Session Information
Date: Monday, November 18, 2024
Title: RA – Treatment Poster III
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Many patients with rheumatic conditions do not completely respond or are refractory to biological therapy. Therefore, there are unmet medical needs in the treatment of such diseases, which should be addressed by novel approaches. Accumulating evidence suggests that extracellular vesicles (EVs) play a role in the development and modulation of rheumatic autoimmune processes. In the current study, we aimed to prove the potential therapeutic and diagnostic potential of patients-derived circulating EVs in rheumatic inflammatory/autoimmune diseases.
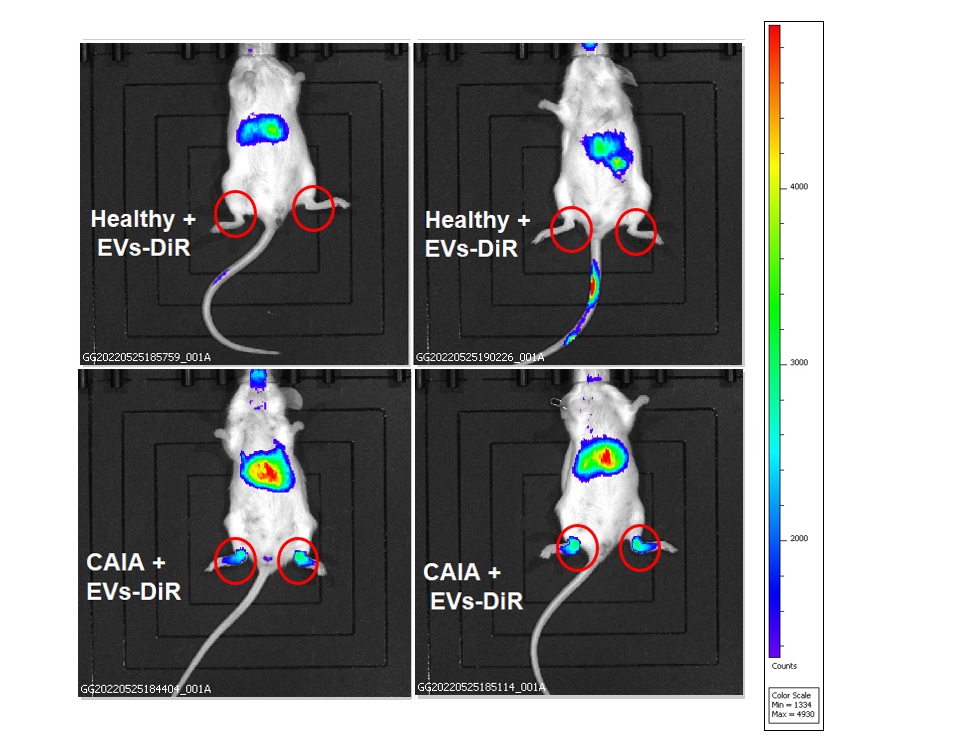
Methods: Plasma/serum-derived EVs were isolated from arthritic mice (collagen-induced arthritis [CIA] model) and from patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and fibromyalgia syndrome (FMS) using: ultrafiltration, a commercial exosome purification kit (NORGEN BIOTEK CORP), and size exclusion chromatography techniques. Characterization of these EVs was conducted using nanoparticle tracking analysis, transition electron microscopy and western blot analysis. The expression of ’tissue-specific homing receptors’ such as integrins, on plasma/serum-derived EVs isolated from arthritic mice (CIA model) or RA patients, was examined, using WB analysis. EVs were labelled using DiR fluorescent dye and their potential in-vivo migration towards inflamed synovia, was explored in collagen antibody-induced arthritis (CAIA) model, using In Vivo Imaging System (IVIS). Cellular uptake of RA patients-derived labelled EVs was conducted using SW982, a human synovial cells.
Results: We found that EVs isolated from arthritic mice (CIA model) express the synovial homing receptor αVβ3 integrin. Importantly, autologous labeled EVs, derived from blood of arthritic mice (CAIA model), can migrate specifically towards inflamed synovia (Fig. 1). These EVs strongly expresses glucose transporter 1 (mGLUT1) which in turn, improves their therapeutic potential to be loaded with anti-inflammatory drugs using glucose-coated gold nanoparticles (GNPs). Moreover, we show that EVs derived from plasma of RA patients express the αVβ3 integrin and can be taken up by LPS/TNFα-induced activated human synovial cell line in vitro.
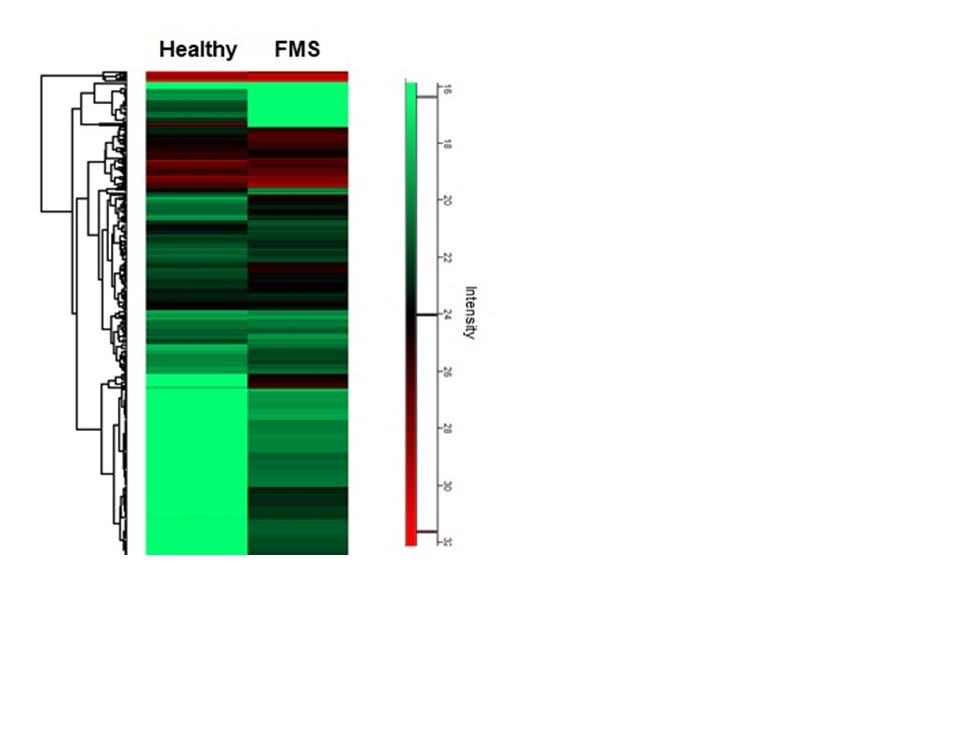
We also found a significant secretion of small EVs in the blood of FMS patients as compared to sex- and age-matched healthy controls. Importantly, proteomic analysis of circulating EVs derived from FMS patients revealed the expression of neurological/pain- (e.g. Cofilin-1), mitochondrial- (SFXN1, MT-C02, VDAC1), immunological- (e.g. Complement component 1q) and ROS/oxidative stress-related proteins (e.g. Superoxide dismutase) in EVs of patients only and not in sex- and age-matched healthy controls (Fig. 2).
Conclusion: We show the potential therapeutic use of autologous plasma-derived EVs in the management of RA and the potential diagnostic use of plasma-derived EVs in FMS. We believe that the use of these natural, non-immunogenic, nano-carriers (‘EVs’) will have a huge impact in the field of diagnosis and drug delivery in rheumatic inflammatory/autoimmune diseases in the near future, as can be already seen in a few ongoing clinical trials.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Halpert G, Moskovitch O, Israel L, Govrin E, Gilburd B, Segal O, Anaki A, Caller T, Yechiali D, Segev S, Gendelman O, Watad A, Mehrian-Shai R, Popovtzer R, Amital H. The Potential Use of Circulating Extracellular Vesicles for Improved Diagnosis and Therapy in Rheumatic Inflammatory/autoimmune Diseases: Proof of Concept Studies [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-potential-use-of-circulating-extracellular-vesicles-for-improved-diagnosis-and-therapy-in-rheumatic-inflammatory-autoimmune-diseases-proof-of-concept-studies/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-potential-use-of-circulating-extracellular-vesicles-for-improved-diagnosis-and-therapy-in-rheumatic-inflammatory-autoimmune-diseases-proof-of-concept-studies/