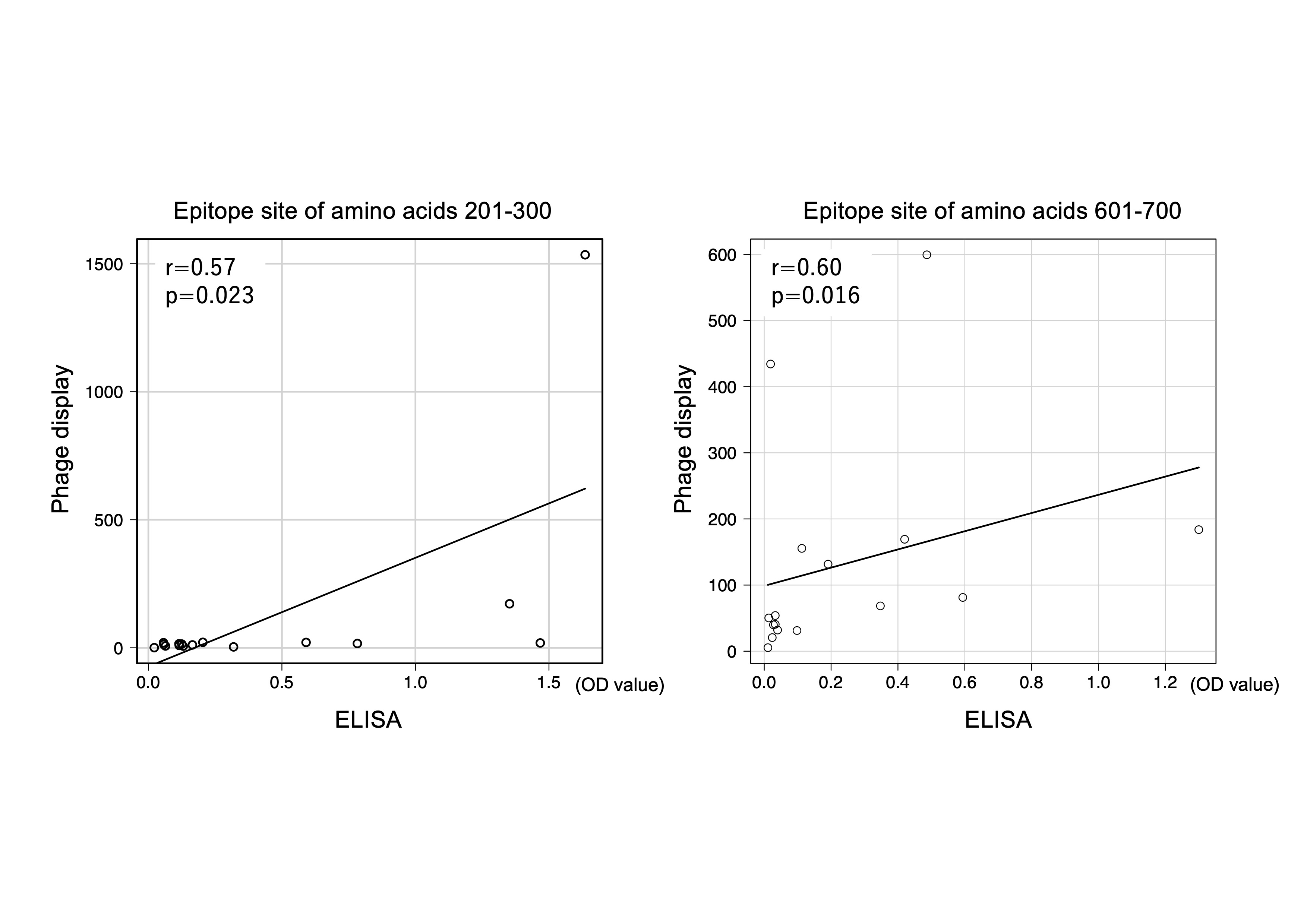
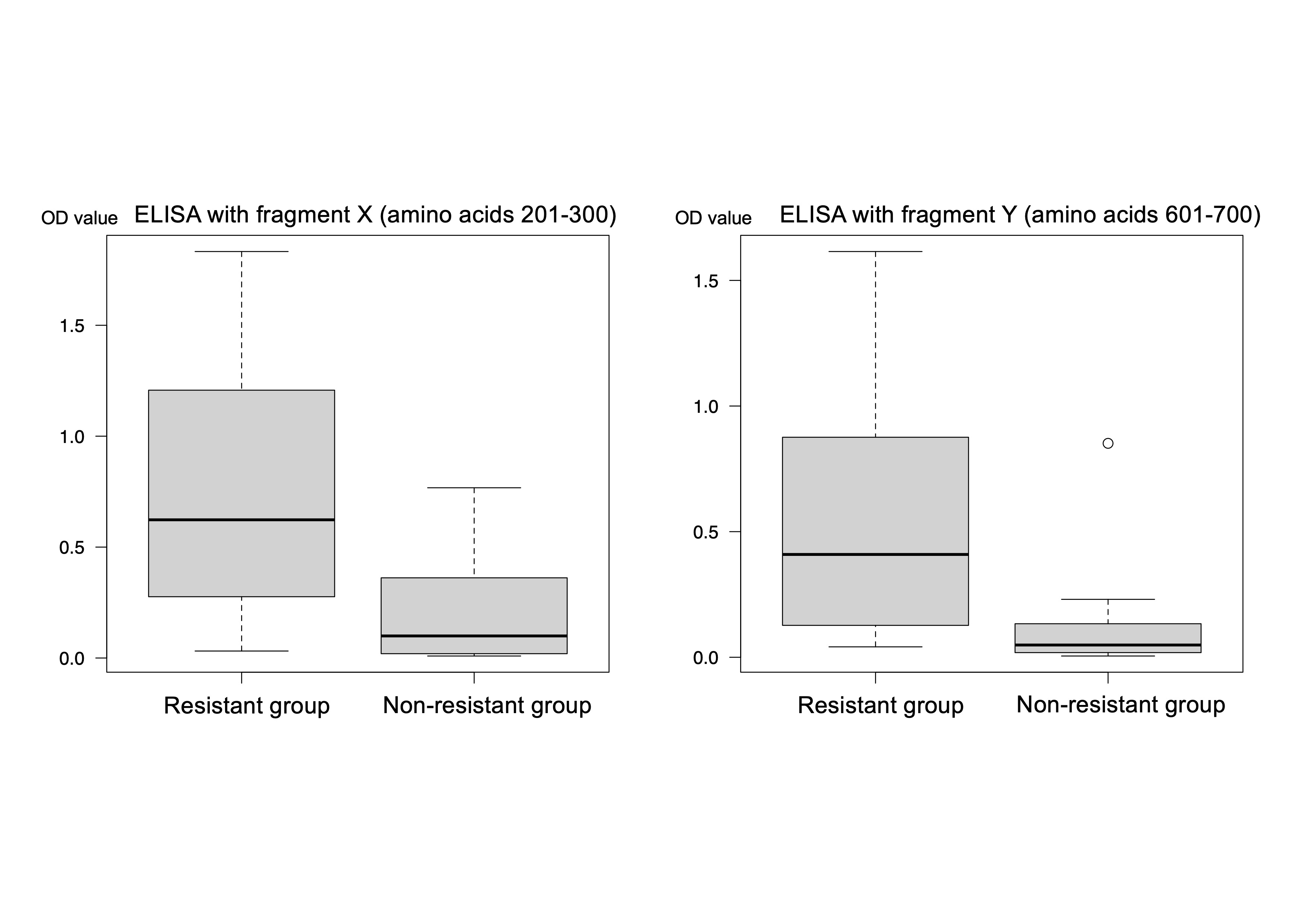
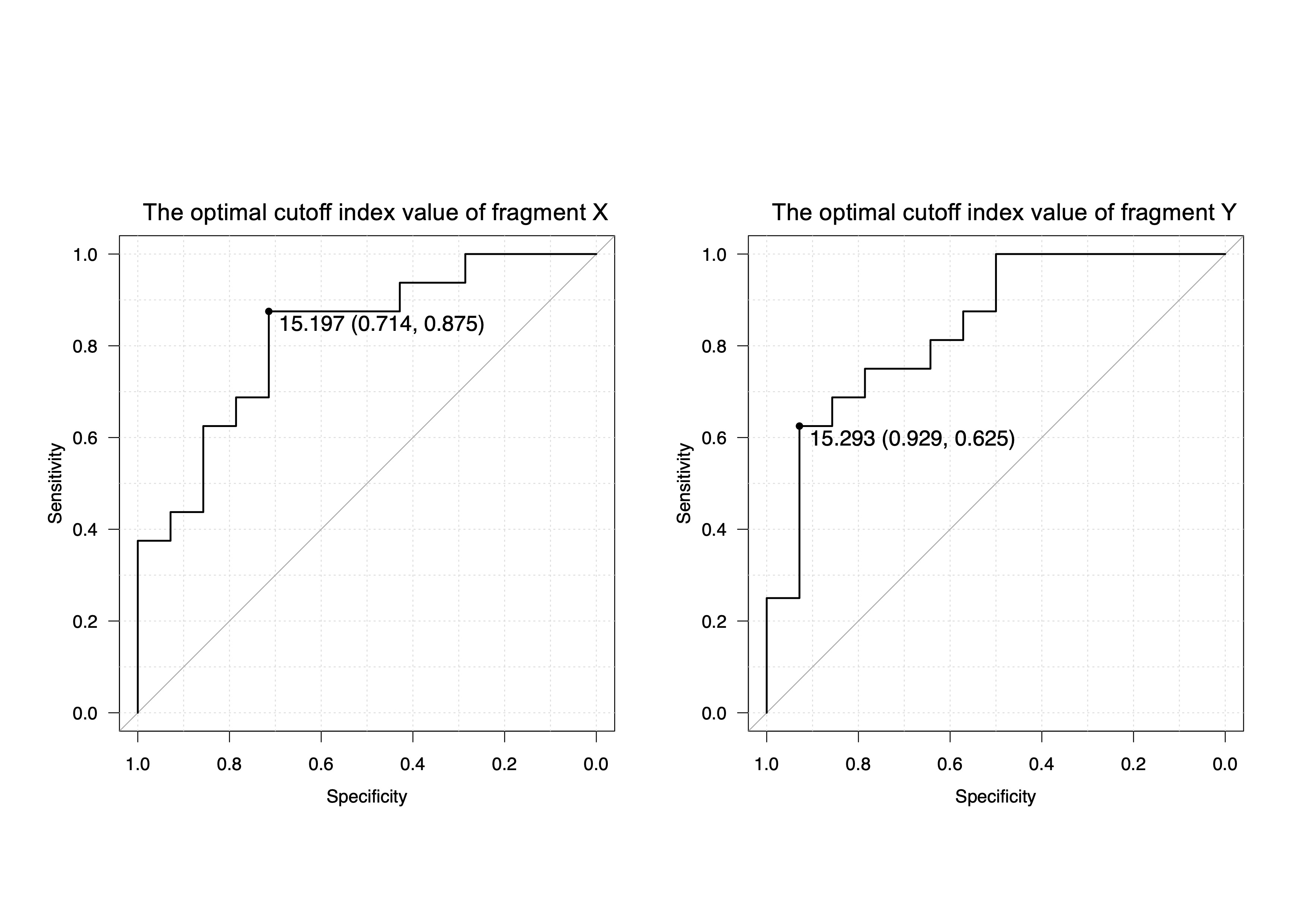
Results: 16 anti-MDA5 sera showed high reactivity to two inter-domain regions, X (amino acids 201-300) and Y (amino acids 601-700), which correlated between phage display and ELISA (r=0.57, p=0.023; r=0.60, p=0.016; respectively, Spearman’s correlation, figure 1), suggesting them as principal epitopes of MDA5. Autoantibody titers measured by ELISA using region X and Y were significantly higher in the resistant group (n=16) compared to the non-resistant group (n=14) (0.623 vs 0.0995, p=0.0021; 0.409 vs 0.0488, p=0.0011; respectively, figure 2). Optimal cutoff values yielded sensitivity and specificity of 87.5% and 71.4% for region X, and 62.5% and 92.9% for region Y, in predicting treatment resistance (figure 3).
Conclusion: Two main epitopes of MDA5 were identified in region X and Y. Autoantibody titers against these regions can effectively predict resistant cases to conventional combinational therapy of immunosuppressants in Japanese anti-MDA5-positive DM-ILD patients.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Sasai T, Nakashima R, Ogawa A, Nonaka M, Nomura N, Nohda Y, Shirakashi M, Hiwa R, Tsuji H, Akizuki S, Yoshifuji H, Mimori T, Morinobu A. Autoantibody Titers Against Specific Epitope Peptides Predict Treatment Resistance in Interstitial Lung Disease Associated with Anti-MDA5 Dermatomyositis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/autoantibody-titers-against-specific-epitope-peptides-predict-treatment-resistance-in-interstitial-lung-disease-associated-with-anti-mda5-dermatomyositis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/autoantibody-titers-against-specific-epitope-peptides-predict-treatment-resistance-in-interstitial-lung-disease-associated-with-anti-mda5-dermatomyositis/