Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: As artificial intelligence (AI) platforms continue to evolve, large language models (LLMs) such as ChatGPT by OpenAI are increasingly being utilized by patients and healthcare providers as a source of health information. However, it is crucial to consider the advantages and limitations of such platforms. The objective of the study is to assess the accuracy and completeness of responses generated by ChatGPT compared to validated information resources on recombinant Zoster vaccination in patients with rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases (RMD).
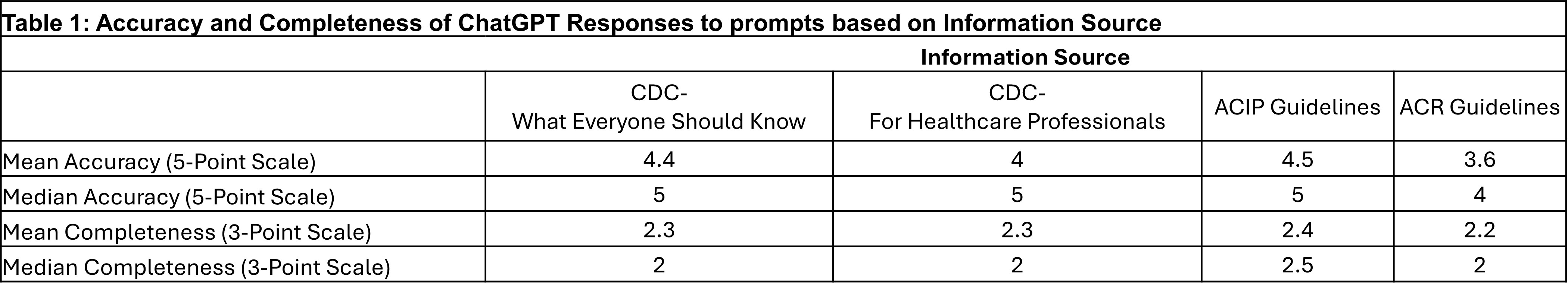
Methods: In this cross-sectional study, twenty prompts derived from three validated sources of information on recombinant Zoster vaccine were entered into ChatGPT 3.5. The sources included: 1) the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), with information from both ‘What Everyone Should Know’ and ‘Healthcare Professionals’ sections; 2) guideline recommendations from the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP); and 3) the American College of Rheumatology (ACR). These guidelines were framed as questions and inputted as prompts into ChatGPT. The responses generated by ChatGPT were assessed for accuracy (5-Point Likert Scale 1 – completely incorrect to 5 – completely correct) and completeness (3-Point scale 1-incomplete to 3-complete) in comparison with the validated information source by five rheumatologists. Scores of accuracy and completeness of the ChatGPT responses were listed descriptively and compared between information sources using non-parametric testing.
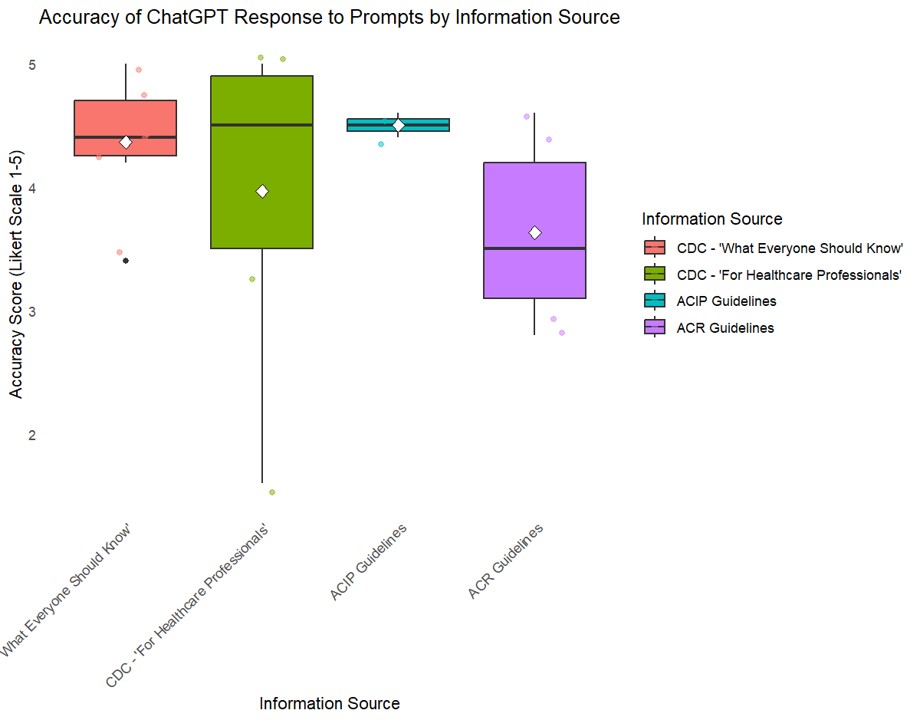
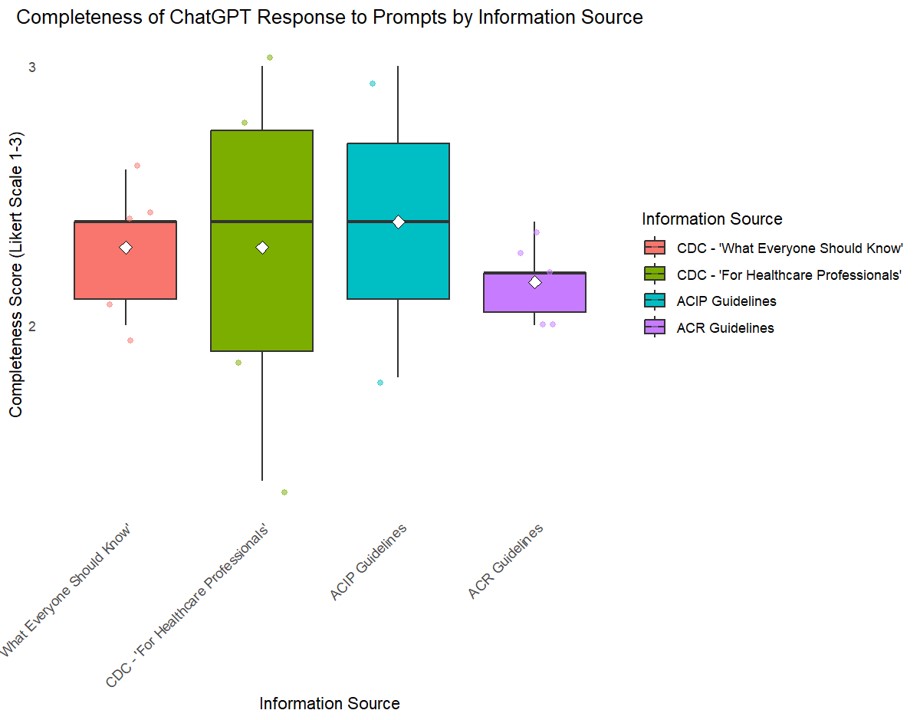
Results: The overall mean accuracy on a 5-point scale was 4.04 +/- 1.22, with 80% of responses scoring ≥ 4. The mean completeness score on a 3-point scale was 2.3 +/-0.63, with 95% of responses scoring ≥2. ChatGPT responses to prompts based on ACIP recommendations scored highest in accuracy (Mean 4.5 +/- 0.71) and completeness (Mean 2.4+/-0.70). It scored lowest in accuracy (Mean 3.6+/- 1.37) and completeness (Mean 2.2 +/- 0.65) to prompts based on ACR guidelines. There were no significant differences in accuracy or completeness when comparing ChatGPT responses between information sources (Kruskal-Wallis p-value > 0.05).
Conclusion: ChatGPT 3.5 is a reliable LLM that can accurately and comprehensively answer specific questions regarding recombinant Zoster vaccine for patients with RMDs. However, responses may deviate from evidence-based guidelines. ChatGPT responses should be interpreted with caution. As LLMs evolve, it is essential to ensure that information from multiple validated sources is built into the AI model.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Sood A, Jahangiri P, Moyer A, Lin J. Assessing the Reliability of ChatGPT on Recombinant Zoster Vaccination for Patients with Rheumatic and Musculoskeletal Diseases [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/assessing-the-reliability-of-chatgpt-on-recombinant-zoster-vaccination-for-patients-with-rheumatic-and-musculoskeletal-diseases/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/assessing-the-reliability-of-chatgpt-on-recombinant-zoster-vaccination-for-patients-with-rheumatic-and-musculoskeletal-diseases/