Session Information
Date: Monday, October 27, 2025
Title: (0934–0954) Systemic Lupus Erythematosus – Animal Models Poster
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
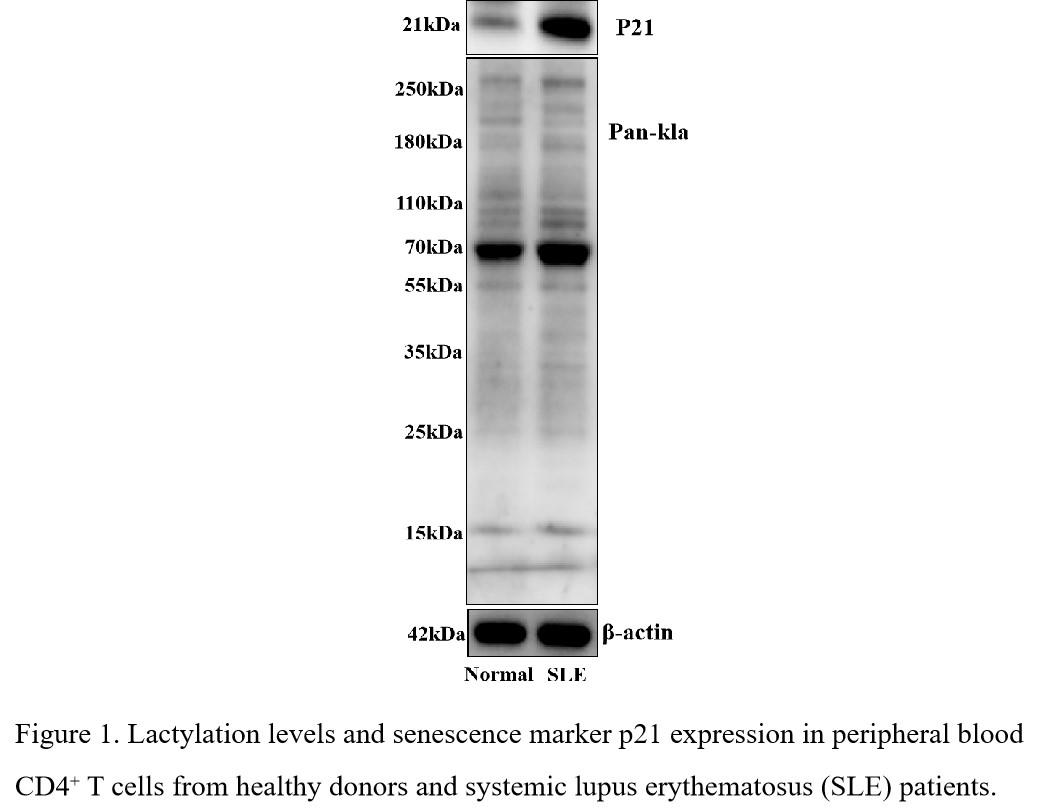
Background/Purpose: Senescent CD4+ T cells are increasingly implicated in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) pathogenesis. While metabolic reprogramming in lupus T cells enhances glycolysis and lactate accumulation, the role of lactate-induced posttranslational modifications (PTMs) in promoting T-cell senescence remains unexplored.
Methods: Peripheral blood CD4+ T cells were isolated from SLE patients and healthy donors to assess lactylation levels and senescence markers (e.g., p21). A pristane-induced lupus model was established in BALB/c mice, and splenic CD4+ T cells were analyzed for lactylation profiles using lactylome proteomics. Co-immunoprecipitation (Co-IP) coupled with mass spectrometry identified lactyltransferases interacting with Rad50, a DNA repair protein. To validate functional roles, CD4creEp300fl/fl mice (with CD4+ T cell-specific EP300 deletion) were generated and subjected to pristane-induced lupus. Rad50 lactylation was quantified using site-specific antibodies, while senescence markers, serum anti-dsDNA/IgG levels, and renal histopathology were evaluated.
Results: SLE patients exhibited elevated lactylation levels in CD4+ T cells compared to healthy controls, paralleled by increased p21 expression (Figure 1). Lactylome profiling identified Rad50 as the most prominently lactylated protein linked to DNA damage repair. Co-IP proteomics revealed Ep300 as the primary enzyme catalyzing Rad50 lactylation (Figure 2). In pristane-induced lupus mice, CD4⁺ T cells displayed heightened Rad50 lactylation, amplified p21-driven senescence, elevated autoantibodies, and severe renal damage. These phenotypes were rescued in CD4creEp300fl/fl mice (Figure 3).
Conclusion: EP300-mediated lactylation of Rad50 disrupts its DNA repair function, fostering genomic instability and pathogenic senescence in CD4+ T cells during lupus progression. Targeting this pathway may offer a novel therapeutic avenue for SLE.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
zhang m, dai h, lan c, sun m. Ep300-Catalyzed Rad50 Lactylation Compromises Genomic Stability and Drives CD4+T cells Cell Senescence in SLE [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/ep300-catalyzed-rad50-lactylation-compromises-genomic-stability-and-drives-cd4t-cells-cell-senescence-in-sle/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/ep300-catalyzed-rad50-lactylation-compromises-genomic-stability-and-drives-cd4t-cells-cell-senescence-in-sle/

.jpg)
.jpg)