Session Information
Date: Monday, November 13, 2023
Title: (0934–0964) Systemic Sclerosis & Related Disorders – Basic Science Poster
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: The presence of autoantibodies, especially directed towards topoisomerase I (ATA), in diffuse cutaneous Systemic Sclerosis (dcSSc) is known to be associated with severe clinical manifestations. Though various detection methodologies are used in the clinic, less is known about the intracellular functionality of this antibody. Analysis of ATAs ability to inhibit topoisomerase 1 (TOP1) may function as a new biomarker of progressive and severe disease.
Methods: ATA was separated from serum from dcSSc patients (n=10) and healthy controls (HC, n=2). The immunoglobulin G (IgG) fraction was separated using a Protein G column (Figure A) followed by column separation towards TOP1. Sensitivity and purity were tested using western blot and biacore affinity analysis. The effect of serum, total IgG, ATA, and ATA depleted IgG from dcSSc patients and serum and IgG from HC on TOP1 catalysis were analyzed. We used a rolling circle amplification activity detection assay (REEAD) measuring the DNA cleavage-ligation activity of TOP1, as well as a nicking assay where TOP1 trapped in covalent complex with one strand of a plasmid DNA. To address the intracellular effect of ATA on TOP1 activity, dcSSc fibroblasts cultures were incubated with ATA or HC IgG mixed with lipofectamine for 6 hours, extracellular matrix protein signalling was analysed by PCR.
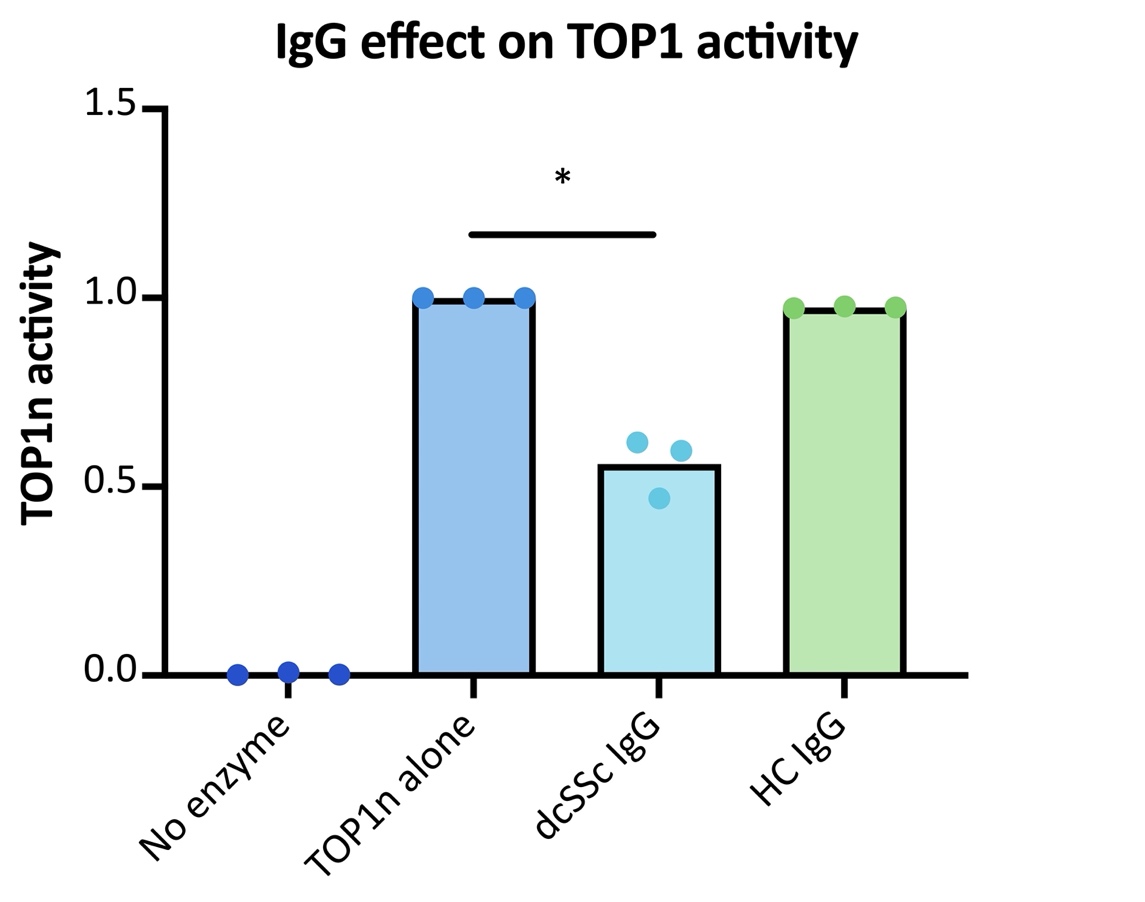
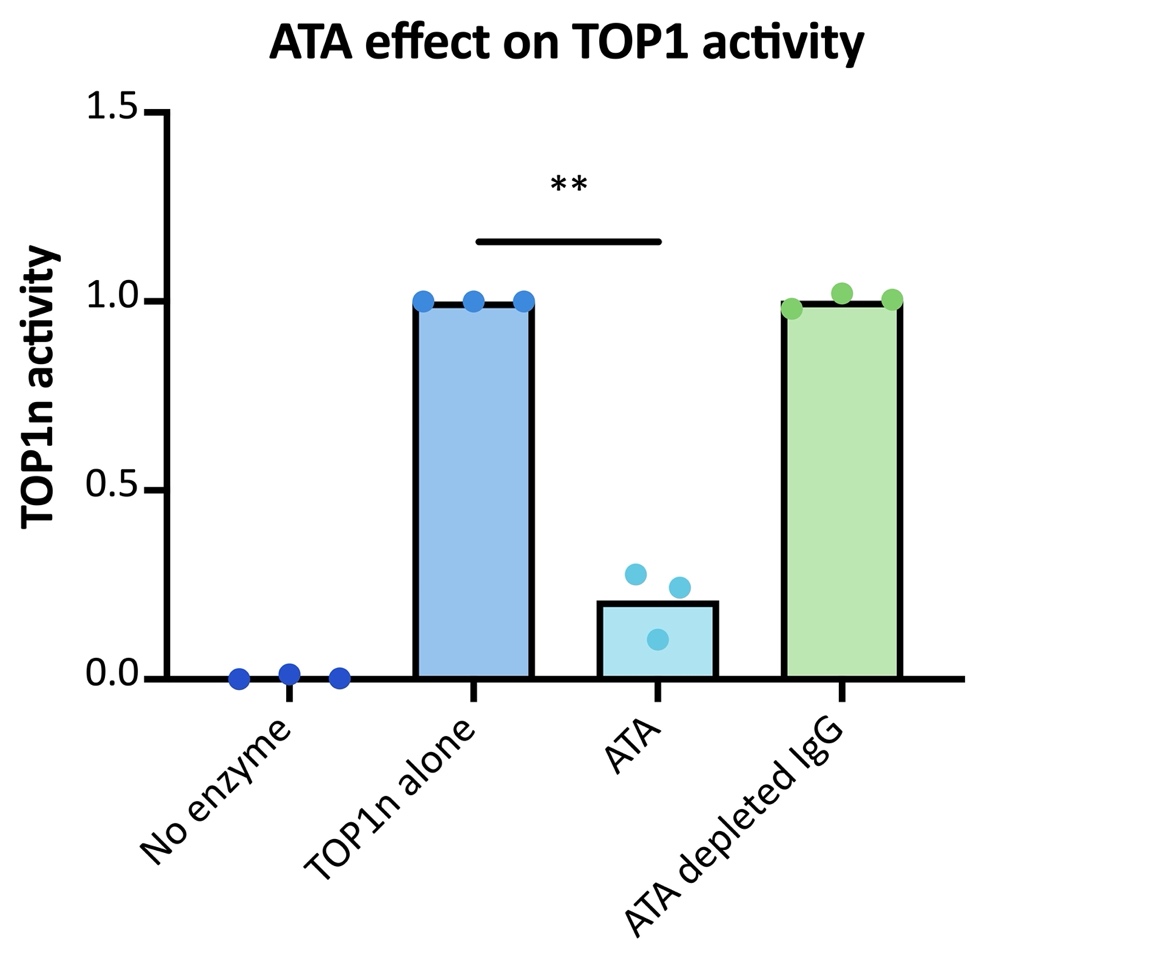
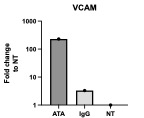
Results: dcSSc serum and IgG showed significant inhibition of TOP1 DNA cleavage-ligation activity when compared to HC serum and IgG, in a dose dependant manner. (Image 1). ATA separated from dSSc patients showed significant inhibition on TOP1 activity and this inhibition was abrogated when the ATA fractions were removed from the IgG pool. (Image 2). DcSSc IgG created TOP1 induced DNA nicks, suggesting that dcSSc IgG to induce accumulation of TOP1 cleavage complexes, which is a well-known inducer of DNA fragmentation in cells (Image not shown). PCR analysis of fibroblast transfected with ATA and HC IgG showed significant increase in signalling for extracellular matrix proteins such as intercellular adhesion molecule (ICAM) and Vascular cell adhesion molecule (VCAM)(Image 3).
Conclusion: We have successfully separated functional ATA from dcSSc patients. These antibodies show significant effect on both nuclear and mitochondrial TOP1 activity. ATA causes DNA nicks and release free DNA into the cytosol, activating a cascade of inflammatory pathways leading to increased production of proinflammatory cytokines and extracellular matrix proteins. This study links ATA to central intracellular pathways, thus providing a better understanding of the disease pathogenesis
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Aspari M, Geertsen Keller-Socin J, Greisen S, Naeser E, Soendergaard K, Knudsen B, Ong V, Denton C, Abraham D, Deleuran B. Anti-Topoisomerase Antibody in dcSSc: Unravelling Its Intracellular Effects in Systemic Sclerosis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/anti-topoisomerase-antibody-in-dcssc-unravelling-its-intracellular-effects-in-systemic-sclerosis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/anti-topoisomerase-antibody-in-dcssc-unravelling-its-intracellular-effects-in-systemic-sclerosis/