Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Monoclonal antibody (mAb) therapy and small interfering RNA (siRNA) therapy represent two cutting-edge approaches in treating various diseases, such as hyperlipidemia. Our study aims to understand the association between autoimmune complications and siRNA therapy using the U.S. cohort study of TriNetX.
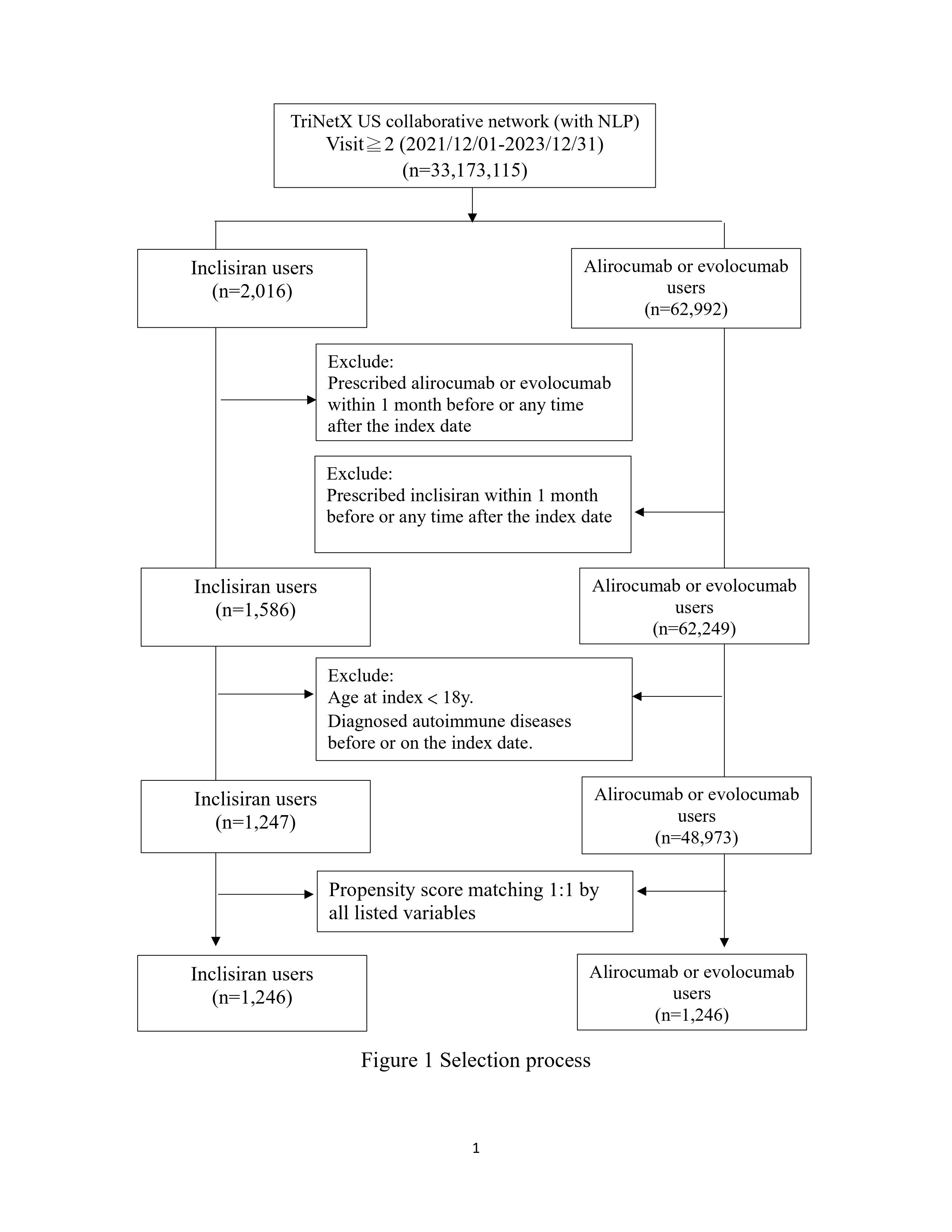
Methods: This retrospective cohort study utilized TriNetX, an extensive real-world data platform, incorporating de-identified health records from over 250 million individuals. Data from 62 US healthcare organizations (HCOs) were analyzed between December 1, 2021, and December 31, 2023. Patients prescribed PCSK9 inhibitors, including inclisiran, alirocumab, and evolocumab, were included. Outcomes, including autoimmune disease incidence, were defined by ICD-10-CM codes. Covariates assessed included demographics, lifestyle factors, medical services, comorbidities, medications, and laboratory results. Propensity score matching (1:1) using nearest neighbor matching with a 0.1 caliper ensured balanced cohorts.
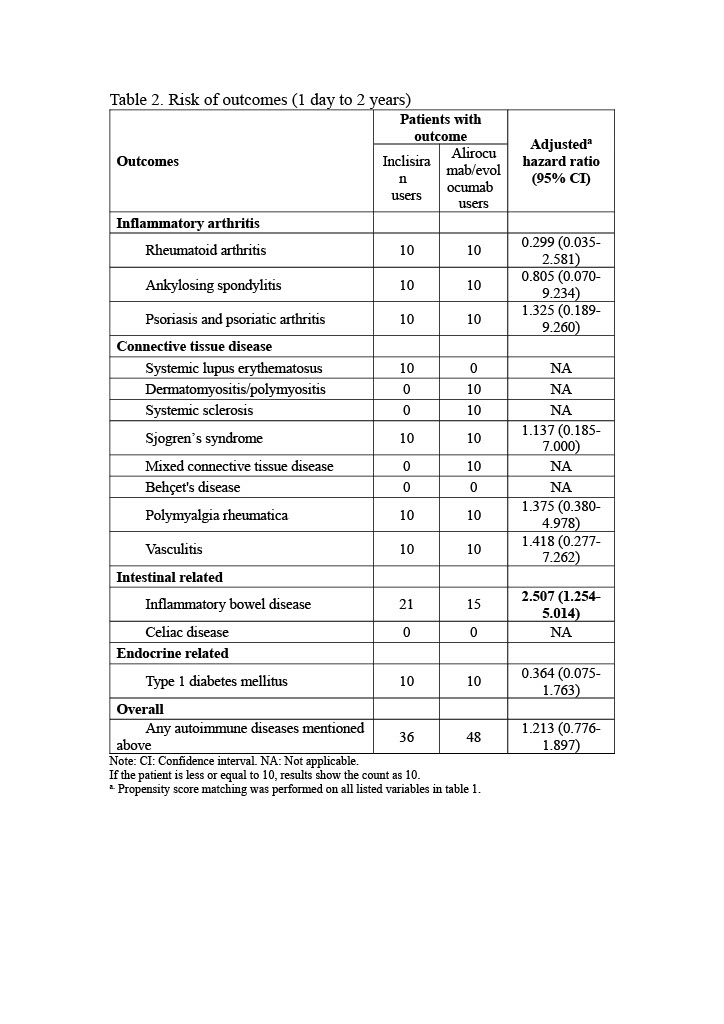
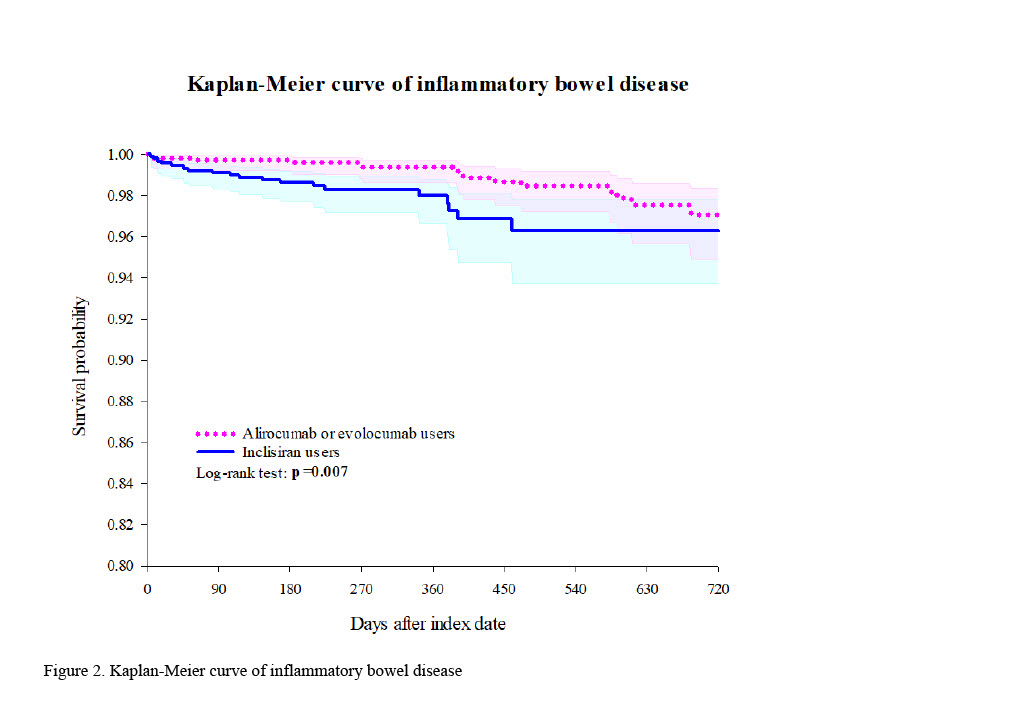
Results: This study included 65,008 participants (2,016 inclisiran users and 62,992 alirocumab/evolocumab users). After propensity score matching, 1,246 participants were in each group. Inclisiran users exhibited a significantly higher risk of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) compared to alirocumab/evolocumab users (hazard ratio [HR]: 2.507, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.254-5.014). No significant differences were observed for other autoimmune diseases. Kaplan-Meier curves indicated a significant difference in IBD incidence between the cohorts (Log-Rank test, p=0.007). Subgroup analyses by gender, age, and race revealed non-significant variations in IBD risk, with inclisiran users generally showing a higher, though not statistically significant, risk across most subgroups.
Conclusion: In our study, inclisiran users demonstrated a significantly higher risk of IBD compared to alirocumab/evolocumab users. Future research should investigate the underlying mechanisms driving this increased risk and evaluate long-term safety across diverse populations. Clinically, monitoring for IBD symptoms in patients receiving inclisiran is recommended to ensure timely intervention and management.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Chen L. Association Between Small Interfering RNA Therapy and Autoimmune Diseases: U.S. Prospective Cohort Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/association-between-small-interfering-rna-therapy-and-autoimmune-diseases-u-s-prospective-cohort-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/association-between-small-interfering-rna-therapy-and-autoimmune-diseases-u-s-prospective-cohort-study/