Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Novel autoantibodies (Ab) capable of identifying unique subgroups of seronegative rheumatoid arthritis (SN-RA) while providing specificity for RA comparable to ACPA reflects an opportunity to provide greater diagnostic and treatment certainty among patients with inflammatory arthritis. Anti-RA33 Ab have demonstrated high specificity for RA in a pair of European RA cohorts [Sieghart D, Platzer A, Studenic P, et al. Front Immunol. 2018;9:876]. The present study aims to empirically derive cutoffs for novel anti-RA33 immunoassays and determine the performance characteristics in a U.S. cohort enriched for SN-RA.
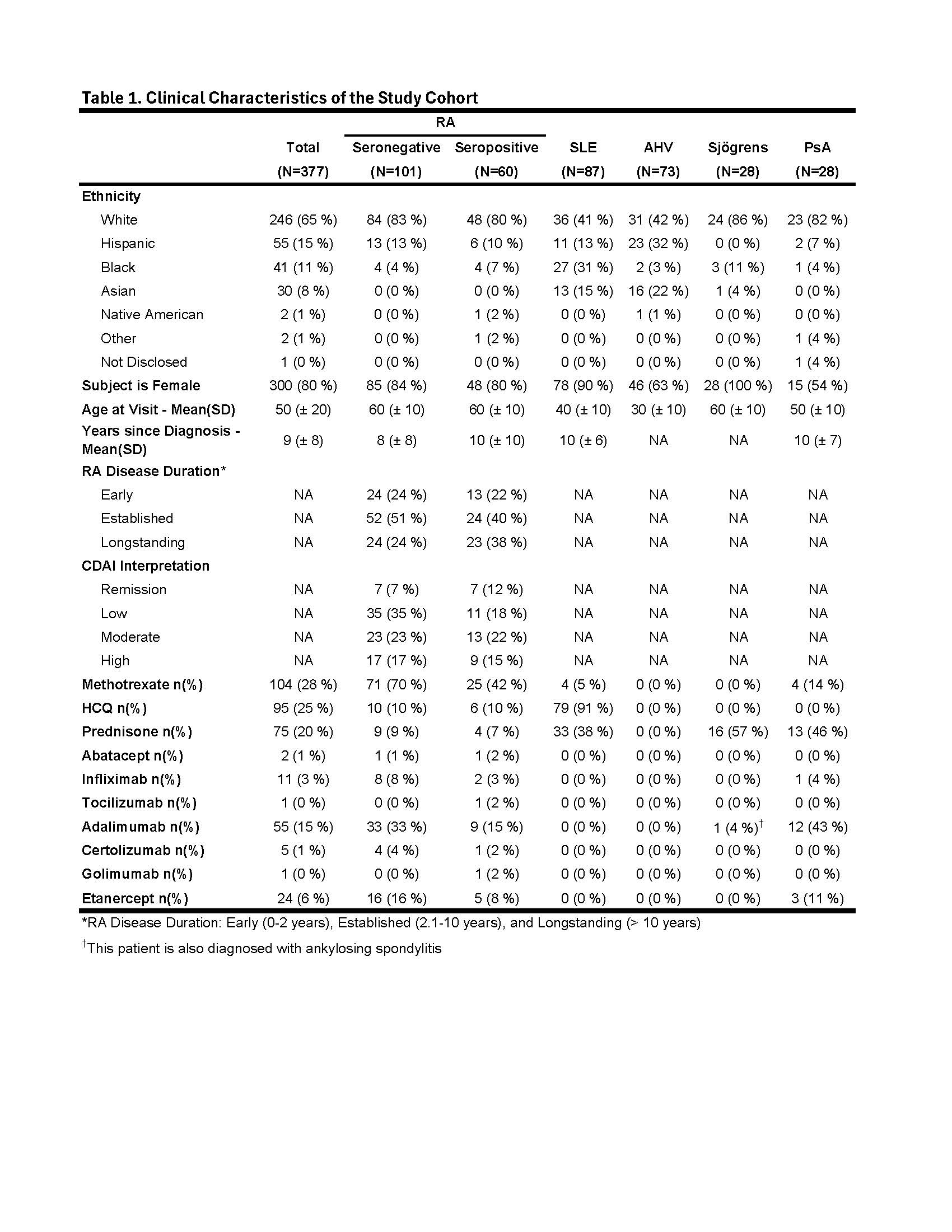
Methods: A cohort of 377 subjects consisting of 161 RA subjects meeting 2010 ACR classification criteria, 87 SLE meeting 1997 ACR classification criteria, 73 apparently healthy volunteers (AHV), 28 clinically diagnosed Sjögrens and 28 clinically diagnosed psoriatic arthritis (PsA) subjects were consented for Ab screening. Enzyme-linked fluorescent immunoassay testing was performed on the Phadia (Thermo Scientific) system to measure anti-CCP2 IgG, RF (IgA and IgM) and anti-RA33 (IgA, IgG and IgM). Cutoffs for anti-CCP and RF were based on manufacturer’s specifications. Anti-RA33 autoantibody cutoffs for each isotype were set above the 95th percentile of AHVs. RA subjects testing negative for anti-CCP and RF IgM and IgA were considered SN-RA for the purposes of analysis. Chi-square analysis was performed to compare frequency of RA33 autoantibodies stratified by disease duration, age and RA disease activity reflected by clinical disease activity index (CDAI) category.
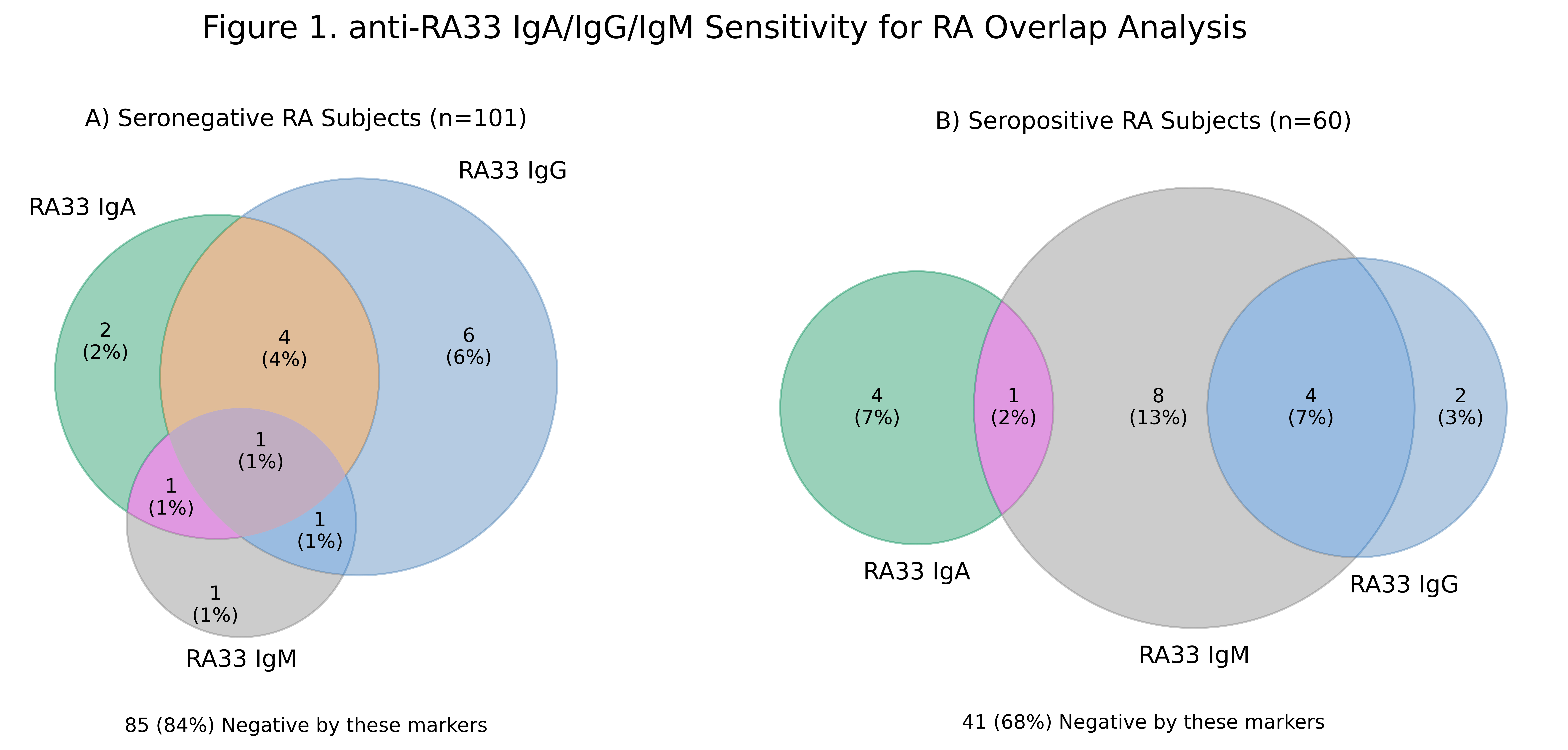
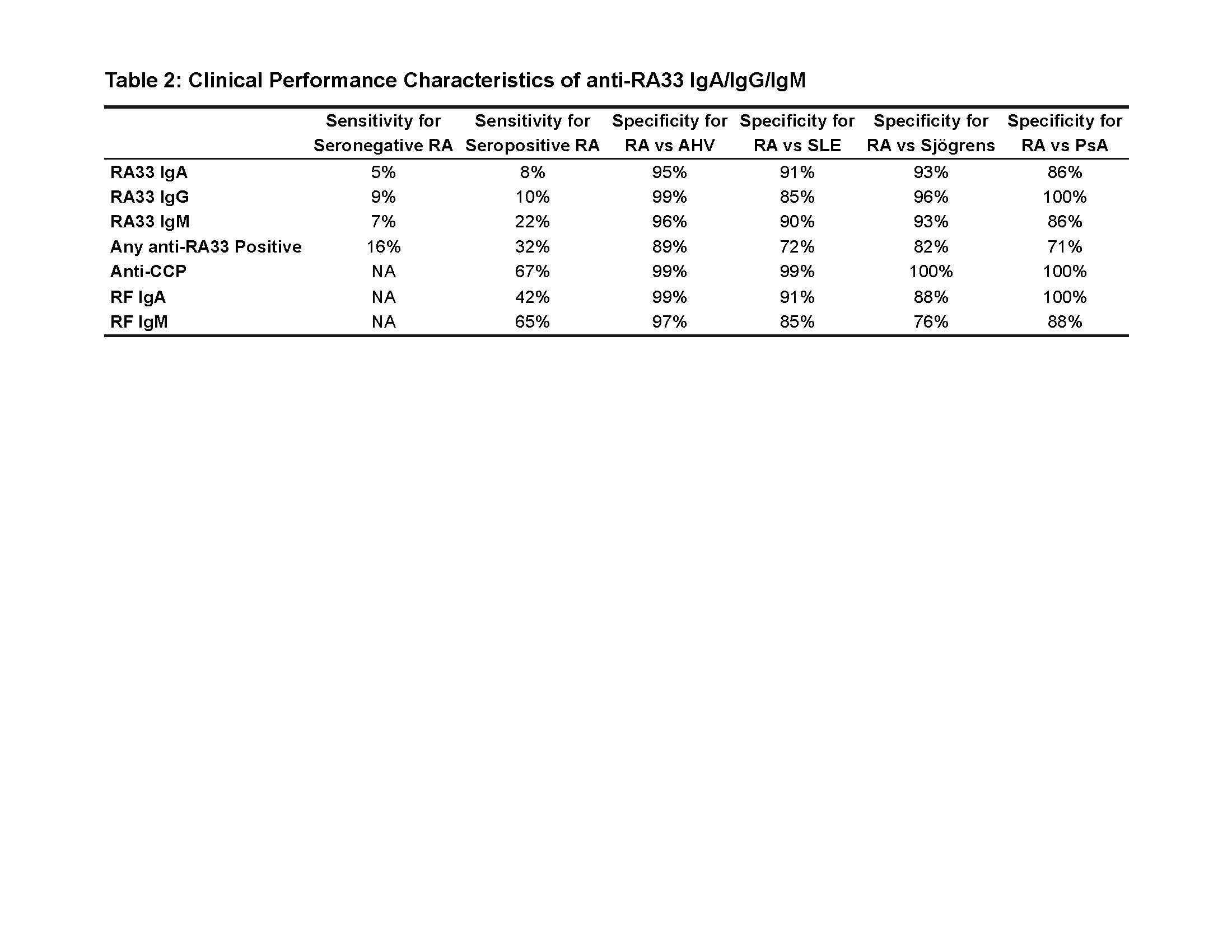
Results: The SN-RA cohort (N = 101) was majority white (83%), female (85%) with a mean (SD) age of 60 (± 10) years (Table 1). A combined 16% were positive for one or more anti-RA33 Ab with IgA, IgG and IgM present in 5%, 9% and 7%, respectively (Fig. 1A). Of the 16 SN-RA subjects testing anti-RA33 positive, 12 (75%) were positive for a single isotype. The seropositive RA (SP-RA) cohort (N = 60) was similar: majority white (80%), female (80%) with a mean age of 60 (± 10) years. A combined 32% were positive for one or more anti-RA33 Ab with IgA, IgG and IgM present in 9%, 10% and 22%, respectively (Fig. 1B). Anti-RA33 IgG was 99% specific for RA vs. AHV, while IgM and IgA were 96% and 95% specific, respectively (Table 2). In the other autoimmune disease groups, anti-RA33 specificity for RA was generally > 90% except for IgG Ab which were 85% specific for RA vs. SLE and IgA and IgM isotypes (86% specific vs. PsA). The frequency of anti-RA33 Ab stratified by disease duration (early [0-2 years since diagnosis], established [2-10 years], and longstanding [ >10 years]), age (>50 vs. < 50 years old) and CDAI categories (remission and low vs. moderate and high) were not significantly different (p > 0.05) for either SP-RA or SN-RA.
Conclusion: The data indicate that while anti-RA33 Ab are present in a significant proportion of SN-RA patients, their prevalence does not appear to vary significantly with disease duration, age, or disease activity. The integration of anti-RA33 Ab measurement with other SN-RA biomarkers may mitigate diagnostic uncertainty in early inflammatory arthritis and attenuate treatment delays.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Concoff A, Warsi T, Taghavi S, Kumar S, Patalinghug A, Schleif C, Partain B, Ahearn J, Wilson N, Manzi S, Joy V, O'Malley T. Anti-RA33 Autoantibodies Are Unique, Sensitive Biomarkers for the Identification of Seronegative Rheumatoid Arthritis in a U.S. Cohort [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/anti-ra33-autoantibodies-are-unique-sensitive-biomarkers-for-the-identification-of-seronegative-rheumatoid-arthritis-in-a-u-s-cohort/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/anti-ra33-autoantibodies-are-unique-sensitive-biomarkers-for-the-identification-of-seronegative-rheumatoid-arthritis-in-a-u-s-cohort/