Session Information
Date: Monday, October 27, 2025
Title: Abstracts: T Cell Biology & Targets in Autoimmune & Inflammatory Disease (0885–0890)
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 10:30AM-10:45AM
Background/Purpose: Immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) therapies for cancer can induce immune-related adverse events (irAEs) involving musculoskeletal (MSK) systems. ICI myotoxicity (ICI-M) can present as a triad of fulminant myocarditis, myositis and myasthenia gravis-like syndrome, calling for rapid recognition and precise therapeutic assessment. Abatacept shown promise as a treatment option for high-grade ICI-M [1]. Previously we identified a clonal CD38hi cytotoxic CD8 T cell population specifically expanded in ICI-arthritis, indicating an irAE specific T cell response in ICI-MSK systems [2]. Regulatory CD8 T cells expressing KIR have been reported in autoimmunity and cancer patients[3]. Whether these T populations can help clinical recognition and therapeutic response assessment in high-grade ICI-M calls for further investigation.
Methods: We performed immunophenotyping, single-cell transcriptomic analysis and TCR analysis of T cells from blood and muscle tissue in a multi-center cohort of ICI-M patients (n=16). Blood of ICI-A (n=7), ICI-without irAE (ICI, n=9), and cancer-without ICI therapy (non-ICI, n=6) were used as control.
Results: scRNA-seq identified 11 distinct T cell clusters in ICI-M and ICI-A (Fig 1a-b). Transcriptomic features of the top four effector memory clusters, C1 GZMB+ GZMH+ GNLY+ cytotoxic CD8 T cells, C3/6 GZMK+KLRB+/HLADR+ cytotoxic CD8 T cells, and C4 KIR+ CD8 T cells, each showing unique cytotoxic characteristics (Fig 1c). C3/6 were identified as CD38hi-like cells using a gene signature we previously identified [2]. Multi-color flow cytometry showed that circulating C3/6 and C4 are expanded in ICI-M (Fig 1d). C3/6 were also identified in muscle tissue of ICI-M patients.TCR repertoire analyses revealed more prominent clonal expansion of cytotoxic CD8 Tem cells in ICI-M over ICI-A, particularly CD38hi-like CD8 T cells (C3+C6) and KIR+ CD8 T cells (C4) (Fig 2a). C3/C6 shared clonality that’s different from C4 (Fig 2b).A tailored dosing of abatacept in addition to corticosteroids +/- ruxolitinib was applied based on the degree of CD80 blockade and successfully rescued clinically fulminant ICI-M in our multi-center cohort. The abatacept regimen altered the composition and clonality of CD8 T cells (Fig 3a-c). Using cellchat algorism, possible interactions were identified among KIR+ CD8 T cells (C4) and CD38like CD8 T (C3+C6) (Fig 3 c).
Conclusion: The dynamic of CD38hi CD8 T cells and KIR+ CD8 T cells effectively identified ICI-M patients and supported their therapeutic assessment during abatacept. Analyzing these populations may provide personalized treatment strategy for life-threatening irAEs.
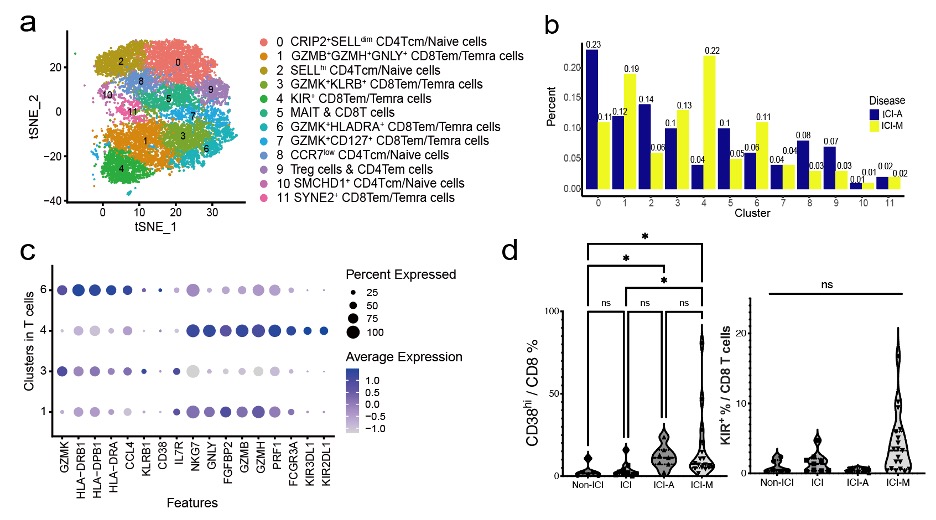 Figure 1. Transcriptomic features of ICI-M peripheral blood. scRNA-seq identified distinct T cell clusters (a) in ICI-M and ICI-A (b). Top four effector memory clusters showed distinct transcriptomic features (c). Frequency of CD38hi-like C3/6 and KIR+ C4 in ICI-M (d). Krustal-Wallis test. ns, not significant. *, p < 0.05.
Figure 1. Transcriptomic features of ICI-M peripheral blood. scRNA-seq identified distinct T cell clusters (a) in ICI-M and ICI-A (b). Top four effector memory clusters showed distinct transcriptomic features (c). Frequency of CD38hi-like C3/6 and KIR+ C4 in ICI-M (d). Krustal-Wallis test. ns, not significant. *, p < 0.05.
.jpg) Figure 2. scRNA-seq TCR analysis showed clonality of ICI-M circulating T cells clusters (a) and their similarity represented with Morisita index (b).
Figure 2. scRNA-seq TCR analysis showed clonality of ICI-M circulating T cells clusters (a) and their similarity represented with Morisita index (b).
.jpg) Figure 3. Therapeutic response to abatacept. tSNE plot showing abatacept altered the composition and clonality (a-b) of CD8 T cells in ICI-M. Flow cytometry analysis showed fold change of circulating CD38hi and KIR+ CD8 T cells in ICI-M before and after abatacept (c). Chord plot showing the inferred communication among T cell clusters. The edge width represents the communication probability. (d).
Figure 3. Therapeutic response to abatacept. tSNE plot showing abatacept altered the composition and clonality (a-b) of CD8 T cells in ICI-M. Flow cytometry analysis showed fold change of circulating CD38hi and KIR+ CD8 T cells in ICI-M before and after abatacept (c). Chord plot showing the inferred communication among T cell clusters. The edge width represents the communication probability. (d).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Wang R, Xiang C, Procureur A, Sanchez-Dal Cin J, Wang Q, Lian X, Rosenzwajg M, Allenbach Y, Rao D, Fu Q, Shen N, Salem J, Ye S. Dynamics of cytotoxic and regulatory CD8 T cells underlies outcome in ICI-myotoxicity [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/dynamics-of-cytotoxic-and-regulatory-cd8-t-cells-underlies-outcome-in-ici-myotoxicity/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/dynamics-of-cytotoxic-and-regulatory-cd8-t-cells-underlies-outcome-in-ici-myotoxicity/
