Session Information
Date: Monday, November 8, 2021
Title: Plenary III (1424–1429)
Session Type: Plenary Session
Session Time: 11:45AM-12:00PM
Background/Purpose: B cell activating factor (BAFF) and a proliferation inducing ligand (APRIL) are TNF superfamily members that bind TACI (transmembrane activator and CAML interactor), BCMA (B cell maturation antigen), and/or BAFF-R on B cells and together support B cell development, differentiation, and survival. Their co-neutralization dramatically reduces B cell survival and function, including antibody (Ab) production, whereas inhibition of either BAFF or APRIL alone mediates relatively modest effects. ALPN-303 is an Fc fusion protein of a human TACI variant TNFR domain engineered by directed evolution (Fig. 1). It mediates significantly improved combined BAFF and APRIL inhibition in vitro and enhanced pharmacokinetic (PK) and immunomodulatory properties in vivo, as compared to wild-type (WT) TACI-Fc molecules. B cell targeting therapies like the WT TACI-Fc fusions atacicept and telitacicept have demonstrated promising clinical potential in B cell-related diseases like SLE. ALPN-303, with enhanced inhibitory activity against BAFF & APRIL, may further improve clinical outcomes.
Methods: Variant TNFR domains (vTD) of TACI that exhibit enhanced affinity for BAFF and APRIL as compared to WT TACI were identified using our directed evolution platform (Fig. 1). The most potent variant TACI domain identified was fused to a human IgG Fc to generate the therapeutic candidate ALPN-303. ALPN-303 was evaluated for functional activity: 1) in vitro in human lymphocyte assays and in a Jurkat/NF-κB reporter cell line transduced with TACI, 2) in mouse KLH immunization models, 3) in the mouse collagen-induced arthritis model, 4) in the bm12àBL/6 induced model of lupus, 5) in the (NZBxNZW)F1 spontaneous mouse model of lupus, and 6) in preclinical PK/pharmacodynamic studies.
Results: ALPN-303 inhibited BAFF- and APRIL-mediated signaling in vitro in human lymphocyte and TACI+ Jurkat assays (Fig. 2), with significantly lower IC50 values than WT TACI-Fc and anti-BAFF Ab comparators. In all mouse models evaluated, administration of ALPN-303 rapidly and significantly reduced key lymphocyte subsets including plasma cells and follicular T helper cells. Furthermore, treatment with ALPN-303 significantly decreased titers of antigen-specific antibodies in immunized mice and in induced disease models, and potently suppressed anti-dsDNA autoAbs, blood urea nitrogen levels, proteinuria, glomerular IgG deposition, and nephritis in the spontaneous NZB/W lupus model (Fig. 3). Following single dose administration to cynomolgus monkeys, ALPN-303 exhibited higher overall serum exposure and notably enhanced suppression of serum immunoglobulins IgA, IgM, and IgG as compared to WT TACI-Fc treatment.
Conclusion: Directed evolution of TNFR domains has successfully facilitated the development of the novel immunomodulator ALPN-303, a potent BAFF/APRIL antagonist that consistently demonstrates encouraging immunomodulatory activity and efficacy in vitro and in vivo, superior in preclinical studies to anti-BAFF Abs and WT TACI-Fc. ALPN-303 may thus be an attractive development candidate for the treatment of multiple autoimmune and inflammatory diseases. Preclinical development to enable clinical trials has been initiated.
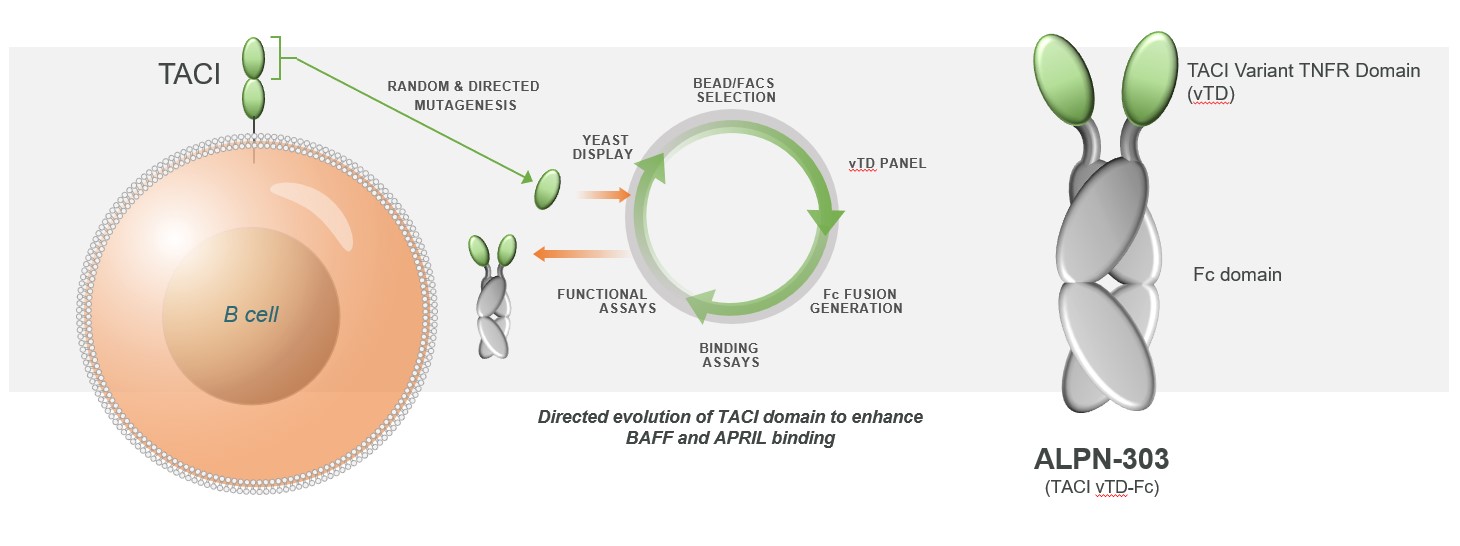 Figure 1: ALPN_303 is a modified TACI-Fc fusion protein generated via directed evolution that mediates enhanced BAFF and APRIL inhibition vs. WT TACI-Fc
Figure 1: ALPN_303 is a modified TACI-Fc fusion protein generated via directed evolution that mediates enhanced BAFF and APRIL inhibition vs. WT TACI-Fc
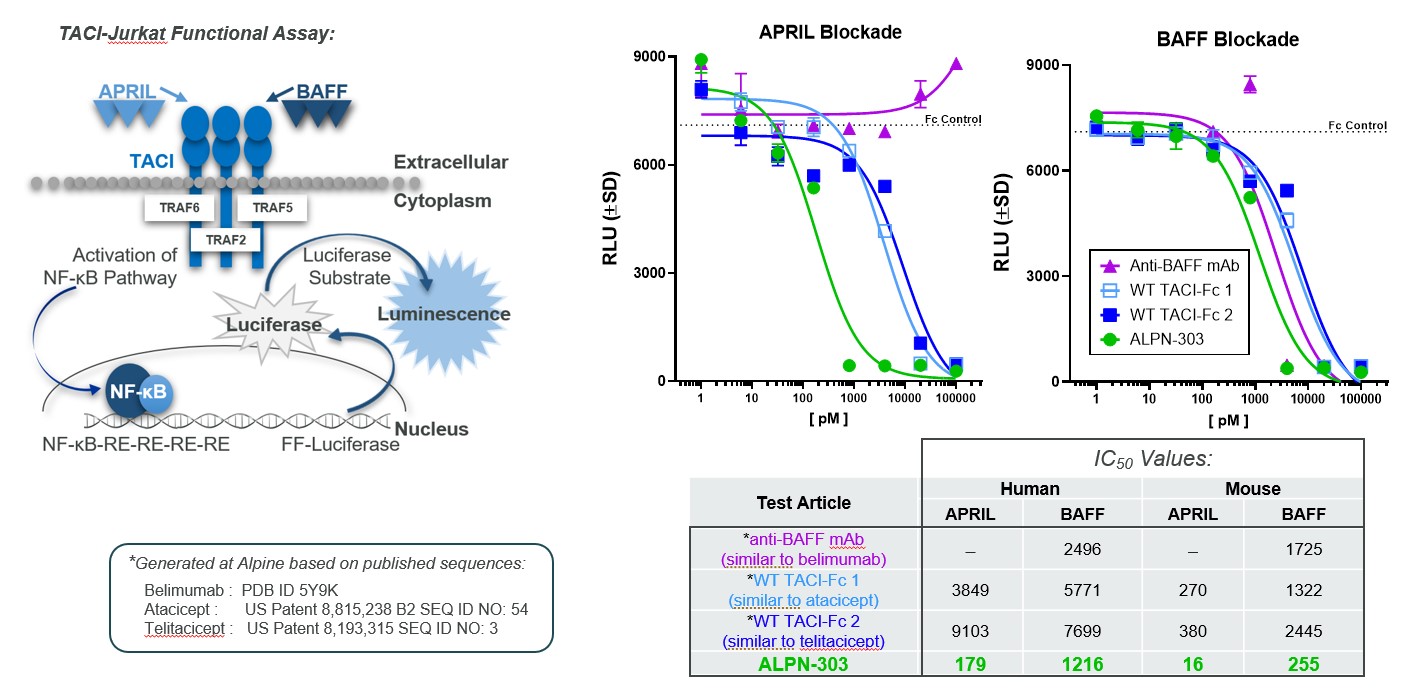 Figure 2: ALPN_303 neutralizes APRIL and BAFF activity more potently than WT TACI-Fc in a cell-based reporter assay
Figure 2: ALPN_303 neutralizes APRIL and BAFF activity more potently than WT TACI-Fc in a cell-based reporter assay
 Figure 3: ALPN_303 suppresses disease in the (NZBxNZW)F1 spontaneous lupus model
Figure 3: ALPN_303 suppresses disease in the (NZBxNZW)F1 spontaneous lupus model
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Dillon S, Evans L, Lewis K, Yang J, Rixon M, Kuijper J, Demonte D, Bhandari J, Levin S, Kleist K, Mudri S, Bort S, Ardourel D, Seaberg M, Wang N, Gudgeon C, Sanderson R, Wolfson M, Hillson J, Holland P, Peng S. ALPN-303, an Enhanced, Potent Dual BAFF/APRIL Antagonist Engineered by Directed Evolution for the Treatment of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) and Other B Cell-Related Diseases [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/alpn-303-an-enhanced-potent-dual-baff-april-antagonist-engineered-by-directed-evolution-for-the-treatment-of-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-sle-and-other-b-cell-related-diseases/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/alpn-303-an-enhanced-potent-dual-baff-april-antagonist-engineered-by-directed-evolution-for-the-treatment-of-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-sle-and-other-b-cell-related-diseases/
