Session Information
Date: Tuesday, October 28, 2025
Title: (2227–2264) Rheumatoid Arthritis – Diagnosis, Manifestations, and Outcomes Poster III
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
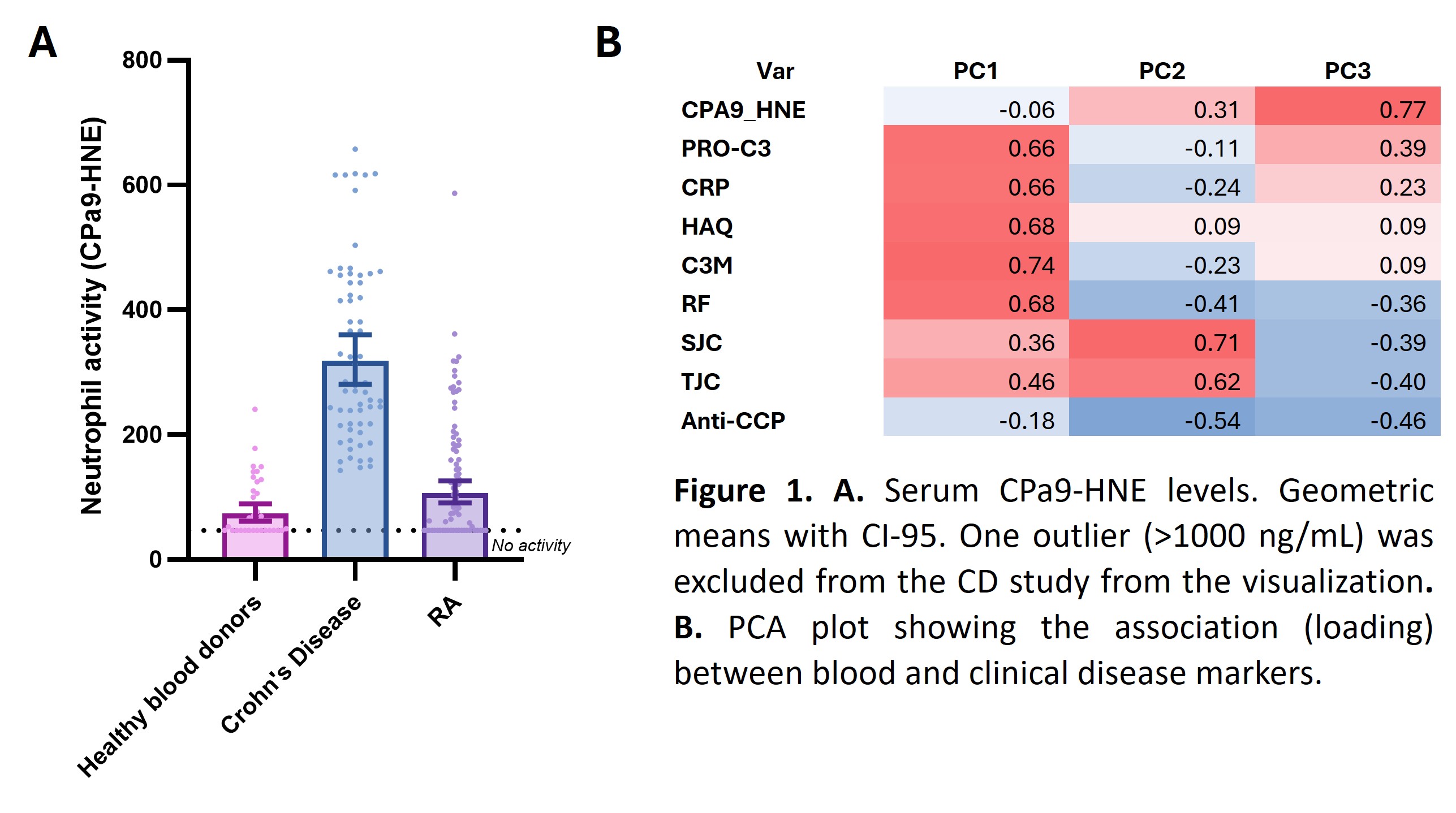
Background/Purpose: Neutrophils are crucial in fibro-inflammatory diseases like Crohn’s disease (CD) and rheumatoid arthritis (RA), but their biomarkers are better established in CD than in RA. Neutrophils are present in the inflamed synovium of the joints, however data on neutrophil count and assessment of blood levels of calprotectin – an alarmin released from neutrophils and monocytes – have pointed in different directions, which may be attributed to patient heterogeneity and/or treatment effect. The novel biomarker CPa9-HNE is a fragment of calprotectin generated by human neutrophil elastase during neutrophil activation and offers potential insight into neutrophil activity in RA. This study aims to explore the association between neutrophil activity, as measured by CPa9-HNE, and disease activity in patients with moderate to severe RA.
Methods: Serum samples from 76 predominantly white (90%), female (76%), seropositive RA patients and active disease (DAS25-CRP >3.4) aged 22-85 years were retrieved from several different biorepositories (Discovery Lifesciences, BioIVT LLC, Protogenex Inc.). None of the patients were biological naïve. CPa9-HNE was measured in the serum sample using the NordicCPA9™ manual ELISA. The markers of fibrogenesis and fibrolysis, PRO-C3 and C3M, were measured to study the link between fibro-inflammation and neutrophil activity. Data from a published Crohn’s disease study (n=65), including healthy blood donors (n=32), was used to compare levels of CPa9-HNE between CD and RA (Mortensen et al. 2022). Undetectable samples were given the value of the assay detection limit (47 ng/ml).
Results: Of the RA patients, 23 out of 76 had undetectable levels of CPa9-HNE, compared to 14 out of 32 healthy donors and none in the of the CD group. The geometric mean [95%-CI] levels were significantly lower in RA patients (107.2 [90.9-126]) than in CD (319 [281-361]), but higher than healthy controls 74.5 [61.7-90.0] (Figure 1A). CPa9-HNE was inversely correlated with rheumatoid factor (rho =-0.62) and to a lesser degree with anti-CCP levels (rho = -0.40). CPa9-HNE showed no correlation (rho >0.4) or association with age, BMI, gender, disease duration, DAS28, CRP, or swollen or tender joint count (SJC/TJC). Nor the fibro-inflammatory markers PRO-C3 and C3M. PCA analysis revealed three clusters explaining 64% of the variation in the dataset: PC1, fibro-inflammatory driven by C3M, RF, HAQ, CRP and PRO-C3, BUT not CPa9-HNE; PC2, symptomatic driven by SJC and TJC; PC3, neutrophilic driven by CPa9-HNE (Figure 1B).
Conclusion: The observation of high RF and low neutrophil activity in RA patients may be due to the heterogeneity of RA, differing immune pathways, treatment effects and disease stage. Thus CPa9-HNE is a relevant biomarker for the neutrophilic RA endotype, as precision medicine tool for RA.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Bay-Jensen A, Sinkeviciute D, Thudium C, Sun s, Christensen M, Karsdal M, Alexdottir m, mortensen J. Inverse Correlation Between Neutrophil Activation and Rheumatoid Factor Concentrations in Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/inverse-correlation-between-neutrophil-activation-and-rheumatoid-factor-concentrations-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-ra/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/inverse-correlation-between-neutrophil-activation-and-rheumatoid-factor-concentrations-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-ra/