Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 19, 2024
Title: Abstracts: Systemic Sclerosis & Related Disorders – Clinical III
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 11:00AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: The extent of skin involvement and its rate of progression can provide prognostic information for systemic sclerosis (SSc)-related morbidity and mortality. Moreover, skin assessment is a key outcome measure in SSc clinical trials. Thus, developing an accurate method to assess this disease manifestation is imperative. Ultrasound (US)-based methods have been proposed as a potential tool for the objective assessment of skin fibrosis in SSc. However, a large-scale comparison of US-based assessment with histological skin fibrosis has not been reported. Herein, we evaluated the US based skin assessments for their face validity (differentiation between involved SSc skin and healthy controls), construct validity (comparison to modified Rodnan Skin score [mRSS]), and criterion validity (comparison to histological fibrosis).
Methods: Patients with SSc and healthy controls (HCs) were enrolled at a specialized scleroderma clinic. All participants underwent clinical and ultrasound assessment followed by a 3-mm forearm punch skin biopsy. Predefined, standardized areas of 1 cm2 size were assessed on the finger, hand, and forearm bilaterally. mRSS, ultrasound, and histological evaluations were performed by blinded, independent assessors. All mRSS assessments were performed by one experienced SSc clinical expert. US assessments were performed with a high frequency (22 MHz) GE LOGIQ P9 machine. Specifically, dermal thickness, echogenicity, and elasticity were assessed. The histological evaluation included measurement of dermal thickness on H&E staining, automated assessment of collagen density on Masson trichrome using Image J, and a semi-quantitative assessment of skin fibrosis by an SSc skin pathology expert (ranging from 0 (normal) to 3 (severely fibrotic). Correlation between US measures and mRSS and histological parameters was assessed using Spearman’s correlation.
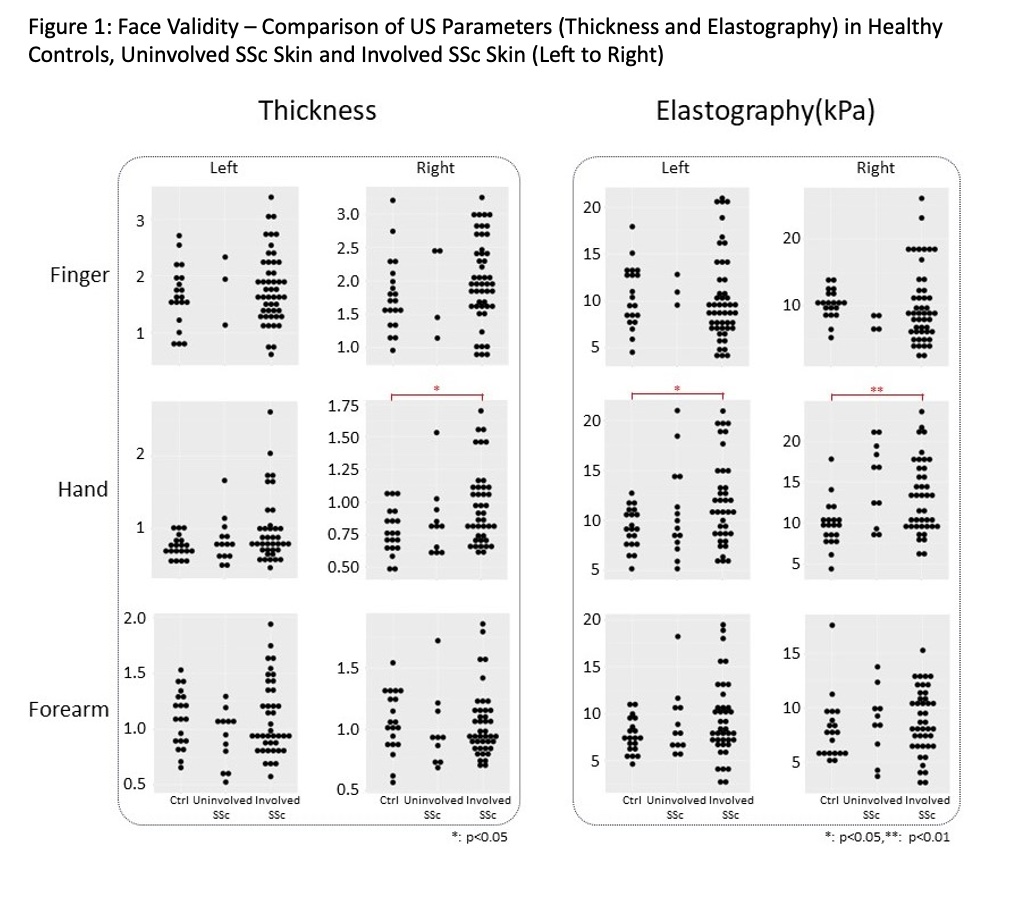
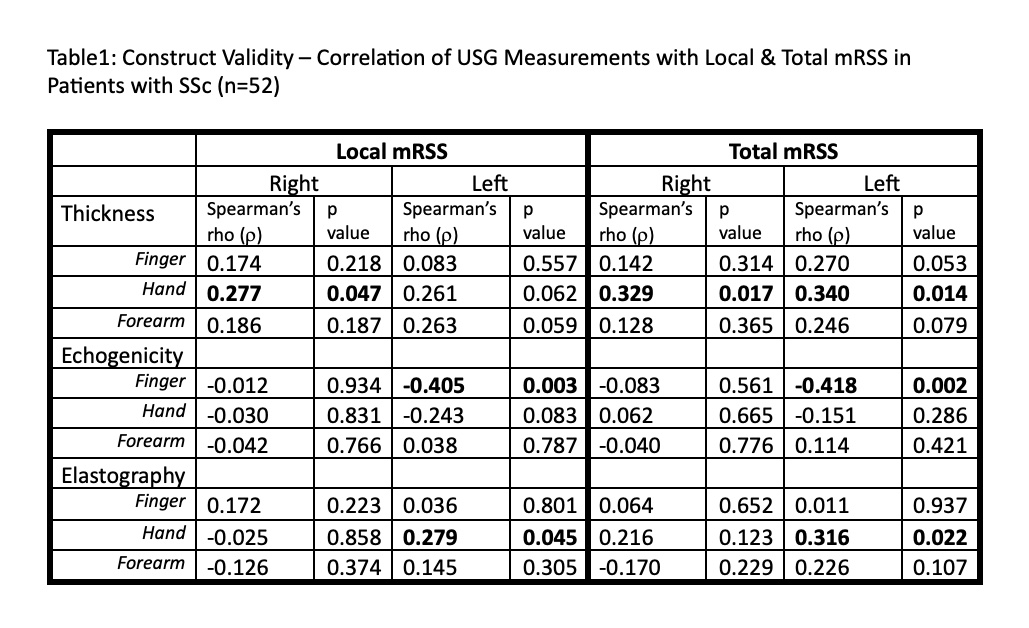
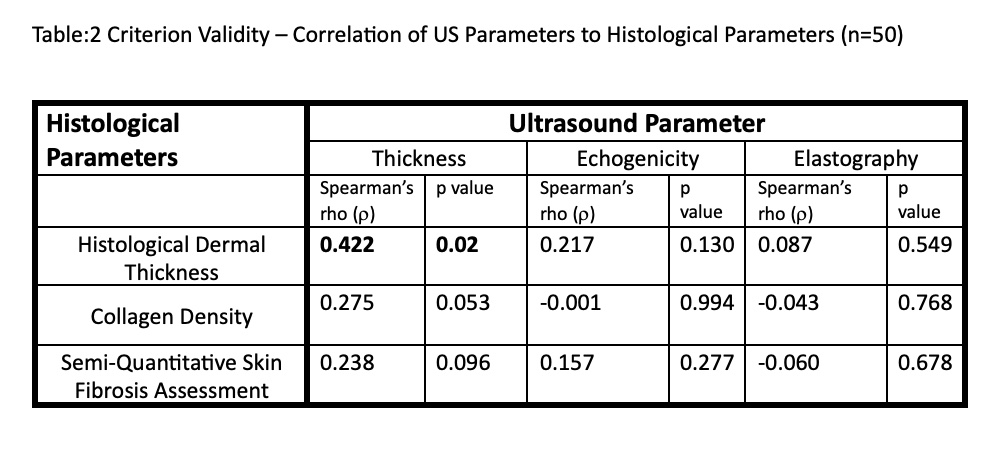
Results: A total of 20 HCs and 52 SSc patients (11 early diffuse, 26 late diffuse, 6 early limited and 9 late limited) were assessed. The demographic background of SSc patients and controls was similar. The SSc patients had a median mRSS of 13.5 and disease duration of 5.41 years. Except in the hand area, the three US variables were unable to differentiate between HCs and patients (see Figure 1 for dermal thickness and elastography – data for echogenicity not shown). There was a weak correlation between US-based thickness and clinical local skin score & mRSS in the hand area (Table 1). Similarly, elastography showed weak correlation in the hand area. Other than moderate correlation between US-based dermal thickness and histological thickness, no other significant correlations between US parameters and histological measurements (Table 2).
Conclusion: In the largest study comparing US-based parameters with skin histological fibrosis to date, high-frequency ultrasound with a commonly used commercial device did not have sufficient face-, construct-, or criterion validity. Alternative methods are needed to provide a more accurate assessment of skin involvement in SSc.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Desai R, Tan F, Wu M, Browning J, Theodore S, Zhang M, Skaug B, Mayes M, Assassi S. Assessment of Skin in Patients with Systemic Sclerosis Using High Frequency Ultrasound : A Comparative Study with Histology and Clinical Parameters of Skin Disease [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/assessment-of-skin-in-patients-with-systemic-sclerosis-using-high-frequency-ultrasound-a-comparative-study-with-histology-and-clinical-parameters-of-skin-disease/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/assessment-of-skin-in-patients-with-systemic-sclerosis-using-high-frequency-ultrasound-a-comparative-study-with-histology-and-clinical-parameters-of-skin-disease/