Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 9, 2021
Title: Abstracts: Metabolic & Crystal Arthropathies – Basic & Clinical Science (1897–1900)
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 10:30AM-10:45AM
Background/Purpose: Bone erosion is a common consequence of tophaceous gout, and leads to joint deformity and disability. In small case series, intensive urate-lowering with intravenous pegylated uricase improved erosion scores in gout. However, the optimal strategy for management of erosive gout with oral urate-lowering therapy (ULT) is currently unknown. The aim of this randomized controlled trial was to determine whether intensive lowering of serum urate to a target to below 0.20mmol/L (3.3mg/dL) results in improved bone erosion scores, compared to the standard serum urate target to below 0.30mmol/L (5mg/L) in patients with erosive gout on oral ULT.
Methods: Two-year, randomized controlled trial of 104 participants with erosive gout on oral ULT and serum urate ≥ 0.30mmol/L. Participants were randomly assigned to serum urate target 0.10-0.19 mmol/L (intensive group) or 0.20-0.29 mmol/L (standard group). Both participants and study staff who had contact with participants were blinded to the serum urate target and serum urate results throughout the trial, and oral ULT was titrated using a standardized protocol until the target was reached (with allopurinol to 900mg daily, probenecid to 2g daily, febuxostat to 120mg daily, and benzbromarone to 100mg daily). The primary endpoint was total CT erosion score, and key secondary endpoint was the gout-modified Sharp-van der Heijde plain radiographic damage score. The OMERACT gout core outcome domains were also secondary endpoints.
Results: Over the study period, the serum urate was significantly lower in the intensive group compared to the standard group (P=0.002). However, fewer participants in the intensive group achieved the randomized serum urate target (at week 52, 53% vs 83%, P< 0.01, and at week 104, 62% vs 83%, P< 0.05). In the intensive group, allopurinol doses were higher (mean (SD) 746 (210) mg/day vs 496 (185) mg/day, P< 0.001), and more combination therapy was used (P=0.0004). Small increases in CT erosion scores were observed in both groups over two years, with no between-group difference (P=0.29), Figure. Similar findings were observed for the plain radiographic damage score (P=0.58), Figure. Other OMERACT gout core outcome domains (gout flares, tophus, pain, patient global assessment, health related quality of life, and activity limitation) improved in both groups over the two-year study period, with no between-group differences. Adverse event and serious adverse event rates were similar between groups.
Conclusion: Intensive serum urate lowering below 0.20mmol/L is difficult to achieve with oral ULT, leads to high medication burden, and does not improve bone erosion scores in patients with erosive gout. When using oral ULT, a serum urate target below 0.30mmol/L is sufficient to achieve clinical benefit in this patient group.
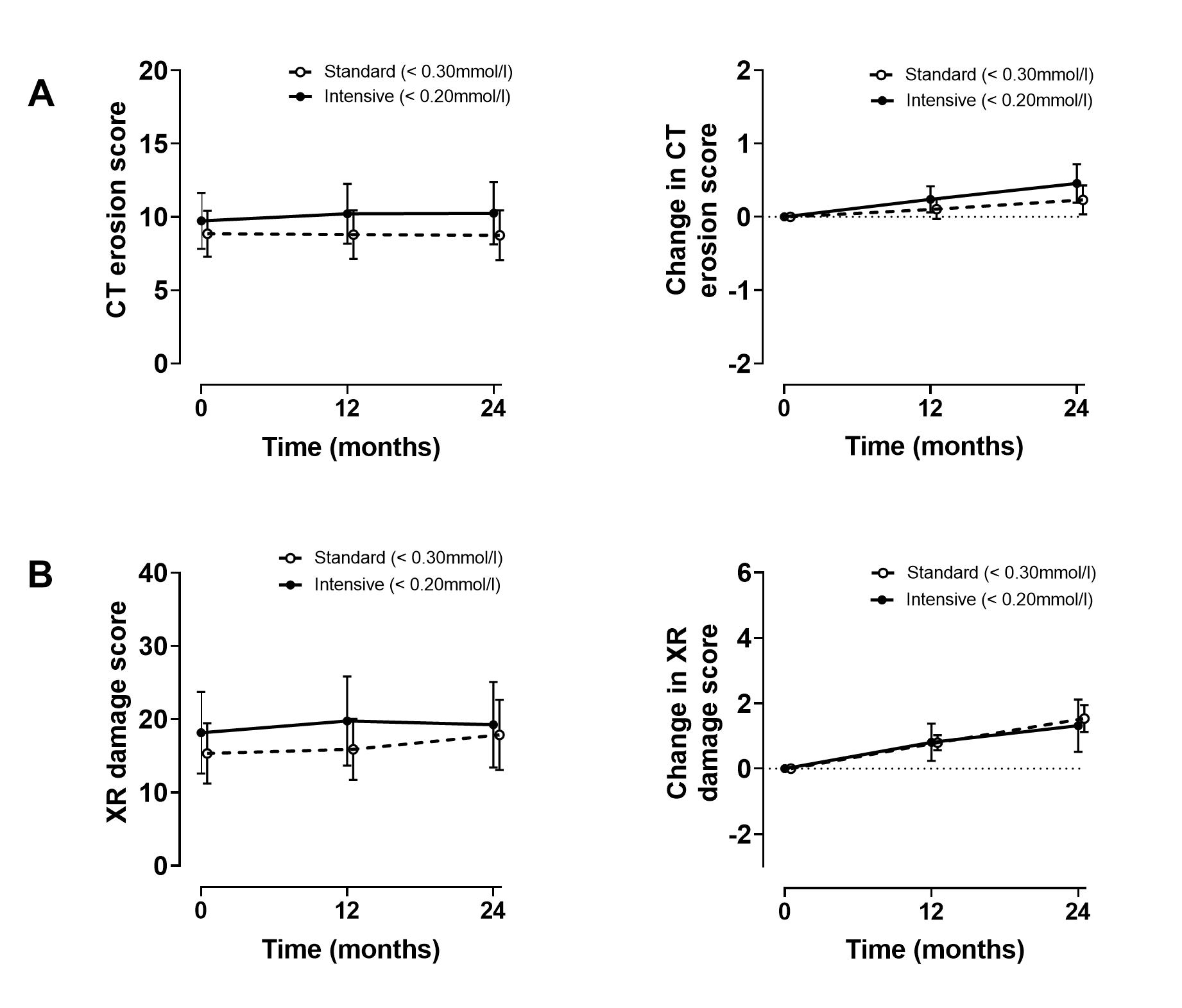 Figure. Primary and key secondary endpoint. A. CT erosion scores. B. Plain radiographic damage scores. Data are presented as mean (95% confidence intervals).
Figure. Primary and key secondary endpoint. A. CT erosion scores. B. Plain radiographic damage scores. Data are presented as mean (95% confidence intervals).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Dalbeth N, Doyle A, Billington K, Gamble G, Tan P, Latto K, Parshu Ram T, Narang R, Murdoch R, Bursill D, Mihov B, Stamp L, Horne A. A Randomized Double-Blind Controlled Trial of Intensive Serum Urate Lowering with Oral Urate-Lowering Therapy for Erosive Gout [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-randomized-double-blind-controlled-trial-of-intensive-serum-urate-lowering-with-oral-urate-lowering-therapy-for-erosive-gout/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-randomized-double-blind-controlled-trial-of-intensive-serum-urate-lowering-with-oral-urate-lowering-therapy-for-erosive-gout/
