Session Information
Date: Monday, October 27, 2025
Title: (1306–1346) Rheumatoid Arthritis – Diagnosis, Manifestations, and Outcomes Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Rheumatoid factor (RF), an autoantibody targeting the Fc portion of IgG, is one of the most studied biomarkers in rheumatoid arthritis (RA). High RF titers have been associated with a more aggressive disease course and reduced efficacy of certain biologic DMARDs (bDMARDs), particularly monoclonal anti-TNF agents. RF levels ≥203 IU/mL have been linked to lower serum drug levels and reduced treatment persistence in these therapies. However, this association has not been observed with pegylated TNFi, and its impact on non-TNFi monoclonal antibodies remains unclear.
Methods: We conducted a retrospective longitudinal study of RA patients from our hospital treated with Certolizumab (CZP), Rituximab (RTX), and/or Tocilizumab (TCZ) as up to third-line therapy. Sociodemographic data, use of csDMARDs, bDMARDs, corticosteroids, RF levels at bDMARD initiation, and baseline and 6-month clinical and analytical inflammatory markers were collected (ET approval PI 6366). Drug discontinuation dates and reasons, up to December 31, 2024, were recorded. Patients were grouped by bDMARD received, and comparisons were made using Chi-square or Fisher’s exact test for categorical variables, and ANOVA or Kruskal-Wallis for continuous variables. Kaplan-Meier analysis was used to assess drug survival, overall and stratified by RF levels (High; HL ≥203 IU/mL vs. Low; LL < 203 IU/mL).
Results: A total of 186 patients with RA were included: 43 (23%) received CZP, 46 (25%) RTX, and 97 (52%) TCZ, with no significant sociodemographic differences between groups (Table 1). Baseline DAS28 and SDAI scores were comparable across treatments. In addition, näive patients to b/tsDMARDs were more frequent in CZP group (81% in CZP vs. 19% in RTX vs. 45% in TCZ, p< 0.001). At 6 months after the initiation of bDMARD, patients with high RF levels treated with TCZ showed higher disease activity (DAS28, SDAI) than those with lower RF levels (Table 2), whereas no statistically significant differences in activity were observed in the other treatment groups based on RF levels. Overall, 66% discontinued treatment (22 CZP, 30 RTX and 71 TCZ); 36% due to inefficacy (10 CZP, 5 RTX and 29 TCZ). In survival analysis, RF levels did not influence drug persistence in CZP, with a similar curve in both subgroups regardless of RF levels (99.9 in HL vs. 76.9 in LL months, p=0.42) (Figure 1A). The same occurs in the RTX group (Figure 1C), even showing a slightly higher median in the group with higher RF titres (45.1 in HL vs. 55.1 in LL months, p=0.87), consistent with the molecule's mechanism of action. However, when looking at the patients treated with TCZ (Figure 1B), the drug survival mean tended to be lower in patients in the group with RF ≥203 although no statistically significant (46.1 in HL vs 70.8 in LL months, p=0.11).
Conclusion: Patients with RF levels above 203 IU/mL did not show significant differences in drug survival for CZP or RTX. Nevertheless, TCZ showed a poorer short-term clinical response and a trend toward shorter drug survival and in patients with high RF levels. These findings suggest that RF levels might influence the persistence and effectiveness of certain bDMARDs, particularly TCZ, and warrant further investigation in studies with larger sample sizes.
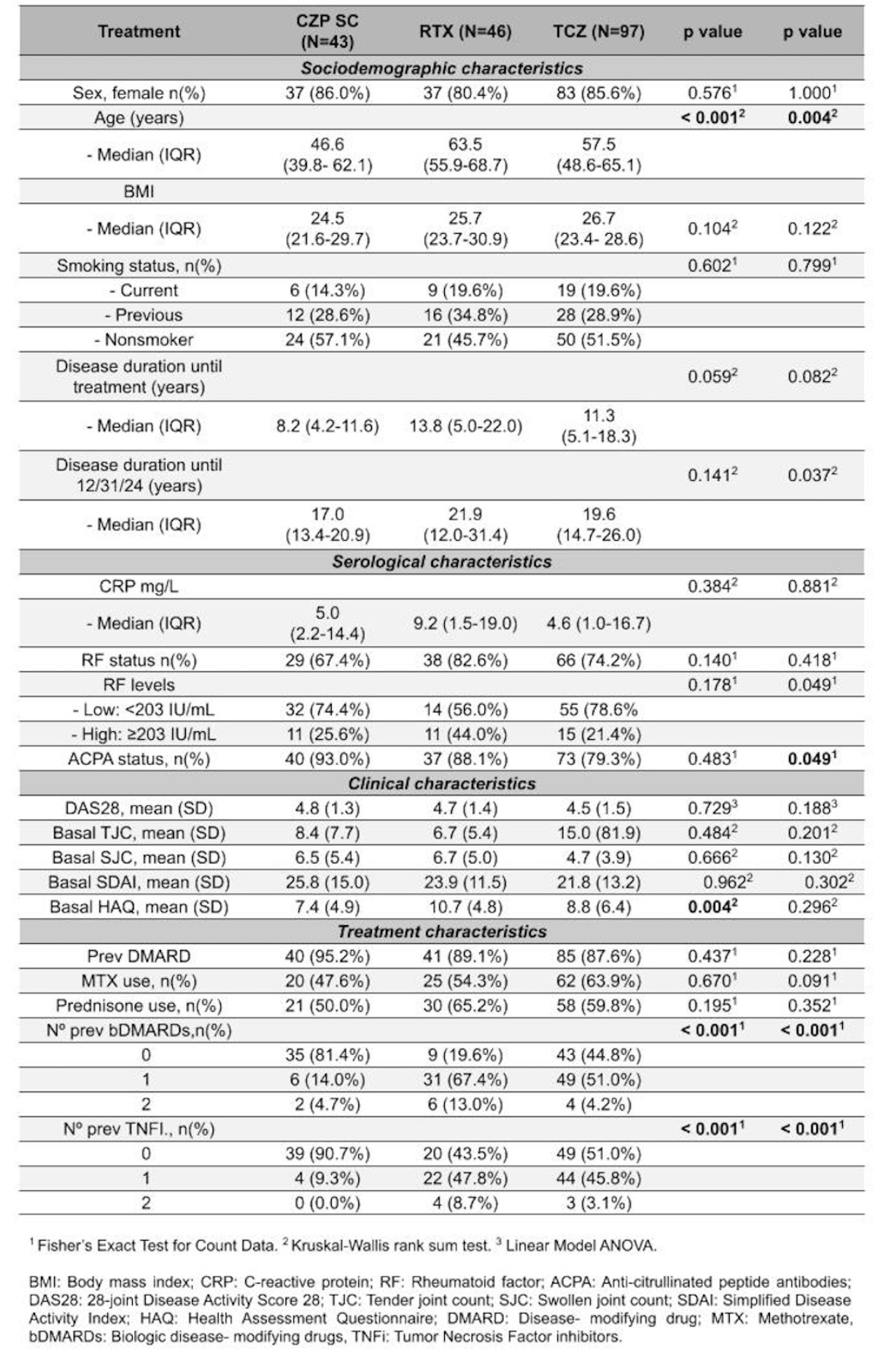 Table 1. Baseline demographic and clinical characteristics of patients.
Table 1. Baseline demographic and clinical characteristics of patients.
.jpg) Table 2. Comparison of DAS28, SDAI, and CRP at 6 months according to RF levels.
Table 2. Comparison of DAS28, SDAI, and CRP at 6 months according to RF levels.
.jpg) Figure 1. Survival drugs analysis (global) vs RF levels. A: Certolizumab Drug Survival vs RFLevels; B: Tocilizumab Drug Survival vs RFLevels; C: Rituximab Drug Survival vs RFLevels
Figure 1. Survival drugs analysis (global) vs RF levels. A: Certolizumab Drug Survival vs RFLevels; B: Tocilizumab Drug Survival vs RFLevels; C: Rituximab Drug Survival vs RFLevels
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Salas Santamaría S, Chao Moreira M, Juárez M, Novella-Navarro M, Nozal P, Martínez A, Tornero C, Bohorquez C, Sánchez A, Cámara C, López E, de Miguel E, Plasencia-Rodríguez C. High Rheumatoid Factor Titers and Biologic Persistence in RA: Beyond TNF Inhibitors [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/high-rheumatoid-factor-titers-and-biologic-persistence-in-ra-beyond-tnf-inhibitors/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/high-rheumatoid-factor-titers-and-biologic-persistence-in-ra-beyond-tnf-inhibitors/
