Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Raynaud’s phenomenon (RP) is a painful and disabling feature of systemic sclerosis (SSc) that significantly impairs quality of life. Tools that integrate subjective symptom assessment with objective microvascular evaluation—ideally collected at the point of care—are essential to evaluate therapeutic response. Among U.S. Veterans, RP is highly prevalent, highlighting the importance of early diagnosis and intervention. Nailfold capillaroscopy (NFC) is the gold standard for direct visualization of microvascular changes. The Associated Raynaud Phenomenon (ASRAP) questionnaire is a patient-reported outcome (PRO) that captures the lived experience of RP. This study assessed the combined use of ASRAP and NFC to evaluate short-term therapeutic responses in Veterans with SSc and hand pain.
Methods: This prospective study enrolled Veterans from the SSc Registry (IRB No. 1618579-17) with SSc and RP initiating a single therapeutic intervention for hand pain. Follow-up was conducted 4–8 weeks after baseline. Participants completed the 10-item ASRAP questionnaire1 and underwent same-day NFC at both visits, using the G-Scope device per standardized protocols. Interventions included the initiation or dosage adjustment of a vasodilator or immunosuppressive agent. Changes in ASRAP scores and NFC parameters—including capillary density, apical diameter, and microhemorrhages—were compared pre- and post-intervention.
Results: Of the total 22 enrolled SSc Registry Veterans, 8 met inclusion criteria between January–April 2025. The majority were male (62%, n=5), with a mean age of 61±12.1 years. Most (75%, n=6) reported military-attributable exposures associated with RP onset. At baseline, all were on a vasodilator; 50% (n=4) were also on immunomodulators (Table 1). The most frequent intervention was initiation or dose increase of phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitors (PDE5-Is) in five subjects (63%). Three participants (38%) discontinued treatment due to gastrointestinal side effects (two vasodilators, one immunosuppressant). Mean ASRAP scores decreased from 52.25±6.02 to 50.76±8.79 (Figure 1). Capillary density slightly decreased (6.01±1.37 µm to 5.85±1.66 µm), apical diameter remained stable (22.08±6.28 µm to 22.27±6.19 µm), and the prevalence of giant capillaries declined (7.33% to 3.20%), while microhemorrhages increased (62.5% to 75%). Two patients had normal NFC throughout (Table 2). One patient who discontinued a vasodilator developed a late scleroderma pattern despite symptom improvement.
Conclusion: Combining ASRAP and NFC provides a multidimensional assessment of RP in Veterans with SSc, particularly in those with military exposure history. Despite short-term improvements in PRO scores, capillaroscopic findings often revealed ongoing or progressive microvascular damage. These findings underscore the need for continued vascular monitoring, early detection of drug intolerance, and proactive strategies for microvascular protection. Larger, longer-term studies are needed to validate these results and optimize RP management in this high-risk population.References: 1. Yu L et al. Arthritis Care & Research. 2023; 75: 8, 1725-34.
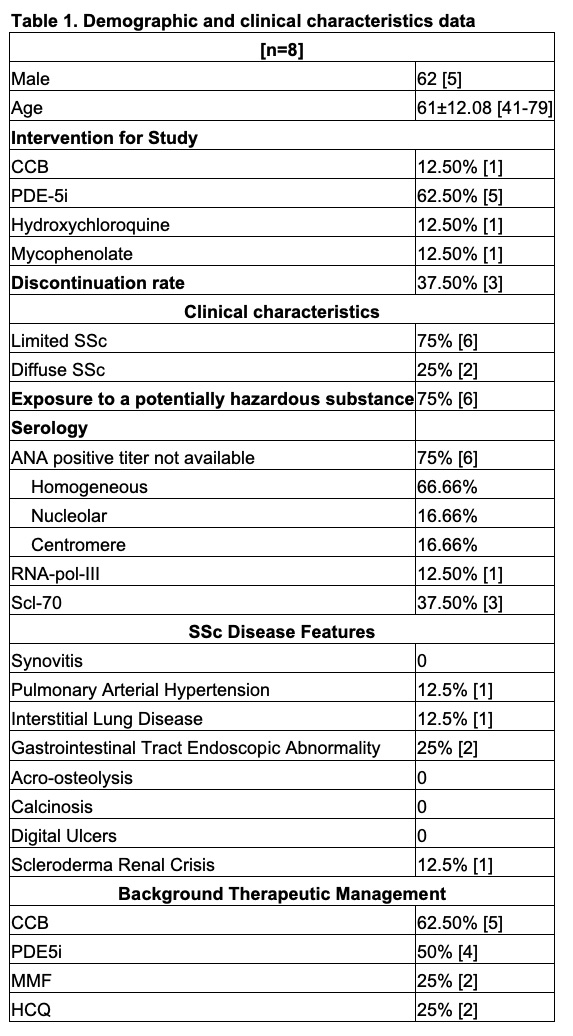 Table 1: Demographic and clinical characteristics data
Table 1: Demographic and clinical characteristics data
.jpg) Table 2: RP evaluation by ASRAP and NVC
Table 2: RP evaluation by ASRAP and NVC
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Maldonado G, Rao S, Frech T. Enhancing Objective Evaluation of Raynaud’s in Veterans with Scleroderma-related Hand Pain: Integrating Patient Reported Outcomes and Nailfold Capillaroscopy [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/enhancing-objective-evaluation-of-raynauds-in-veterans-with-scleroderma-related-hand-pain-integrating-patient-reported-outcomes-and-nailfold-capillaroscopy/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/enhancing-objective-evaluation-of-raynauds-in-veterans-with-scleroderma-related-hand-pain-integrating-patient-reported-outcomes-and-nailfold-capillaroscopy/

.jpg)