Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 17, 2024
Title: Innate Immunity Poster
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Interactions between fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLSs) and macrophage-like synoviocytes (MLSs) are pivotal in the pathogenesis of RA and PsA. FLSs both activate and are activated by macrophages, contributing to the inflammatory milieu. MLSs and FLSs are present in cartilage erosions, indicating a cooperative role in extracellular matrix invasion and degradation. This study aims to evaluate the response of FLSs to inflammatory cytokines (LPS and IFNγ) and anti-inflammatory cytokines (IL-4 and IL-13) in synoviocytes isolated from healthy donors, RA patients, and treated and untreated PsA patients, separated from MLSs. Additionally, we sought to analyze the expression profile of healthy, RA, and PsA-MLSs.
Methods: Synoviocytes were isolated from the knee synovium of healthy donors (h), RA patients, and PsA patients (both treated and untreated with MTX). Cells were selected using immunomagnetic beads with anti-CD14 antibodies. FLSs (CD14-) were cultured in vitro for 24 hours in wild-type (wt) conditions or with the addition of 100 ng/ml LPS and 20 ng/ml IFNγ or 10 ng/ml IL-4 and IL-13. FLSs and MLSs (CD14+) were lysed with Trizol reagent for RNA real-time PCR analysis, and with NP-40 containing phosphatase and protease inhibitors for western blot analysis.
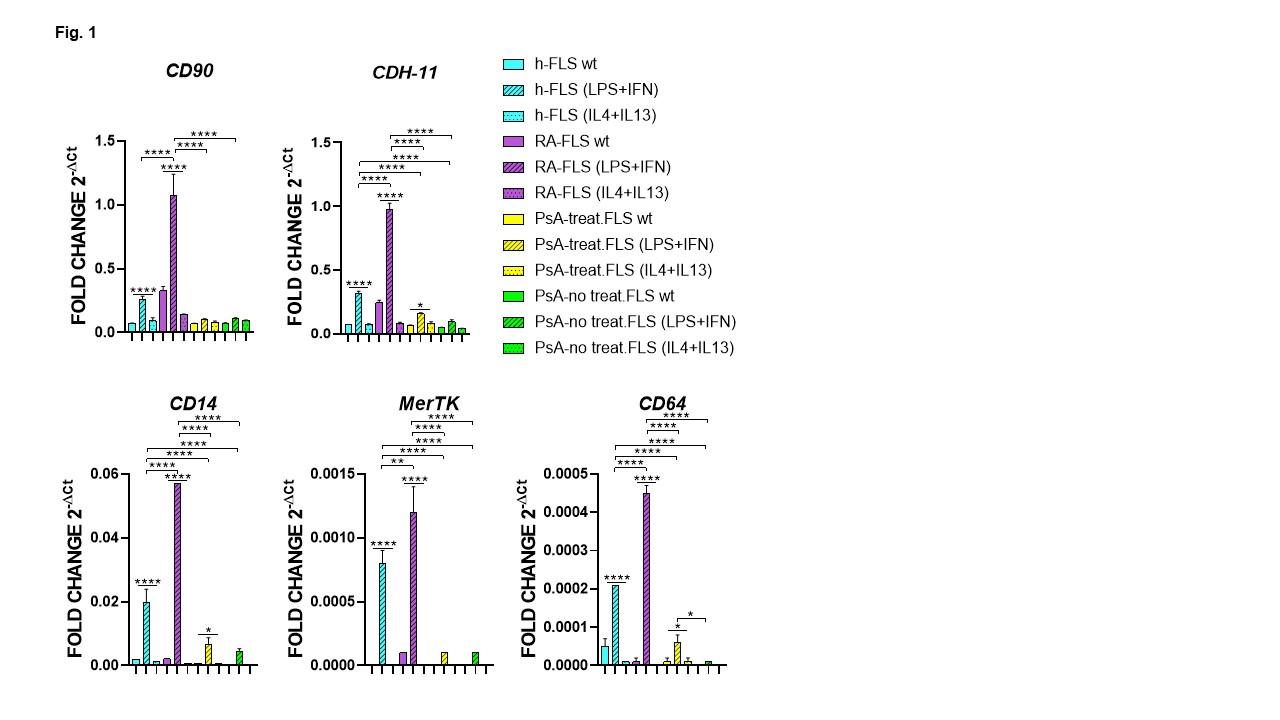
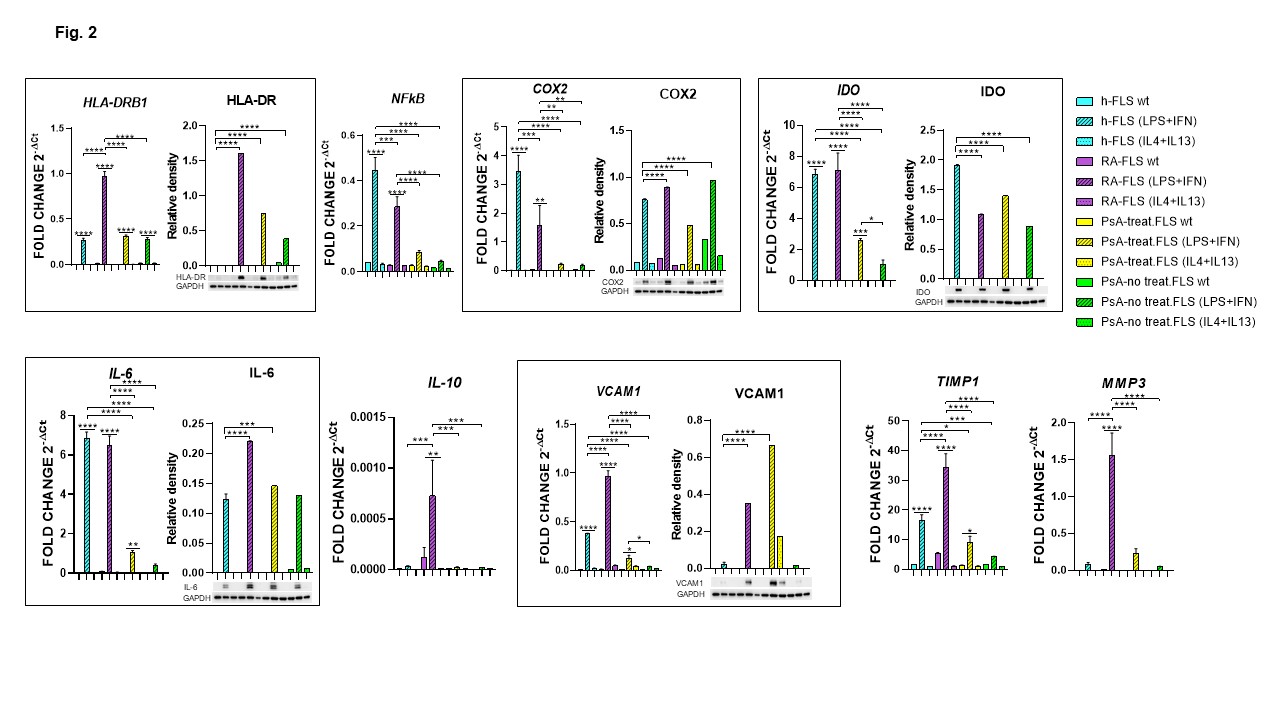
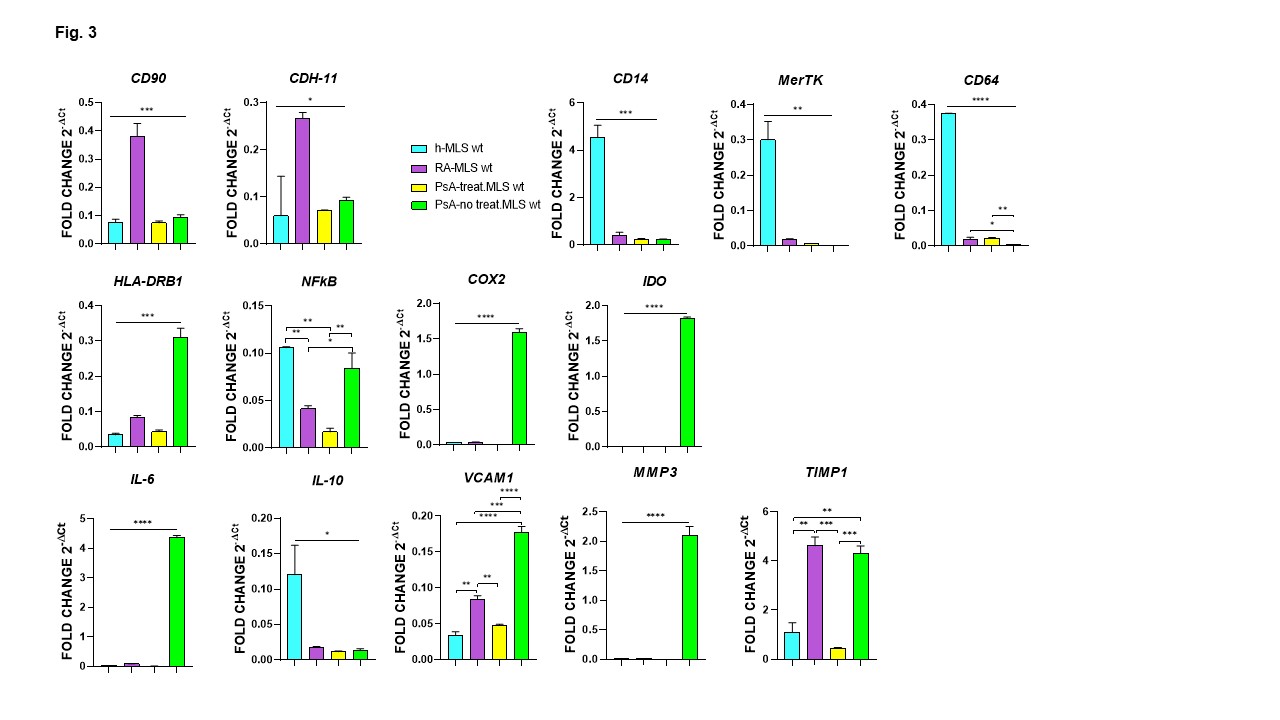
Results: IL-4 and IL-13 treatment did not affect gene and protein expression in healthy, RA, or PsA-FLSs. In contrast, treatment with LPS and IFNγ increased the expression of all analyzed genes in RA patients, almost all genes in healthy subjects except for IL-10 and MMP3, eight out of 14 genes in treated PsA-FLSs, and only the HLA-DRB1 gene in untreated PsA-FLSs (Fig. 1, 2). RA-FLSs showed significantly higher expression of CD90, CDH-11, CD14, MerTK, CD64, HLA-DRB1, IL-10, VCAM1, MMP3, and TIMP1 compared to h-FLSs, along with elevated IL-6 and COX2, and reduced IDO protein levels. Compared to h-FLSs, both treated and untreated PsA-FLSs showed reduced expression of all genes except for CD90, HLA-DRB1, IL-10 and MMP3. Treated PsA-FLSs displayed increased expression of HLA-DR, IL-6, and VCAM1, with reduced expression of COX2 and IDO proteins. Untreated PsA-FLSs showed increased protein expression of HLA-DRB1 and COX2, and decreased expression of IDO compared to h-FLSs (Fig. 2). RA-MLSs, compared to h-MLSs, showed increased expression of CD90, CDH-11, VCAM1, and TIMP1 (Fig. 3). RA-, treated PsA-, and untreated PsA-MLSs showed reduced expression of CD14, MerTK, CD64, and IL-10. Treated PsA-MLSs also showed reduced NFkB expression, whereas untreated PsA-MLSs exhibited elevated expression of HLA-DRB1, COX2, IDO, IL-6, VCAM1, MMP3, and TIMP1 (Fig. 3).
Conclusion: The inflammatory environment led to excessive activation of RA-FLSs in a dendritic manner, and RA-MLSs appeared less responsive in controlling inflammation. Untreated PsA-FLSs did not react to the inflammatory stimulus similarly to healthy FLSs, while untreated PsA-MLSs were more prone to a pro-inflammatory status. MTX treatment appears to be effective in reducing inflammation by acting on both FLSs and MLSs in PsA patients.
FLS and MLS markers expression observed in FLSs. Relative mRNA expression of FLS markers (CD90 and CDH_11) and STM markers (CD14, MerTK and CD64) in FLS isolated from healthy subject (h-FLSs), rheumatoid arthritis patients (RA-FLSs), treated psoriatic arthritis patients (PsA treat-FLS) and not treated PsA patients (PsA no treat-FLS). **p<0.01, ****p<0.0001.
Gene and protein expression of immune response-related molecules observed in FLSs. Relative mRNA expression and representative western blot and densitometric analysis of proteins immune-probed. GAPDH levels were used as protein loading control. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001.
FLS (CD90 and CDH_11) and MLS (CD14, MerTK and CD64) markers expression and immune response-related molecules observed in MLSs. Relative mRNA expression observed in MLSs isolated from healthy subject (h-FLSs), rheumatoid arthritis patients (RA-FLSs), treated psoriatic arthritis patients (PsA treat-FLS) and not treated PsA patients (PsA no treat-FLS). *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Maccaferri m, Zambianchi F, Salvarani C, Pignatti E. In Vitro Study of Fibroblast-Like Synoviocytes and Macrophages-Like Synoviocytes Isolated from Rheumatoid Arthritis, Psoriatic Arthritis Patients and Healthy Subjects [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/in-vitro-study-of-fibroblast-like-synoviocytes-and-macrophages-like-synoviocytes-isolated-from-rheumatoid-arthritis-psoriatic-arthritis-patients-and-healthy-subjects/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/in-vitro-study-of-fibroblast-like-synoviocytes-and-macrophages-like-synoviocytes-isolated-from-rheumatoid-arthritis-psoriatic-arthritis-patients-and-healthy-subjects/