Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: JDM is a heterogenous systemic autoimmune disease with muscle and skin pathology, which can be clinically subgrouped by MSAs (ex: anti-TIF1, anti-MDA5 autoantibodies (Ab)). Pathogenesis is poorly understood. We aimed to better understand proteomic expression and clinical correlations in JDM overall and MSA group.
Methods: SomaLogic SOMAscan aptamer-based proteomic assay (Boulder, CO) analyzed 1,305 serum proteins in JDM patients. Clinical traits were compared (MSA vs. rest of JDM) by Mann-Whitney U test. Weighted-gene co-expression analysis (WGCNA) was used to create protein co-expression modules, which were correlated with clinical traits. Highly correlated protein module-clinical traits pairs (rho >0.45) were functionally annotated by Gene Ontology Biological Processes (GOBP) overrepresentation analysis. Significant GOBPs (q< 0.05, 3+ proteins, fold enrichment > 20) for JDM overall (n=39), anti-TIF1 Ab (n=19) and anti-MDA5 Ab (n=10) patients were grouped into functional categories.
Results: JDM patients were 66% female, 58% Caucasian, mean age of 9.7 years, and mean Physician Global Activity (PGA) of 4.0/10. Significant differences included Disease Activity Score (DAS) Skin higher in anti-TIF1 Ab, MMT26 (Manual Muscle Testing-26) higher in anti-MDA5 Ab, more Caucasians in anti-TIF1 Ab, and shorter disease duration in anti-MDA5 Ab vs. rest of JDM patients.
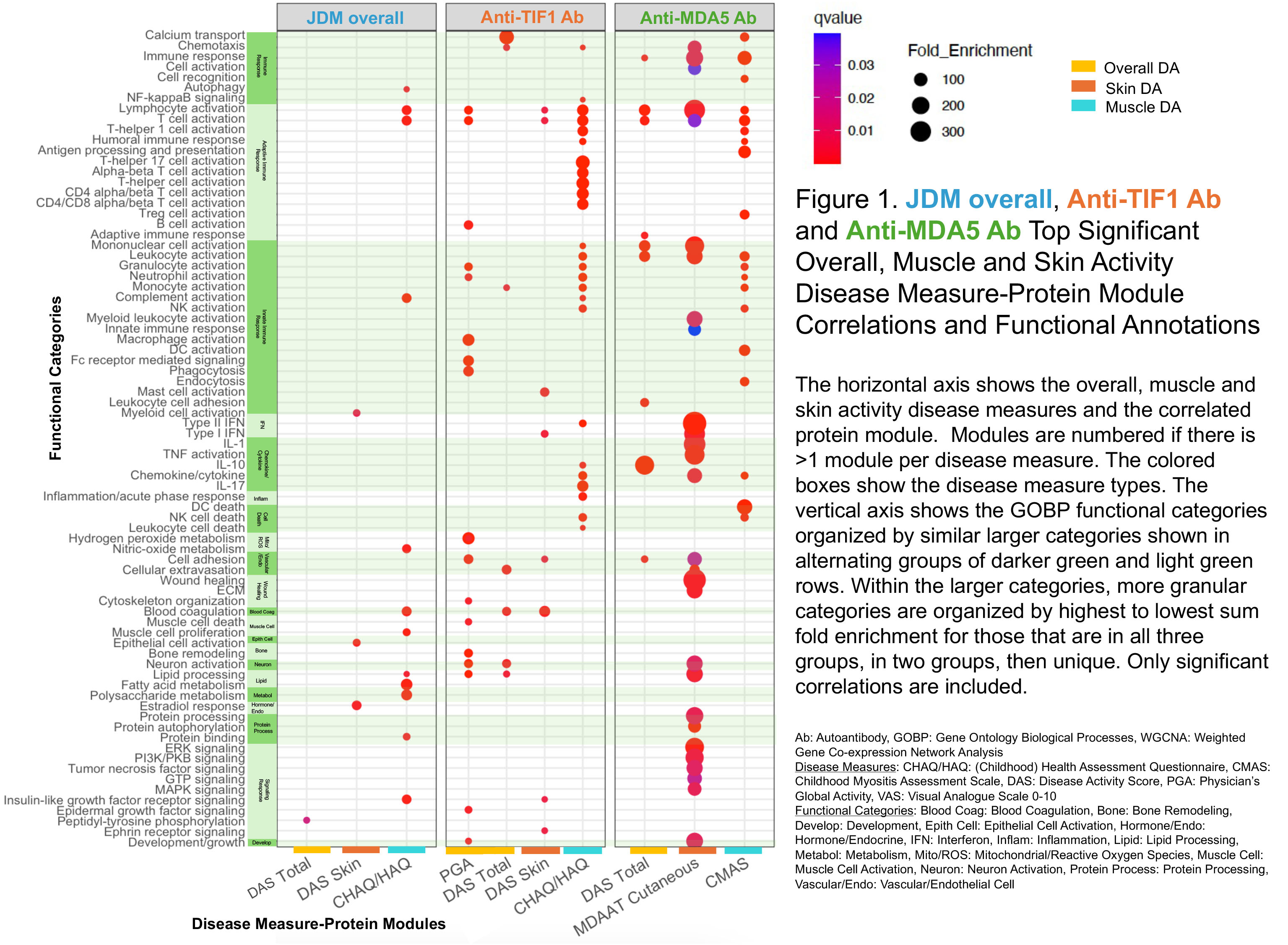
The top immune-related functional category (highest fold enrichment GOBP), for skin disease activity (DA) were innate immune response in JDM overall and anti-TIF1 Ab; interferon (IFN) in anti-TIF1, anti-MDA5; epithelial cell activation in JDM overall; wound healing and cytokine/chemokine in anti-MDA5 Ab patients (Figure 1). Other top functional categories were hormone/endocrine for JDM overall and blood coagulation for anti-TIF1 Ab patients.
Top immune-related categories for muscle DA were adaptive immune response in all groups; cytokine/chemokine, innate immune response in anti-TIF1 Ab; cell death and immune response in anti-MDA5 Ab. Other top functional categories were lipid processing and metabolism for JDM overall patients.
For overall DA, the top immune-related categories were IL-10, lymphocyte activation and mononuclear cell activation in anti-MDA5 Ab and macrophage activation in anti-TIF1 Ab. Other top categories included signaling response in JDM overall, and calcium transport, hydrogen peroxide metabolism in anti-TIF1 Ab patients.
IFN had associations with skin DA in anti-MDA5 Ab and both skin DA and function/muscle in anti-TIF1 Ab. In anti-TIF1 Ab patients, IFN had top associations with multiple disease traits (skin DA, extramuscular, muscle DA, damage), not shown.
Conclusion: We identified distinct protein modules and functions associated with clinical traits by MSA group (anti-TIF1 Ab, anti-MDA5 Ab) and in JDM overall. For skin DA, anti-MDA5 Ab and anti-TIF1 Ab shared IFN association, while for muscle DA, all groups shared adaptive immune response association. IFN showed differences in clinical associations by MSA group. These similarities and differences could have pathogenic and therapeutic implications for JDM patients in specific MSA groups.
Acknowledgments
NIH IRP, NIAMS, NIEHS, NIAID, CC, Cure JM.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kaneshiro A, Chin A, Rider L, Miller F, Cheung F, Darrell M, Biancotto A, Zajmi U, Kim H. Broad Proteomic Analysis Reveals Top Differential Protein Modules and Functional Annotations with Clinical Traits in Juvenile Dermatomyositis (JDM) and Myositis-Specific Autoantibody (MSA) Groups [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/broad-proteomic-analysis-reveals-top-differential-protein-modules-and-functional-annotations-with-clinical-traits-in-juvenile-dermatomyositis-jdm-and-myositis-specific-autoantibody-msa-groups/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/broad-proteomic-analysis-reveals-top-differential-protein-modules-and-functional-annotations-with-clinical-traits-in-juvenile-dermatomyositis-jdm-and-myositis-specific-autoantibody-msa-groups/