Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: The voltage-gated sodium channel, NaV1.8, marks the majority of C-fiber nociceptors. We have used NaV1.8 tdTomato reporter mice to describe the nociceptive innervation of the mouse knee (PMID: 31351964). We reported that 16 weeks after destabilization of medial meniscus (DMM), osteoarthritic (OA) joint damage is accompanied by extensive remodeling of nociceptors in the medial compartment of the knee, including increased NaV1.8+ innervation in the medial synovium and within subchondral bone channels. Distinct functional classes of C-fibers have been identified, where it has been proposed that TRPV1+ C-fibers mediate heat sensitivity and C-fibers that express the G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR), Mrgprd, mediate behavioral sensitivity to mechanical stimuli. Their potential role in mechanosensation makes Mrgprd neurons an interesting subject in the context of OA pain, which is why we developed Mrgprd-EGFP reporter mice and investigated if they are present in the murine joint.
Methods: DMM surgery was performed in the right knee of 10-week old male C75BL/6 Mrgprd-EGFPf mice. Knees were harvested from 10-week old naïve mice (n=5), 26-week old naïve mice (n=3), and 16 weeks after DMM (n=3). Mice were perfused transcardially with paraformaldehyde. Knees were harvested, decalcified and cryo-sectioned. Twenty-µm thick coronal sections were collected throughout the joint. Sections were imaged using laser-scanning confocal microscope (Olympus IX70) and the fluorescence signal was quantified using image J by an observer blinded to the groups.
Results: Mrgprd signal was present in the knee joint of 10-week old naïve mice, specifically at the insertions of the cruciate ligaments and in bone marrow cavities. By the age of 26 weeks, Mrgprd+ innervation decreased significantly in the cruciate ligament insertions (Fig 1a), which is similar to the age-related decline seen in the cruciate ligaments of NaV1.8-tdTomato mice. No signal was observed in the medial synovium of young or old naïve mice (Fig 1b). Sixteen weeks after DMM, OA knees showed further decrease in the Mrgprd+ innervation of the cruciate ligament insertions, compared to 26-week old naïve knees (Fig 1a). In contrast to the increase in the medial synovial NaV1.8+ innervation we previously observed in NaV1.8-tdTomato mice, no change was observed in the Mrgprd+ innervation of the medial synovium after DMM (Fig 1b). Interestingly, Mrgprd signal was present in channel like structures in the subchondral bone of the medial femoral condyle and tibial plateau of the OA knee (Fig 1c), similar to findings in NaV1.8-tdTomato mice.
Conclusion: The intra-articular Mrgprd innervation changed markedly with age and after DMM. The innervation pattern of this mechanosensitive subset was different than the pattern we observed for NaV1.8, which marks all nociceptors. Sixteen weeks after DMM, at which point there is extensive joint damage, mechanosensitive Mrgprd nerve fibers were recruited in subchondral bone channels, but not in the synovium. In contrast, Mrgprd fibers declined significantly in cruciate ligament insertions with age and after DMM. The biological significance of these findings needs to be further explored
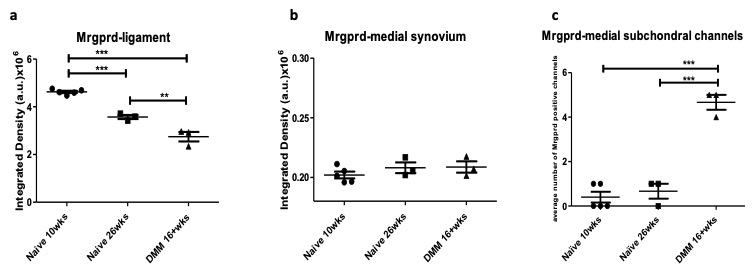 Figure 1 : Quantification of MRGPRD+ signal in knees of 10- and 26-week old naïve mice and 16 weeks after DMM surgery, in (a) cruciate ligament insertions; (b) medial synovium; (c) within subchondral channels.** p < 0.01 , *** p < 0.001; mean±SEM
Figure 1 : Quantification of MRGPRD+ signal in knees of 10- and 26-week old naïve mice and 16 weeks after DMM surgery, in (a) cruciate ligament insertions; (b) medial synovium; (c) within subchondral channels.** p < 0.01 , *** p < 0.001; mean±SEM
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Obeidat A, Miller R, Malfait A. Anatomical Distribution of Mrgprd-expressing Nonpeptidergic C-fibers in the Mouse Knee [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/anatomical-distribution-of-mrgprd-expressing-nonpeptidergic-c-fibers-in-the-mouse-knee/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/anatomical-distribution-of-mrgprd-expressing-nonpeptidergic-c-fibers-in-the-mouse-knee/
