Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 17, 2024
Title: RA – Treatment Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
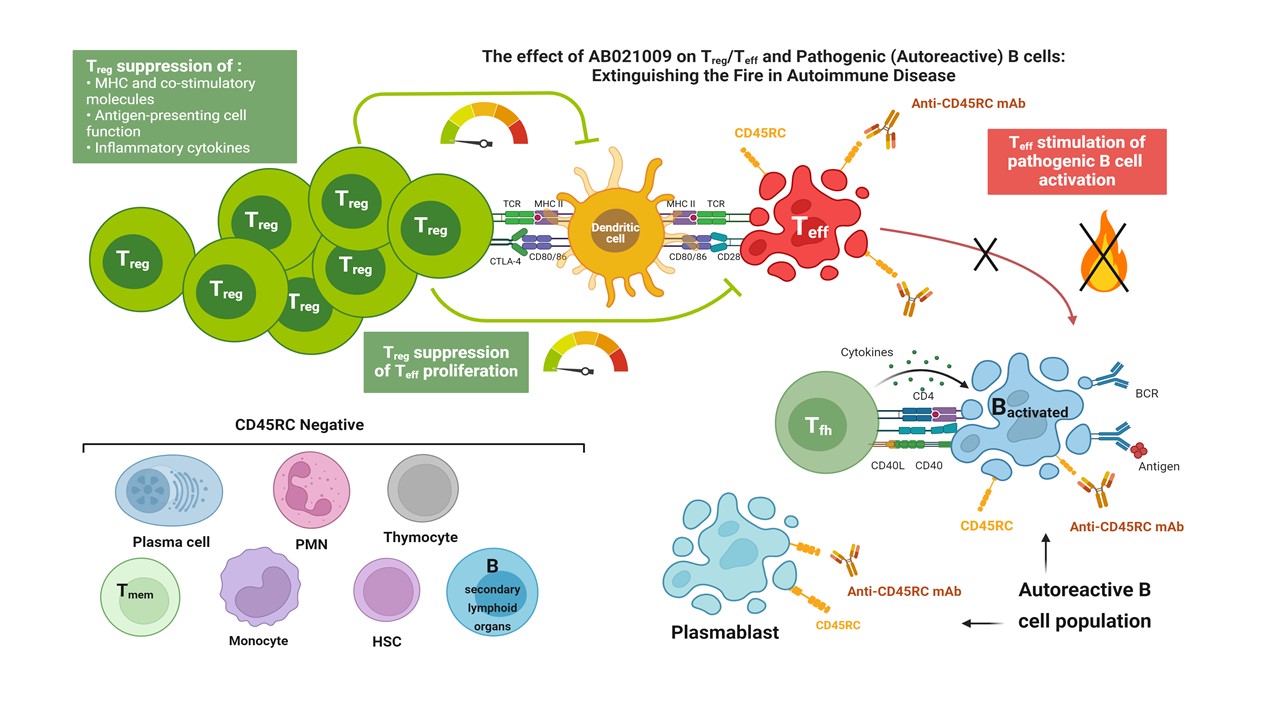
Background/Purpose: CD45RC is an isoform of CD45, a transmembrane tyrosine phosphatase, essential regulator of T and B cells antigen receptor signaling, expressed by most blood B cells and some T cell subsets (Th1 and precursors, TEMRA cells). We demonstrated that administration of an anti-CD45RC mAb in preclinical models of transplant rejection, graft versus host disease (GvHD), Duchene dystrophy or APECED leads to prevention or control of the disease. RA is a chronic relapsing/remitting disease characterized by synovitis, joint deformity, loss of function and increased mortality. While T-cells are a major component in the pathogenesis, B-cells are also pathogenic.
In this study, we deciphered the mechanism of action of the anti-human CD45RC mAb and assessed its effect in vitro and in vivo on human immune cell populations. We then assessed the potential of the anti-CD45RC mAb in an experimental model of rheumatoid arthritis.
Methods: Cells were isolated from peripheral blood. Apoptosis, antibody-Dependent Cellular Cytotoxicity (ADCC), antibody-Dependent Cellular Phagocytosis (ADCP) and Complement-Dependent Cytotoxicity (CDC) were assessed by Annexin V/DAPI staining and cell count. In vivo studies were performed in CD34+ immune-humanized NSG mice, in a model of xenogeneic GVHD in human PBMC-reconstituted immunodeficient NSG mice or in a model of collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) in rat.
Results: We demonstrated that the humanized anti-human CD45RC mAb induced CD45RChigh T and B cell death mainly by direct apoptosis of CD45RChigh cells, inducing signaling but not cytokine release. We demonstrated contribution of cross linking and ADCP. Using in vivo studies in CD34+ immune-humanized NSG mice, we showed that a single iv administration of anti-CD45RC mAb induced an efficient killing of CD45RChigh T and B cells as soon as day 1, this effect was dose and time-dependent and targeted cells recovered by day 24. We also showed a dose dependent efficacy in a model of xenogeneic GVHD in human PBMC-reconstituted immunodeficient NSG mice.
Treatment with an anti-rat CD45RC mAb in a rat model of CIA efficiently prevented the disease, completely inhibited anti-collagen antibody production, inflammation of the paws and GM-CSF secretion in the sera. Efficacy of the anti-CD45RC mAb correlated with depletion of CD45RChigh T and B cells by d3 ( >94%) and until sacrifice with conserved Treg numbers. Analysis of RA patients showed a strong infiltration by CD45RChigh cells of synovial tissues using IHC.
Conclusion: Altogether our study demonstrates the mechanisms by which anti-human CD45RC mAb mediates CD45RChigh T and B cell death to control immune responses and that anti-CD45RC mAb treatment is a potent immunomodulatory agent rebalancing the Treg/teff ratio to reduce joint inflammation and disease activity in RA and a potential alternative for first line DMARD.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Bergua C, Besnard M, Ahmil G, Ouisse L, Vimond N, Salama A, Evrard B, Brisebard E, Collette A, Blanchard F, Larcher T, Van Brempt R, Le Goff B, Anegon I, Guillonneau C. Elimination of CD45RChigh T and B Cells by anti-CD45RC mAb Lead to Efficient Control of Experimental Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/elimination-of-cd45rchigh-t-and-b-cells-by-anti-cd45rc-mab-lead-to-efficient-control-of-experimental-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/elimination-of-cd45rchigh-t-and-b-cells-by-anti-cd45rc-mab-lead-to-efficient-control-of-experimental-rheumatoid-arthritis/