Session Information
Date: Tuesday, October 28, 2025
Title: (1972–1989) Measures & Measurement of Healthcare Quality Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Autoimmune diseases, including rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and spondyloarthritis (SpA)—which encompasses ankylosing spondylitis (AS) and psoriatic arthritis (PsA)—are associated with chronic inflammation and increased cardiovascular morbidity and mortality. Despite guidelines recommending routine lipid testing for these patients, many fail to receive appropriate screening. Obtaining lipid panels helps calculate the Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease (ASCVD) risk score to guide preventive treatment for patients that are deemed high risk. This quality improvement (QI) project at Houston Methodist Hospital (HMH) aimed to increase lipid screening rates among patients with RA and SpA (including AS and PsA) in the rheumatology fellows’ continuity clinic.
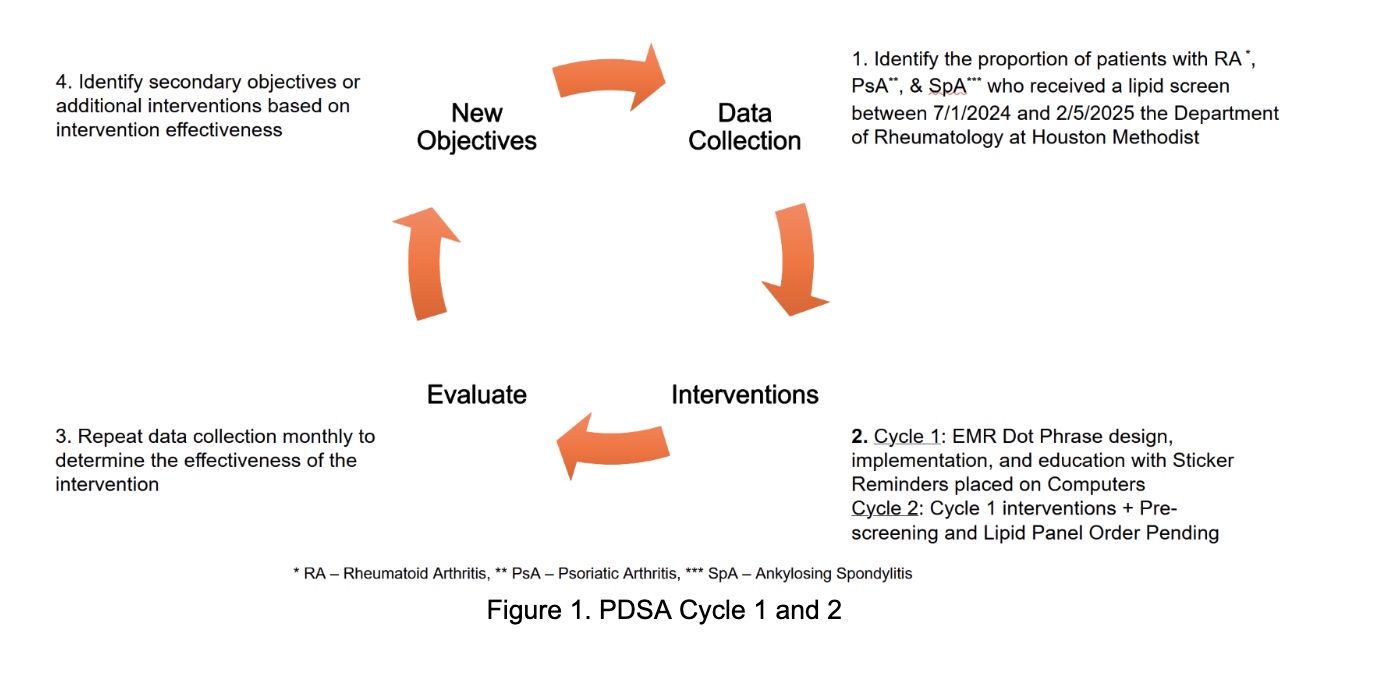
Methods: Patients seen at HMH in the rheumatology fellows’ clinic from July 2024 to February 2025 with ICD codes for RA, AS, or PsA (diagnosed by a rheumatologist) were analyzed for lipid panel screening in the year prior to their visit. This percentage served as a baseline. Two Plan-Do-Study-Act (PDSA) cycles were implemented from March to May 2025. PDSA 1 focused on a house staff education session on lipid screening protocols, creation of an Epic dot phrase and workstation reminder stickers. Lipid panel orders were collected via retrospective chart review. PDSA 2 involved pre-screening patients and pending a lipid panel order in Epic prior to arrival. Upon chart completion of the visit, these orders were signed by the fellows and data was again collected via retrospective chart view.
Results: At baseline, 0% of fellows were ordering lipid panels in their continuity clinics. After PDSA 1, 49 patients with seropositive RA, AS, or PsA were identified over 4 weeks. Of these, 26 (53.1%) had a lipid panel within the prior 12 months. These were ordered by PCPs predominantly. The remaining 23 patients had no recent lipid panel, and 2 new orders were placed by rheumatology fellows, resulting in a post-intervention rate increase of 8.6%. In PDSA 2, 14 patients were identified as lacking appropriate lipid panels within the prior year. After intervention, 13/14 (92.8%) patients received appropriate screening over 4 weeks.
Conclusion: Pre-charting to identify high risk patients and then pre-pending lipid panel orders prior to clinic visits in the fellows’ clinic were more effective than educational interventions alone. This agrees with current research that suggests education alone is a low-value improvement intervention. This workflow modification reduced the burden on fellows during busy clinic sessions and led to a higher and more consistent screening rate, suggesting that system-level changes can improve lipid screening. Ongoing data collection and refinement of this QI strategy will help sustain and expand improvements. Future steps will include treatment of patients with elevated ASCVD scores.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Javed M, Jagannath D, Morgan L, Patel R, Avenatti E, Monga K, Williams K. Improving Lipid Screening Rates in Rheumatic Disease Patients: An Academic Fellowship Quality Improvement Project [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/improving-lipid-screening-rates-in-rheumatic-disease-patients-an-academic-fellowship-quality-improvement-project/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/improving-lipid-screening-rates-in-rheumatic-disease-patients-an-academic-fellowship-quality-improvement-project/