Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 14, 2023
Title: (2352–2369) Systemic Sclerosis & Related Disorders – Clinical Poster III: Translational Science
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Systemic sclerosis (SSc, scleroderma) is an autoimmune connective tissue disease that causes autoimmunity, vascular dysfunction, and fibrosis of the skin, lungs, and other organs. Pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) is a severe complication of SSc which can cause right heart failure and is associated with a high rate of morbidity and mortality. Insulin-like growth factor binding protein 7 (IGFBP7) has been shown to be a biomarker for heart failure, and to be elevated in SSc skin. This study assessed IGFBP7 in pulmonary arteries from mice with pulmonary hypertension, and then looked at the potential role of IGFBP7 as a serum biomarker in both mice and patients with SSc-PAH.
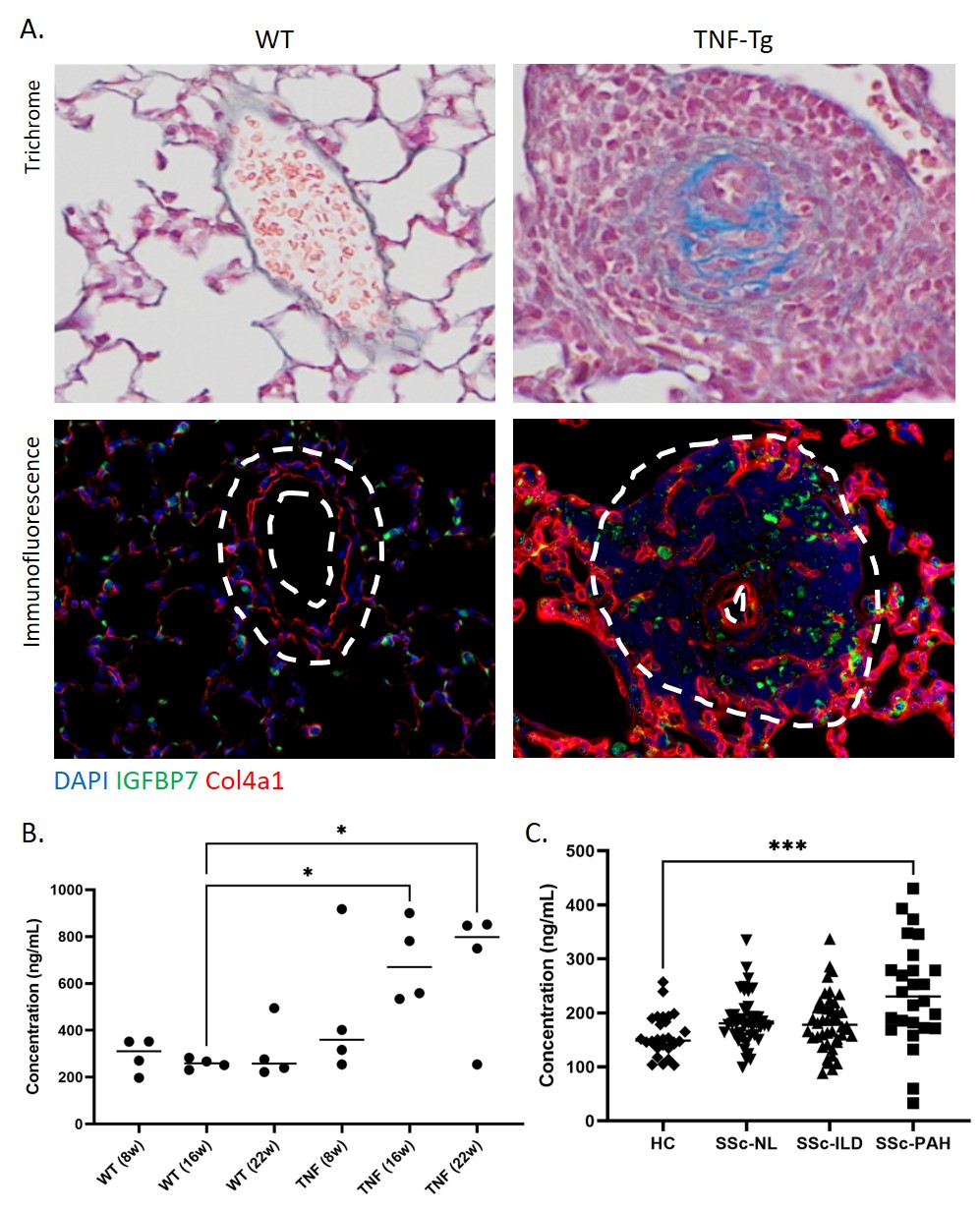
Methods: Single cell RNA sequencing was performed on wild-type (WT) and TNF transgenic (TNF-Tg) mice with pulmonary hypertension. After identification of cell types with Seurat, differential gene expression analysis was performed and volcano plots were generated to identify the most differentially regulated genes in each cell type. Trajectory analysis was performed with Monocle, and pseudotime was assessed with Tradeseq. Lungs from WT and TNF-Tg mice were subsequently stained for IGFBP7 (n=6 per genotype) and its binding partner collagen 4a1. Serum from WT and TNF-Tg mice was collected over a time-series (n=4 per condition) and ELISA was performed to determine serum IGFBP7 levels. Blood from SSc patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension (SSc-PAH, n = 26), interstitial lung disease (SSc-ILD, n = 44), no lung disease (SSc-NL, n=44), or healthy control (HC, n =28) were collected and ELISA was performed to determine serum IGFBP7 levels.
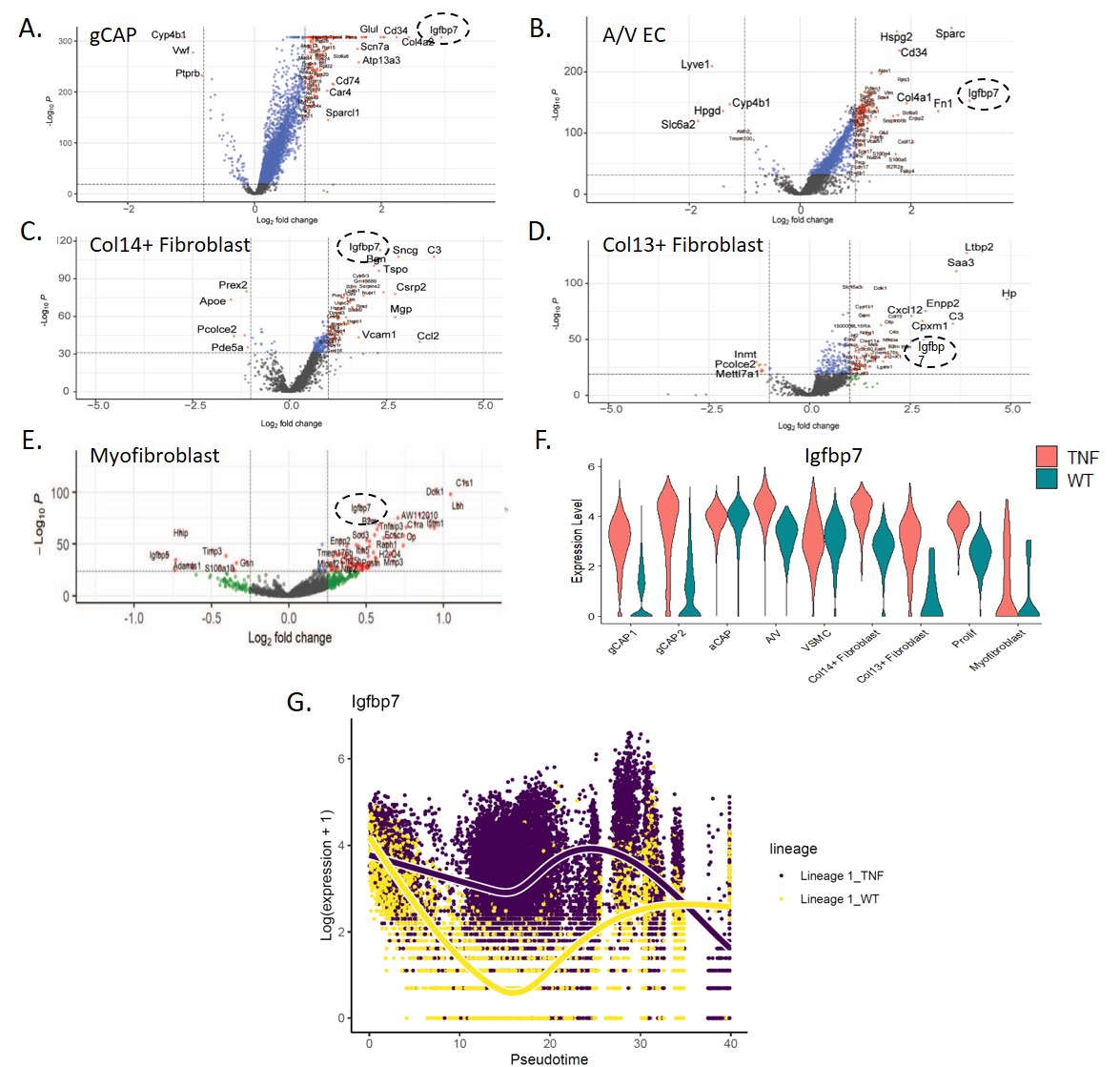
Results: TNF-Tg mice develop progressive pulmonary hypertension as they age, making the model suitable for identification of potential disease severity biomarkers. Volcano plots from single cell RNA-sequencing demonstrated that IGFBP7 was among the most overexpressed genes in general capillary cells (Fig.1A), arteriovenous endothelial cells (Fig.1B), Col14+ fibroblasts (Fig.1C), Col13+ fibroblasts (Fig.1D), and myofibroblasts (Fig.1E). Gene expression was elevated across multiple cell types and pseudotime analysis showed IGFBP7 was the gene most elevated in TNG-Tg vs WT lungs across all lineages (Fig. 1F-G). Elevation of IGFBP7 was also observed at the protein level with immunofluorescence staining demonstrating an increased number of perivascular IGFBP7+ cells in close proximity to Col4A1+ cells. Serum concentration of IGFBP7 was elevated in the TNF-Tg mice compared to the WT and showed an increase over time (Fig.2B). To confirm the relevance of these findings in human SSc lung disease, ELISA was performed for IGFBP7 and showed that patients with SSc-PAH had significantly higher serum IGFBP7 concentration compared to controls or SSc patients with ILD or without lung disease.
Conclusion: IGFBP7 is significantly upregulated in a TNF-Tg model of pulmonary hypertension across endothelial cells and fibroblasts, and serum levels increase as disease progresses. Patients with SSc-PAH have elevated levels of IGFBP7. Taken together, our data suggest that IGFBP7 is involved in PAH pathogenesis and may serve as a putative biomarker for SSc-PAH.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Jeong Y, Bhattacharya S, Garcia-Hernandez M, Rangel-Moreno J, Xu Q, Korman B. Role of Insulin-like Growth Factor Binding Protein-7 (IGFBP7) in Pulmonary Hypertension Pathogenesis and as a Biomarker Systemic Sclerosis-Associated Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (SSc-PAH) [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/role-of-insulin-like-growth-factor-binding-protein-7-igfbp7-in-pulmonary-hypertension-pathogenesis-and-as-a-biomarker-systemic-sclerosis-associated-pulmonary-arterial-hypertension-ssc-pah/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/role-of-insulin-like-growth-factor-binding-protein-7-igfbp7-in-pulmonary-hypertension-pathogenesis-and-as-a-biomarker-systemic-sclerosis-associated-pulmonary-arterial-hypertension-ssc-pah/