Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 19, 2024
Title: Abstracts: Muscle Biology, Myositis & Myopathies – Basic & Clinical Science II
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 11:00AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Many myositis patients have myositis-specific autoantibodies (MSA) that define unique clinical phenotypes. For instance, dermatomyositis (DM) patients with anti-Mi2 autoantibodies have weaker muscles, higher levels of serum muscle enzymes, and more severe inflammatory infiltrates on muscle biopsies compared to DM patients with other MSAs. The aim of this study was to identify novel myositis-specific autoantibodies.
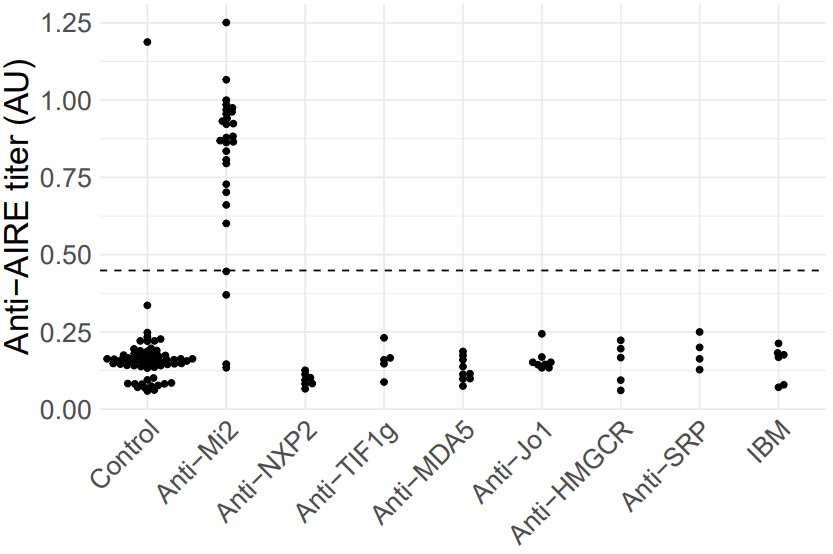
Methods: Phage Immunoprecipitation Sequencing (PhIP-Seq) was conducted using sera from 804 healthy controls and 411 patients with adult or juvenile myositis. PhIP-Seq suggested that autoimmune regulator (AIRE) is a novel autoantigen in myositis patients with anti-Mi2 autoantibodies. To confirm these findings, we performed an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) to screen for anti-AIRE autoantibodies. We tested serum samples from a separate group of 72 myositis patients (27 with anti-Mi2, 7 with anti-NXP2, 6 with anti-TIF1, 9 with anti-MDA5, 8 with anti-Jo1, 5 with anti-HMGCR, 4 with anti-SRP autoantibodies, and 6 with IBM) and 63 healthy comparators. To determine if the same autoantibodies that bind Mi2 also target AIRE, we affinity purified anti-Mi2 autoantibodies from the sera of three different anti-Mi2 myositis patients who tested positive for anti-AIRE autoantibodies by ELISA. We also collected the immunoglobulin fraction depleted of these anti-Mi2 autoantibodies. Then, we assessed anti-AIRE reactivity by ELISA in both the anti-Mi2 enriched and depleted fractions.
Results: PhIP-Seq suggested that anti-AIRE autoantibodies are present in sera only from anti-Mi2 dermatomyositis patients, and not in the other myositis patients that were screened. The AIRE peptides recognized by PhIP-Seq were highly homologous to Mi2 protein sequences. Assessing anti-AIRE reactivity by ELISA showed that 88.9% of anti-Mi2-positive DM patients, 0% of other myositis patients, and 1.6% of healthy comparators had anti-AIRE autoantibodies (Figure 1). Affinity-purified anti-Mi2 autoantibodies were positive for both anti-Mi2 and anti-AIRE reactivity by ELISA. In contrast, anti-Mi2-depleted immunoglobulin fractions were negative for both anti-Mi2 and anti-AIRE reactivity by ELISA.
Conclusion: In this study, we have discovered that anti-AIRE autoantibodies exist specifically in patients with anti-Mi2 dermatomyositis. Given AIRE’s critical role in maintaining immune tolerance and preventing autoimmune reactions, future studies are needed to explore the pathological implications of anti-AIRE reactivity within muscle tissue.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Musai J, Jayaraman S, Pak k, Pinal-Fernandez I, Muñoz-braceras S, Casal-Dominguez M, Cho E, Fitisemanu F, milisenda j, Rider L, Schiffenbauer A, Selva-O’Callaghan A, Lloyd T, Christopher-Stine L, Burbelo P, Larman B, Mammen A. Anti-Mi2 Autoantibodies in Dermatomyositis Patients Also Recognize Autoimmune Regulator (AIRE) Protein [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/anti-mi2-autoantibodies-in-dermatomyositis-patients-also-recognize-autoimmune-regulator-aire-protein/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/anti-mi2-autoantibodies-in-dermatomyositis-patients-also-recognize-autoimmune-regulator-aire-protein/