Session Information
Date: Sunday, October 26, 2025
Title: (0671–0710) Systemic Sclerosis & Related Disorders – Clinical Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Total lung capacity (TLC) is seldom assessed in the prediction of systemic sclerosis (SSc) disease severity.Herein, we utilized the French SSc national database to analyse TLC in SSc patients, examine its longitudinal trajectories, and explore its associations with organ involvement and patient survival.
Methods: We performed a retrospective multicentre study of SSc patients enrolled in the French national SSc cohort with at least one TLC assessment, described patients based on baseline TLC measurements, modelized TLC trajectories in SSc, and associated TLC measures with disease prognosis. Only patients who met the 2013-American College of Rheumatology (ACR)/European Alliance of Associations for Rheumatology (EULAR) SSc classification criteria and had baseline TLC measure available were included in the study.
Results: Two thousand three hundred and forty-seven patients were included in the study. Median [interquartile] (IQR) age at SSc diagnosis was 52 [41-63] years. The proportion of females was 81%, and the proportion of dcSSc patients was 30%. Thirty percent, 38%, and 4% of patients were positive for ATA, anti-centromere (ACA), and anti-RNA polymerase III antibody (ARA), respectively. Thirty-nine percent and 28%, had ILD and LF, respectively. At baseline, forty-three percent had a TLC above or equal to 100 % and 24 % had a TLC below 80%. During a median [IQR] follow-up of 4.6 [2.5-7.9] years, 190 (16%) patients died, 617 (53%) developed de novo interstitial lung disease (ILD), 499 (43%) developed de novo LF, 175 (15%) were diagnosed with PAH following right heart catheterization, and 69 (6%) developed scleroderma renal crisis (SRC). Kaplan-Meier curves showing the overall 20-year probabilities of survival and survival without ILD, LF, and PAH after SSc diagnosis according to baseline TLC showed that a lower TLC was associated with worse survival and a higher risk of ILD, LF, or PAH occurrences (p < 0.001) (Figure 1).Among 2347 patients with at least one TLC measure, 988 (42%) patients had at least 2 TLC measures. Individual TLC trajectories varied among patients. Different models of TLC trajectories were assessed using latent process mixed models. The best model showed that the vast majority of SSc patients had stable TLC trajectories and clustered patients into three groups predictive of SSc survival, ILD, LF, and PAH (p < 0.05). Interestingly, a 10% decrease of TLC was found to be predictive of a 5% decrease in forced vital capacity (FVC)(p < 0.0001), a 10% decrease in DLCODLCO (p < 0.001), and consequently an earlier predictive marker of ILD and LF than FVC (Figure 2).
Conclusion: The present study shows that TLC measurement is associated with SSc severity and prognosis. It suggests that TLC may be an early marker of ILD and PF development, and that a 10% TLC decrease is a useful and early marker of FVC or DLCO decreases, as well as ILD or LF occurrence. Overall, our findings support the use of TLC along with FVC in monitoring and assessing ILD and LF in both clinical practice and clinical trials.
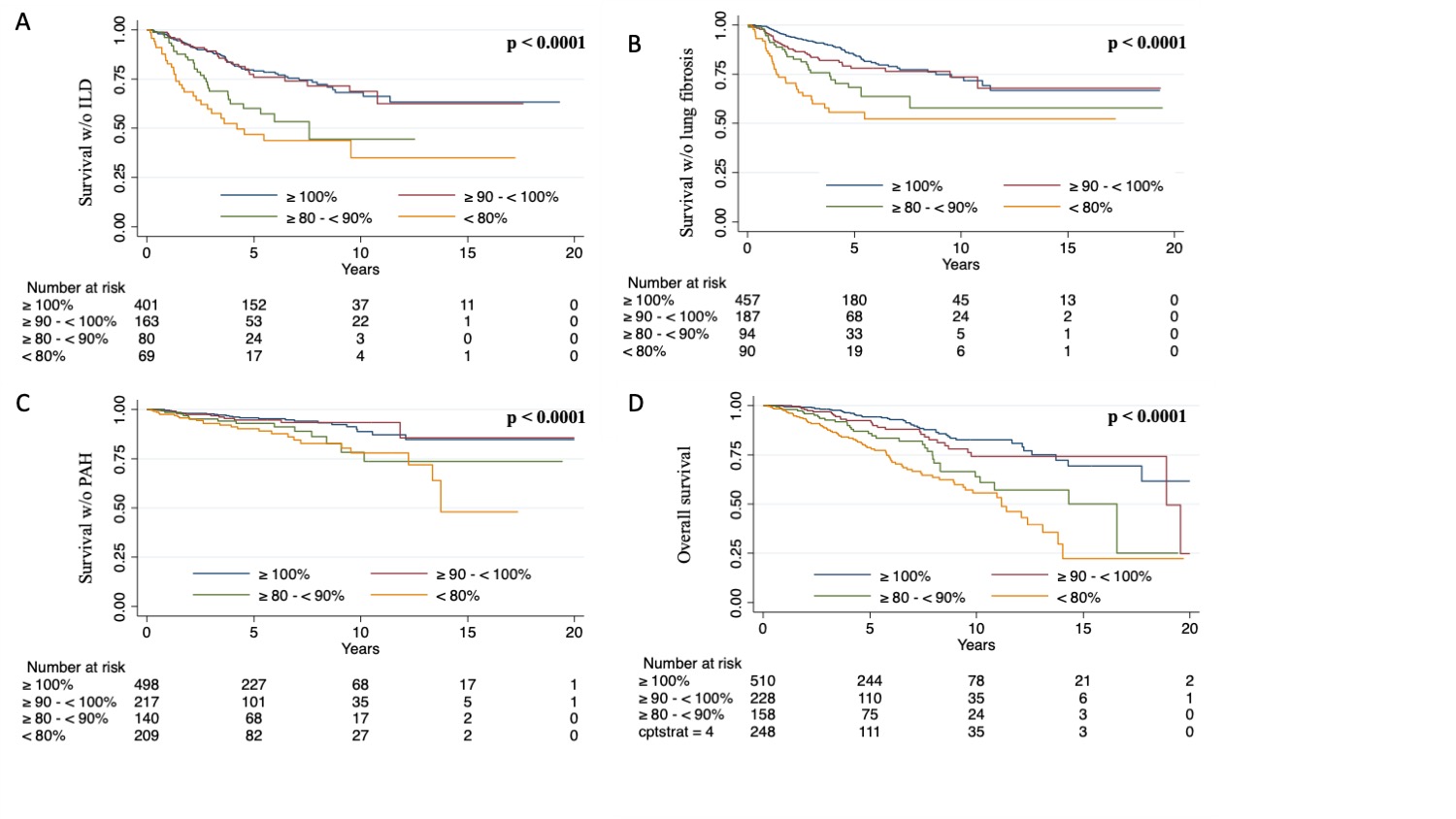 Figure 1. Overall probability of survival according to total lung capacity in patients with systemic sclerosis
Figure 1. Overall probability of survival according to total lung capacity in patients with systemic sclerosis
.jpg) Figure 2. Overall probability of time to interstitial lung disease and lung fibrosis onset according to total lung capacity and forced vital capacity decrease in patients with systemic sclerosis
Figure 2. Overall probability of time to interstitial lung disease and lung fibrosis onset according to total lung capacity and forced vital capacity decrease in patients with systemic sclerosis
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Chaigne B, bense A, Aubourg F, AGARD C, Allanore Y, berezne A, Pugnet G, Hachulla E, Cottin V, Hot A, Dunogue b, Kanagaratnam A, Palat S, Lescoat A, berthier S, Chatelus E, Rivière S, Launay D, Truchetet M, Dinh-Xuan A, Mouthon L. Total lung capacity is predictive of disease severity and survival in systemic sclerosis: a longitudinal analysis in 2347 patients from the French National Cohort Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/total-lung-capacity-is-predictive-of-disease-severity-and-survival-in-systemic-sclerosis-a-longitudinal-analysis-in-2347-patients-from-the-french-national-cohort-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/total-lung-capacity-is-predictive-of-disease-severity-and-survival-in-systemic-sclerosis-a-longitudinal-analysis-in-2347-patients-from-the-french-national-cohort-study/
