Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 1:00PM-2:30PM
Background/Purpose: Cartilage acidic protein1 (CRTAC1) is a potential biomarker linked to osteoarthritis (OA) and cartilage degeneration. This study aimed to compare CRTAC1 levels in the synovial fluid (SF) and plasma of OA patients and healthy controls (HCs), including plasma levels in other rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases (RMDs), assess CRTAC1 across different OA subtypes, and identify deregulated miRNAs targeting CRTAC1 in OA patients.
Methods: The study involved 562 participants (OA = 184, RA = 98, HC = 144, SSc = 71, IIM = 43, AxSpA = 20). Plasma and SF samples were analyzed for CRTAC1 levels using mass-spectrometry (PeptiQuant) and IQ-ELISA (Ray-Biotech). miRNA profiles were obtained using sequencing (Next-Flex) and digital PCR (Qiagen). Knee radiographs were evaluated using the Kellgren-Lawrence grading scale.
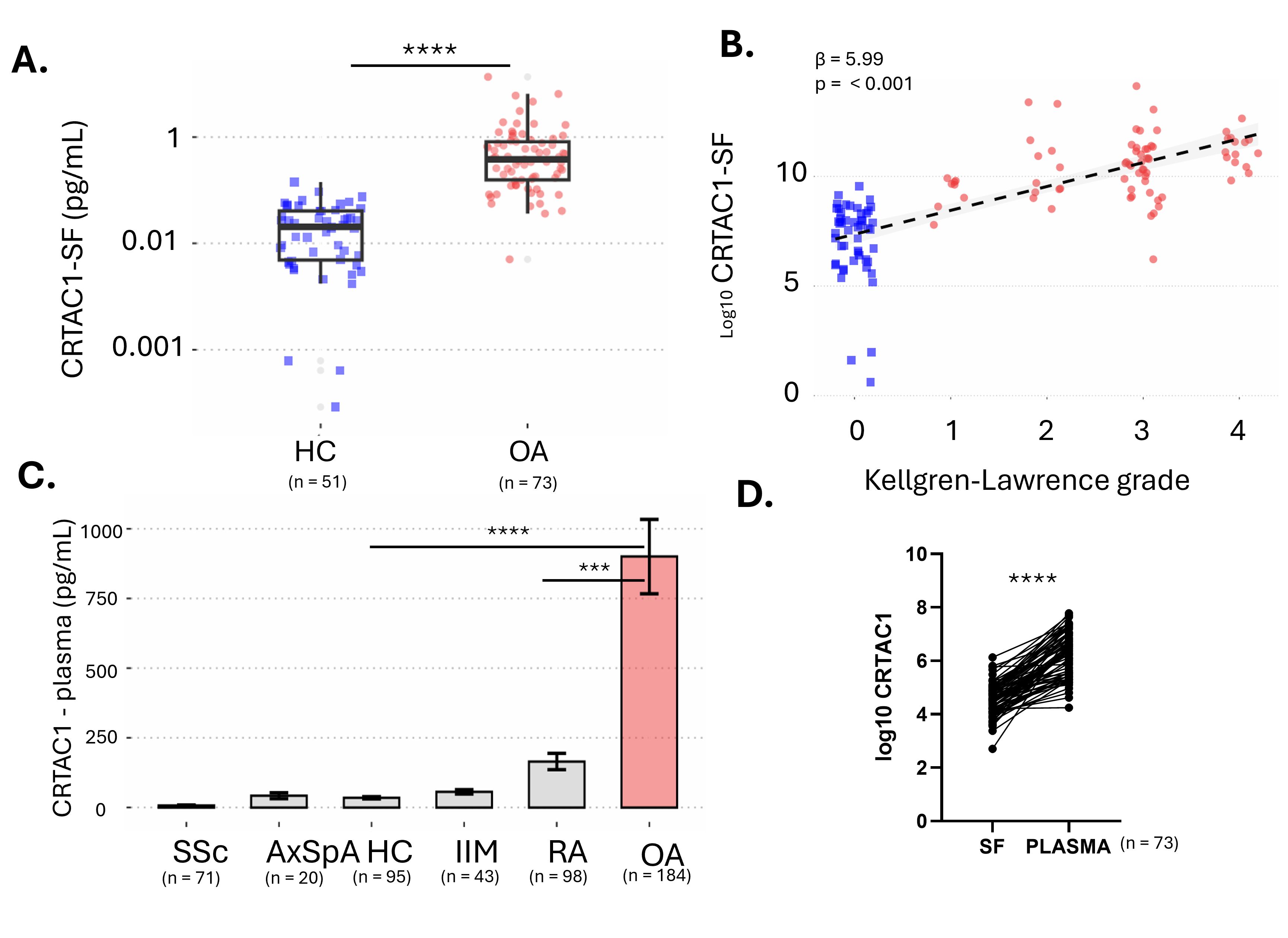
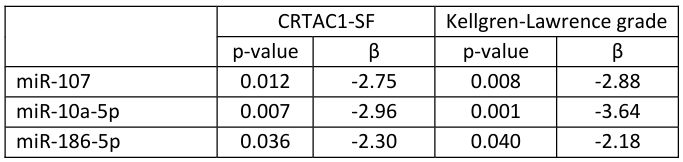
Results: CRTAC1 levels were significantly higher in OA patients than in HCs, both in plasma and SF (p< 0.001), with higher concentration in plasma, and compared to other RMDs (Fig1). Local CRTAC1 concentrations positively correlated with OA severity (p< 0.001), whereas no such correlation was observed in plasma. CRTAC1 levels did not differ among hands, knee and hip OA. Additionally, miR-16-5p (p< 0.001), miR-107 (p=0.1), and miR-186-5p (p< 0.001) were downregulated in the SF of OA patients compared to HCs, and were negatively associated with local CRTAC1 levels and OA severity (Tab1).
Conclusion: The higher CRTAC1 concentration in OA compared to HCs/RMDs suggests CRTAC1 is a promising OA biomarker, while local CRTAC1 levels indicate joint severity. This study emphasizes the miRNAs’ regulatory influence on CRTAC1 expression and their potential impact on OA progression.
Acknowledgement: This work was supported by GAUK-266523, MHCR 023728, and SVV 260638.
Abbreviations: AxSpA, Axial Spondyloarthritis; HC, healthy controls; IIM, Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathies; OA, Osteoarthritis; RA, Rheumatoid Arthritis; SF, Synovial Fluid; SSc, Systemic Sclerosis
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Prokopcová A, Baloun J, Navrátilová A, Mocová K, Ondrejčáková L, Juhaszova J, Kropáčková T, Storkanova H, Tomcik M, Gatterova J, Sleglova O, Ruzickova O, Kriegova E, Gallo J, Ballay R, Fulin P, Vencovský J, Šenolt L. CRTAC1 in Osteoarthritis: Implications for Disease Severity and miRNA Regulation [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/crtac1-in-osteoarthritis-implications-for-disease-severity-and-mirna-regulation/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/crtac1-in-osteoarthritis-implications-for-disease-severity-and-mirna-regulation/