Session Information
Date: Monday, October 27, 2025
Title: (0934–0954) Systemic Lupus Erythematosus – Animal Models Poster
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a complex autoimmune disease that disproportionately affects women, underscoring the critical role of sex chromosomes and sex hormones—particularly estrogen—in disease pathogenesis. Estrogen signaling via estrogen receptor alpha (ERα) has been implicated in both the onset and progression of SLE; however, the therapeutic potential of selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs) remains underexplored. PaPE-1, also known as “pathway preferential estrogen,” is a low-affinity, non-nuclear ERα agonist that selectively activates extranuclear estrogen signaling pathways. PaPE-1 has demonstrated beneficial effects in non-reproductive tissues, including reduction of proinflammatory cytokines and enhancement of endothelial repair, while avoiding classical estrogenic actions such as cell proliferation in breast and reproductive tissues. These properties suggest that PaPE-1 could attenuate inflammation and tissue damage in lupus without increasing estrogen-related risks, making it a promising candidate for therapeutic intervention in SLE.
Methods: We utilized ex vivo bone marrow–derived dendritic cells (BMDCs) from female wild-type C57BL/6J and NZM2410 lupus-prone mice. To model lupus-relevant innate immune activation, BMDCs were stimulated with the Toll-like receptor 7 (TLR7) agonist loxoribine (Lox). Cells were cultured in charcoal-stripped, phenol red-free medium and treated with PaPE-1 or vehicle control. Inflammatory responses were assessed by mRNA expression of key cytokines at 45 minutes and 24 hours post-stimulation using quantitative PCR. All experiments included biological replicates.
Results: PaPE-1 modulated TLR7-induced proinflammatory cytokine expression in a dose-dependent manner in BMDCs from both wild-type and lupus-prone NZM2410 mice. Treatment with PaPE-1 significantly reduced MCP-1 and TNFα mRNA expression at 45 minutes post-stimulation. In wild-type BMDCs, IL-1β expression also showed a clear dose-dependent reduction. This effect was not observed in NZM2410 BMDCs, likely due to a markedly attenuated IL-1β response to TLR7 stimulation at this early timepoint (~5-fold in NZM2410 vs. ~45-fold in wild-type). These 45-minute findings are shown in Figure 1. The blunted early cytokine response in NZM2410 BMDCs may reflect altered kinetics or reduced TLR7 sensitivity due to chronic immune activation. However, by 24 hours, PaPE-1 induced a dose-dependent reduction in IL-1β and IL-6 expression in NZM2410 BMDCs, suggesting altered timing of immune-regulatory effects in lupus DCs.
Conclusion: These preclinical findings support PaPE-1 as a promising therapeutic candidate for SLE. Its selective activation of non-nuclear ERα signaling and ability to attenuate TLR7-induced inflammatory responses highlight its potential to modulate pathogenic immune activation in lupus. The observed time-dependent effects underscore the importance of kinetic profiling in future studies. Further investigation is warranted to clarify PaPE-1’s mechanisms of action and assess its translational relevance, including studies in human immune cells and at extended timepoints.
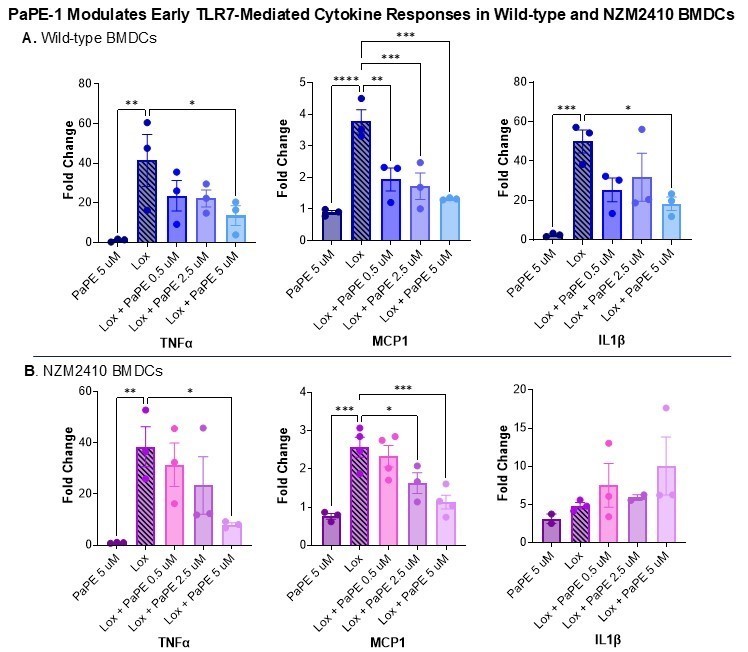 Figure 1. mRNA expression of inflammatory cytokines was measured by qPCR in BMDCs 45 minutes after TLR7 stimulation and PaPE-1 treatment. Fold change was calculated relative to housekeeping gene RPL30. Error bars represent standard error of the mean (SEM). Statistical analysis was performed using one-way ANOVA. Data represent biological replicates.* < 0.05, ** < 0.01, *** < 0.001, **** < 0.0001
Figure 1. mRNA expression of inflammatory cytokines was measured by qPCR in BMDCs 45 minutes after TLR7 stimulation and PaPE-1 treatment. Fold change was calculated relative to housekeeping gene RPL30. Error bars represent standard error of the mean (SEM). Statistical analysis was performed using one-way ANOVA. Data represent biological replicates.* < 0.05, ** < 0.01, *** < 0.001, **** < 0.0001
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Werner R, Wirth J, Gilkeson G, Cunningham M. Therapeutic Potential of PaPE-1 in Reducing TLR7-Mediated Inflammation in a Murine Model of Lupus [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/therapeutic-potential-of-pape-1-in-reducing-tlr7-mediated-inflammation-in-a-murine-model-of-lupus/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/therapeutic-potential-of-pape-1-in-reducing-tlr7-mediated-inflammation-in-a-murine-model-of-lupus/
