Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Methotrexate (MTX) polyglutamates (MTX-PGs), the intracellular active forms of MTX, are hypothesized to reflect cumulative exposure and potentially predict therapeutic efficacy in rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Prior studies have shown contrasting results. This study aimed to assess association of total MTX-PG levels, PG1–PG5 with EULAR response at 16 weeks in treatment-naïve RA patients undergoing standardized MTX escalation.
Methods: This was a prospective observational cohort study including 65 treatment-naïve RA patients initiated on oral or subcutaneous MTX using a standardized protocol. At 16 weeks, MTX-PG levels (total, PG1–PG5, short-chain-MTX PG1-2, long-chain-MTX PG3-5) were measured using HPLC. The primary outcome was EULAR response at week 16 (Good, Moderate, None). Descriptive statistics, independent t-tests, ANOVA, Tukey post hoc analysis, and logistic and linear regression were used to explore associations between MTX-PG levels and response, adjusting for age, sex, BMI, RA duration, route of administration, baseline CRP, and DAS28.
Results: A total of 65 seropositive treatment-naïve rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients were included. The median age was 44.5 years (interquartile range [IQR]: 38–53), and 76.9% were female. 86.2% were RF-positive and 95.4% were anti-CCP–positive. The median disease duration at baseline was 17.2 months (IQR: 12–24), and the median baseline DAS28-CRP was 5.9 (IQR: 5.2–6.6)Among 65 patients, 21 (32.3%) achieved Good response, 34 (52.3%) Moderate, and 10 (15.4%) No response. No significant difference was found in total MTX-PG levels between responders (good and moderate) and non-responders (112.05 ± 54.1 vs 112.26 ± 73.1 nM; p = 0.992). Also, short-chain and long-chain MTX-PG levels did not differ significantly. Univariate analysis showed a trend toward higher BMI and longer RA duration in non-responders.However, ANOVA revealed significant higher PG3 levels with moderate responders showing higher PG3 than good responders (p = 0.025, Tukey). Multivariable logistic regression did not identify any independent predictors of EULAR response. In linear regression, age was the only significant predictor of total MTX-PG levels (p = 0.033).
Conclusion: In this real-world prospective study, neither total MTX-PG levels nor specific PG subtypes independently predicted EULAR response at 16 weeks. Further studies incorporating longitudinal sampling, genetic polymorphisms, and safety outcomes are warranted to clarify the pharmacodynamic utility of MTX-PG monitoring in RA.
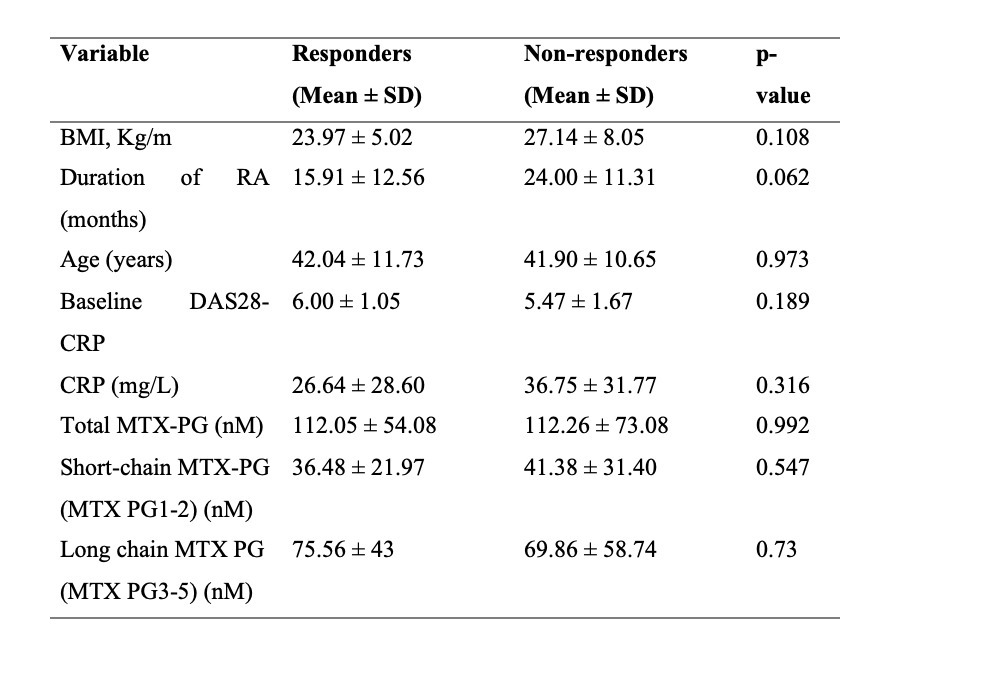 Table 1: Univariate analysis to identify predictors of response from baseline variables and MTX-PG levels.
Table 1: Univariate analysis to identify predictors of response from baseline variables and MTX-PG levels.
.jpg) Table 2. Multivariable Logistic Regression for EULAR Response at 16 Weeks
Table 2. Multivariable Logistic Regression for EULAR Response at 16 Weeks
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
MN C, KHULLAR A, Leishangthem B, Naidu S, Dhir V, Jain S. Intracellular Methotrexate Polyglutamate Profiles Do Not Correlate with Early Clinical Response in Treatment-Naïve Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Prospective Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/intracellular-methotrexate-polyglutamate-profiles-do-not-correlate-with-early-clinical-response-in-treatment-naive-rheumatoid-arthritis-a-prospective-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/intracellular-methotrexate-polyglutamate-profiles-do-not-correlate-with-early-clinical-response-in-treatment-naive-rheumatoid-arthritis-a-prospective-study/
