Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 7, 2021
Title: Epidemiology & Public Health Poster II: Inflammatory Arthritis – RA, SpA, & Gout (0560–0593)
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Lipid mediators are endogenously derived from the metabolism of omega-3 and omega-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) and have important roles in promoting and resolving inflammation. As such PUFAs have been implicated in the pathogenesis of systemic inflammatory and autoimmune diseases including rheumatoid arthritis (RA). As lipid mediators share common pathways and enzymes, individual lipid mediators do not act in isolation and therefore must be analyzed in combination as a profile. The goal of this study was to determine the association of polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA)-derived lipid mediator profiles with progression from pre-diagnosis RA-related autoimmunity to clinically apparent inflammatory arthritis (IA).
Methods: Using the Studies of the Etiologies of Rheumatoid Arthritis (SERA), we examined a prospective cohort that includes first-degree relatives (FDRs) of individuals with RA (FDR cohort) and individuals who screened positive for RA-related autoantibodies at health fairs (screened cohort). We followed 133 anti-CCP3.1 positive participants, of which 29 participants subsequently developed IA during follow-up (mean time to IA development = 1.15 years). Exposures included concentrations (pg/ml) of lipid mediators quantified from baseline plasma samples via liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry with profiles identified via principal component analysis (PCA). Multivariable Cox proportional hazard models were then developed for each lipid mediator profile, either stratified by or adjusted for HLA-DRB1 shared epitope status (dependent on presence of effect modification between lipid mediator profile and shared epitope).
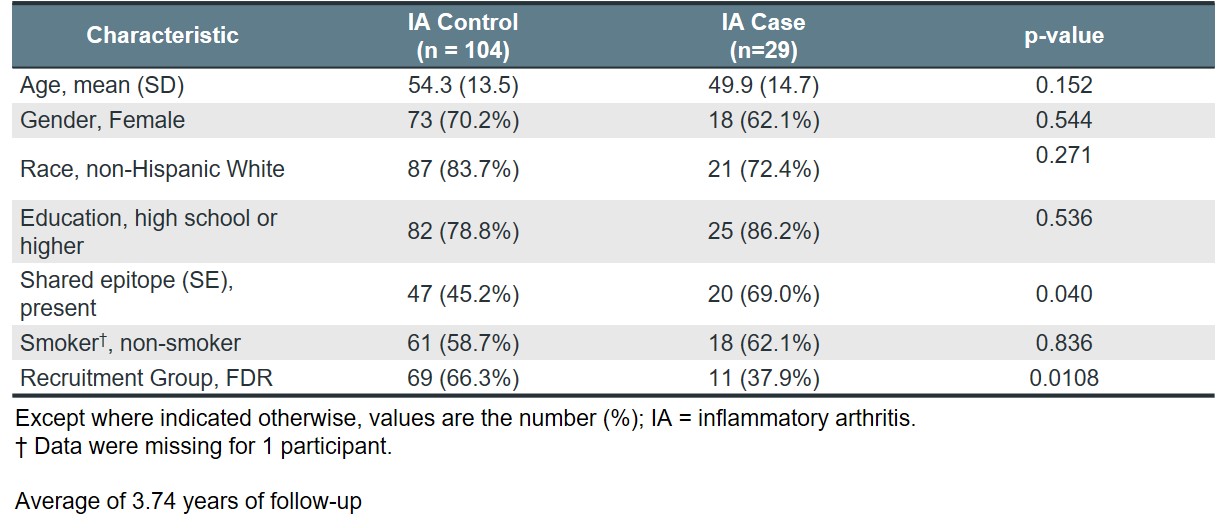
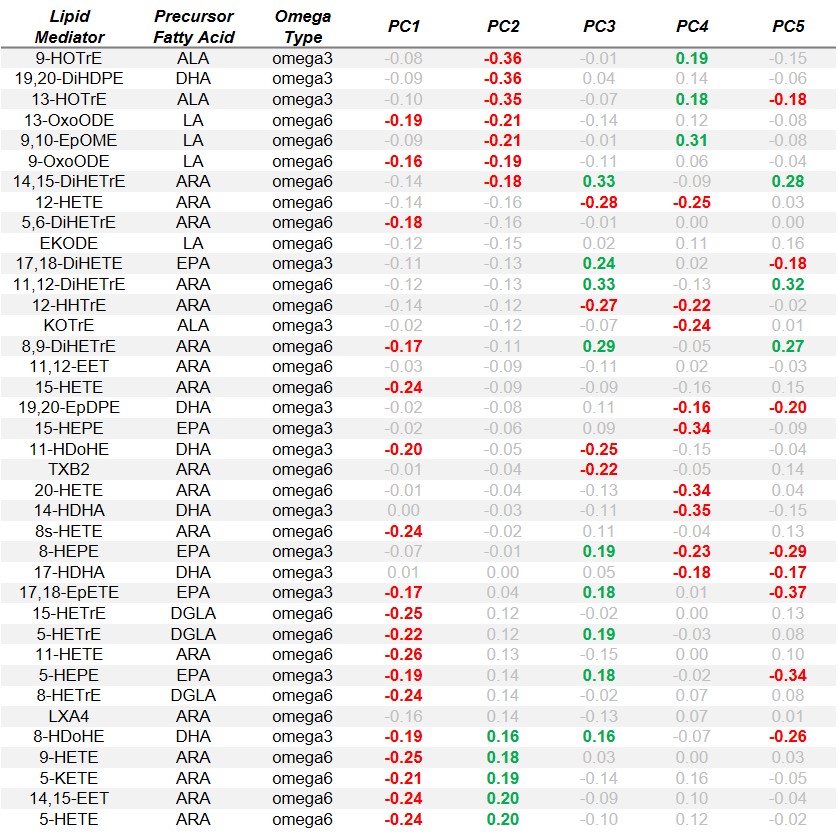
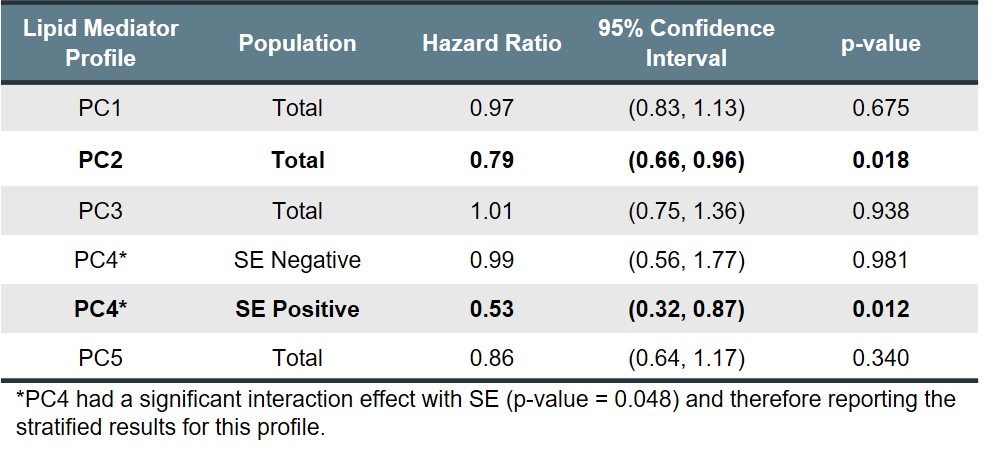
Results: Baseline characteristics of the study population is shown in Table 1. The top 5 PCA components (PC) explained >50% of all variance among the lipid mediators, with the factor loadings of each lipid mediator shown in Table 2. Of these lipid mediator profiles, PC2 had a significant protective effect on IA risk (HR 0.79, 95% CI: 0.66-0.96, p-value = 0.018) in the total study population (Table 3). For profile PC2, the important lipid mediators had a mix of positive and negative loadings for lipid mediators in the cytochrome P450 soluble epoxide hydrolase (CYP sEH) and 15-lipoxygenase (15-LOX) enzymatic pathways. PC4 also demonstrated a significant protective effect on IA risk, but only within the shared epitope positive study population (HR 0.53, 95% CI: 0.32-0.87, p-value = 0.012). For profile PC4, the vast majority of important lipid mediators had negative loading factors and are downstream products from omega-3 parent fatty acids. Other lipid profiles identified showed no association with the risk of IA.
Conclusion: Our study revealed two lipid mediator profiles to be significantly associated with incident IA in a high-risk pre-diagnosis cohort characterized by ACPA positivity. These findings suggest specific PUFA metabolite profiles impact on the early evolution of RA and ultimately the development of IA, some working solely within the SE positive population.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Vanderlinden L, Bemis E, Polinski K, Demoruelle K, Feser M, Seifert J, Mikuls T, Weisman M, Buckner J, Deane K, Clare-Salzler M, Holers V, Norris J. Association of Lipid Mediator Profiles and Development of Future Incident Inflammatory Arthritis in a High Risk, Anti-citrullinated Protein Antibody Positive Population [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/association-of-lipid-mediator-profiles-and-development-of-future-incident-inflammatory-arthritis-in-a-high-risk-anti-citrullinated-protein-antibody-positive-population/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/association-of-lipid-mediator-profiles-and-development-of-future-incident-inflammatory-arthritis-in-a-high-risk-anti-citrullinated-protein-antibody-positive-population/