Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: We previously reported that a combination of TNF-α and IL-6 induces mouse osteoclast (OC)-like cells and human OCs with bone resorption activity [Arthritis & Rheumatology, 2014, 2021]. Interestingly, the number of OCs induced by TNF-α and IL-6 from peripheral blood mononuclear cells in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients showed a positive correlation with the modified total Sharp score, whereas RANKL-induced OCs did not. In this study, we aimed to: 1) clarify the association between disease activity and TNF-α and IL-6-induced OCs or RANKL-induced OCs in peripheral blood monocytes (PBMs) from RA patients; 2) evaluate the effects of the JAK inhibitor (JAKi) filgotinib (FIL) on the differentiation of these OCs; 3) identify TNF-α and IL-6-induced OCs, characterized as TRAP+ MMP-3+ RANK– OCs, and RANKL-induced OCs, characterized as TRAP+ MMP-3– RANK+ OCs, in the joint bone tissue.
Methods: PBMs from 13 RA patients were stimulated with TNF-α and IL-6 or RANKL. The number of tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase (TRAP)-positive multinucleated cells was quantified as osteoclasts. Disease activity and serological inflammatory markers were also assessed. We analyzed the number of OCs induced by either TNF-α and IL-6 or RANKL in RA PBMs both before and 24 weeks after treatment with FIL. Decalcified tibial bones from five RA patients and four osteoarthritis (OA) patients undergoing joint surgery were stained with TRAP and immunohistochemically with anti-MMP-3 or anti-RANK antibodies to analyze marker expressions.
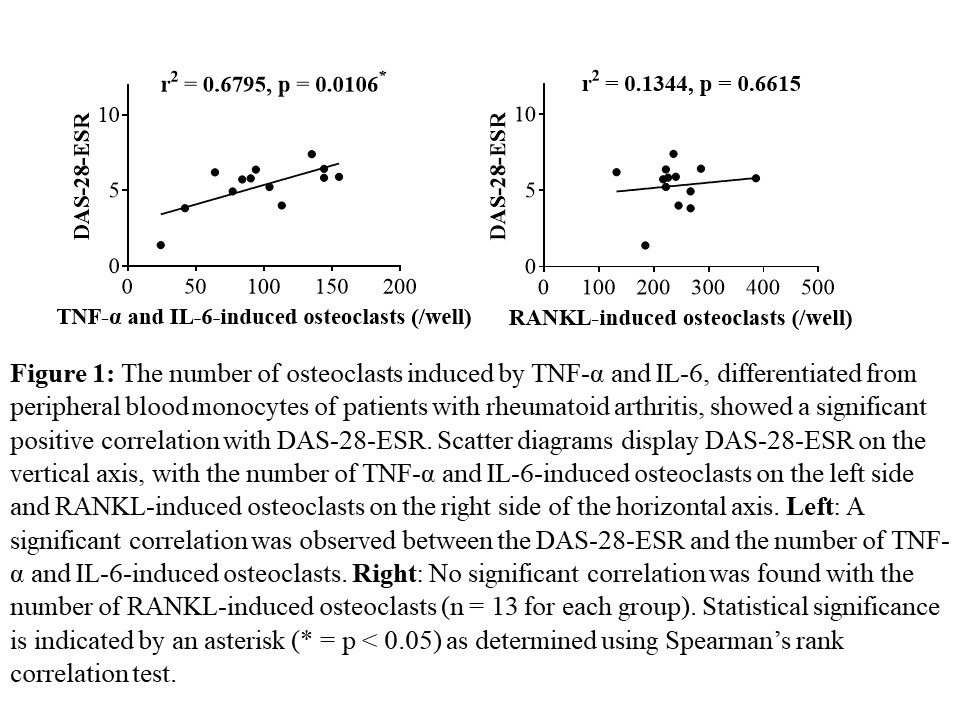
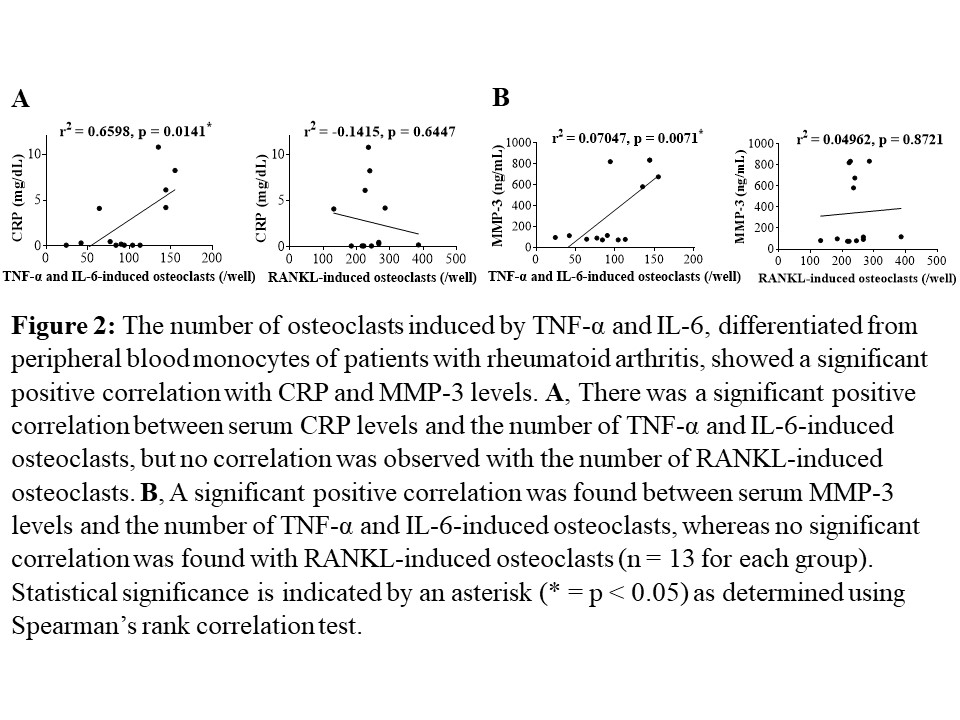
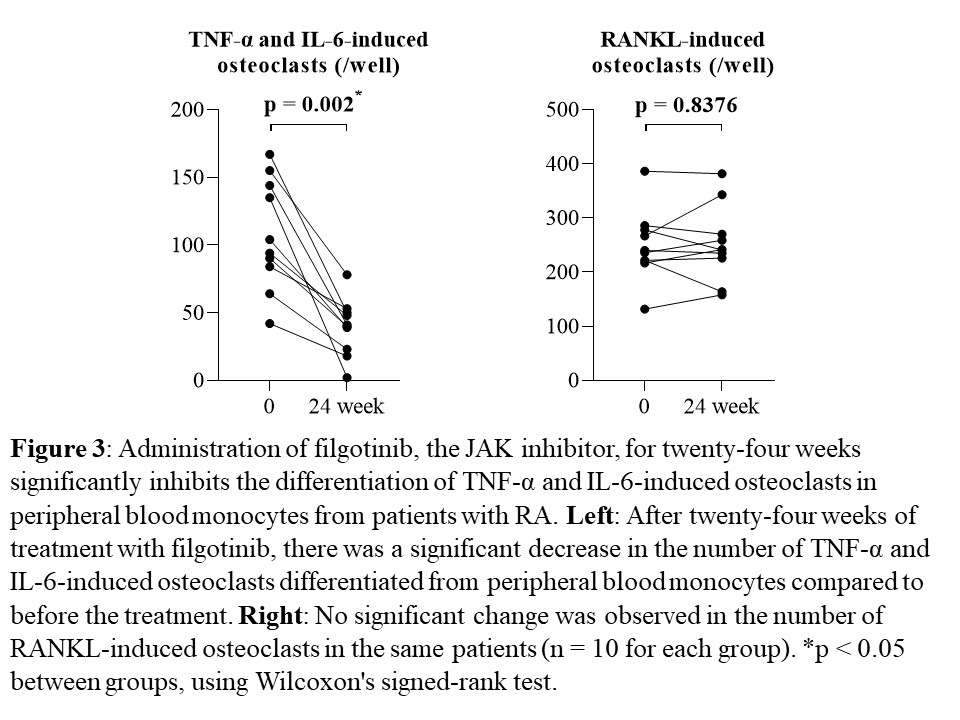
Results: The number of OCs induced by TNF-α and IL-6 from PBMs showed significant positive correlations with DAS-28-ESR, SDAI, and CDAI, as well as with serum levels of CRP, ESR, and MMP-3 in the same patients (each n = 13, p < 0.05, Fig. 1, 2). No such correlations were observed for RANKL-induced OCs. After twenty-four weeks of treatment with FIL, the number of TNF-α and IL-6-induced OCs differentiated from PBMs significantly decreased compared to that before the treatment (n = 10, p = 0.002). No significant changes were observed in the number of RANKL-induced OCs during a 24-week administration of FIL in the same patients (n = 10, p = 0.8376, Fig. 3). On the bone surface, the number of TRAP+ MMP-3+ RANK– OCs, the expression pattern of which was the same as that shown in TNF-α and IL-6-induced OCs in vitro, was significantly higher in patients with RA than in OA patients. Notably, in the bone erosion regions of RA patients, there were considerably more TRAP+ MMP-3+ RANK– OCs compared to TRAP+ MMP-3– RANK+ OCs.
Conclusion: Our results demonstrated that TNF-α and IL-6-induced OCs may contribute to the pathological and inflammatory bone destruction in patients with RA. In particular, targeting TNF-α and IL-6-induced OCs is anticipated to create new therapeutic strategies such as JAKi.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kazuhiro Y, Aizaki Y, Sekikawa M, Kajiyama H, Araki Y, Kadono Y, Akiyama Y, Mimura T. Disease Activity and Serological Inflammatory Markers Are Associated with TNF-a and IL-6-Induced Osteoclasts, but Not with RANKL-Induced Osteoclasts in Peripheral Blood Monocytes from Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/disease-activity-and-serological-inflammatory-markers-are-associated-with-tnf-a-and-il-6-induced-osteoclasts-but-not-with-rankl-induced-osteoclasts-in-peripheral-blood-monocytes-from-patients-with-rh/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/disease-activity-and-serological-inflammatory-markers-are-associated-with-tnf-a-and-il-6-induced-osteoclasts-but-not-with-rankl-induced-osteoclasts-in-peripheral-blood-monocytes-from-patients-with-rh/