Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 4:00PM-5:30PM
Background/Purpose: The COVID-19 pandemic prompted a rapid transition to increased telehealth utilization, with many rheumatology providers replacing in-person clinical visits with telehealth visits or expanding their telehealth offerings. Understanding trends in telehealth utilization and satisfaction among people with rheumatic diseases (RDs) is crucial as telehealth options continue to be offered and used even as COVID-19 safety measures are scaled down. We investigated trends in telehealth utilization and satisfaction among individuals with RDs from the onset of the pandemic to the present.
Methods: The study population included participants in the FORWARD Databank who completed semiannual questionnaires from June 2020 to April 2023 with items related to their telehealth utilization in 6-month time periods from January 2020 through December 2022. In each of the questionnaires offered, participants were asked if they had any telehealth appointments and if so, they were asked to rate their satisfaction on a Likert scale. Descriptive statistics were calculated for participant characteristics, and comparisons were made by telehealth vs no telehealth and by satisfied vs not satisfied with telehealth. Multivariable logistic regression models (adjusted for age, sex, race, education, rural/urban residence, smoking history, BMI, autoimmune diagnosis, Rheumatic Disease Comorbidity Index, glucocorticoid use, opioid use, and Patient Activity Scale-II) were used to identify factors associated with telehealth utilization and satisfaction over time.
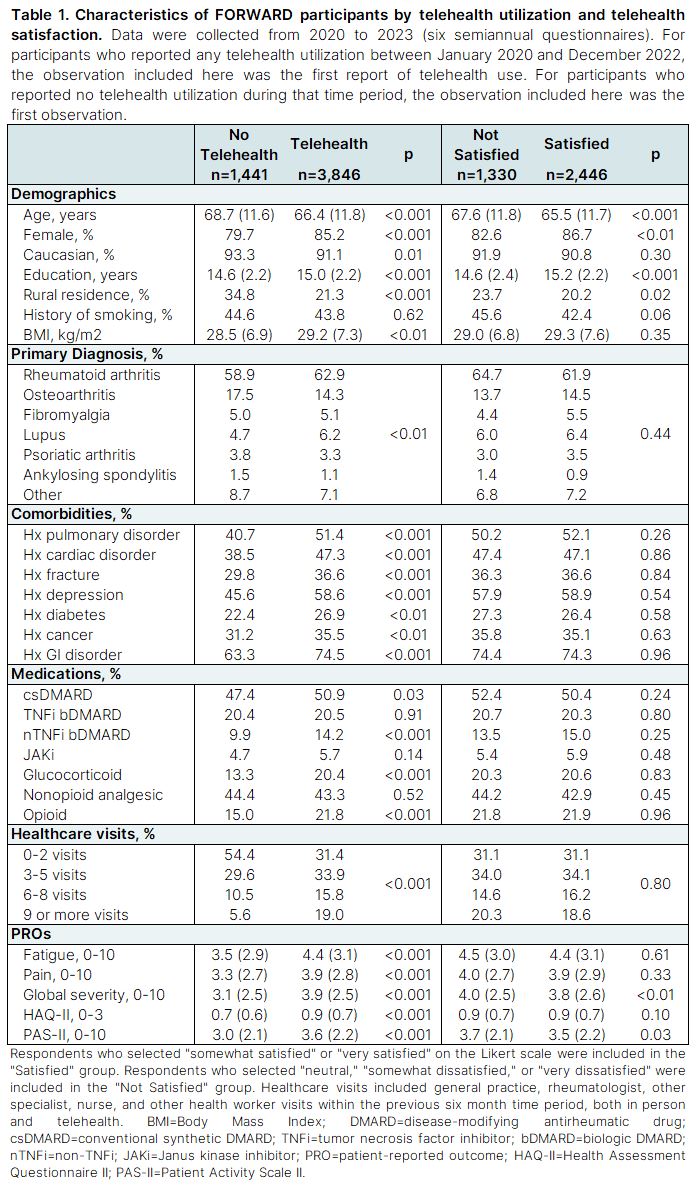
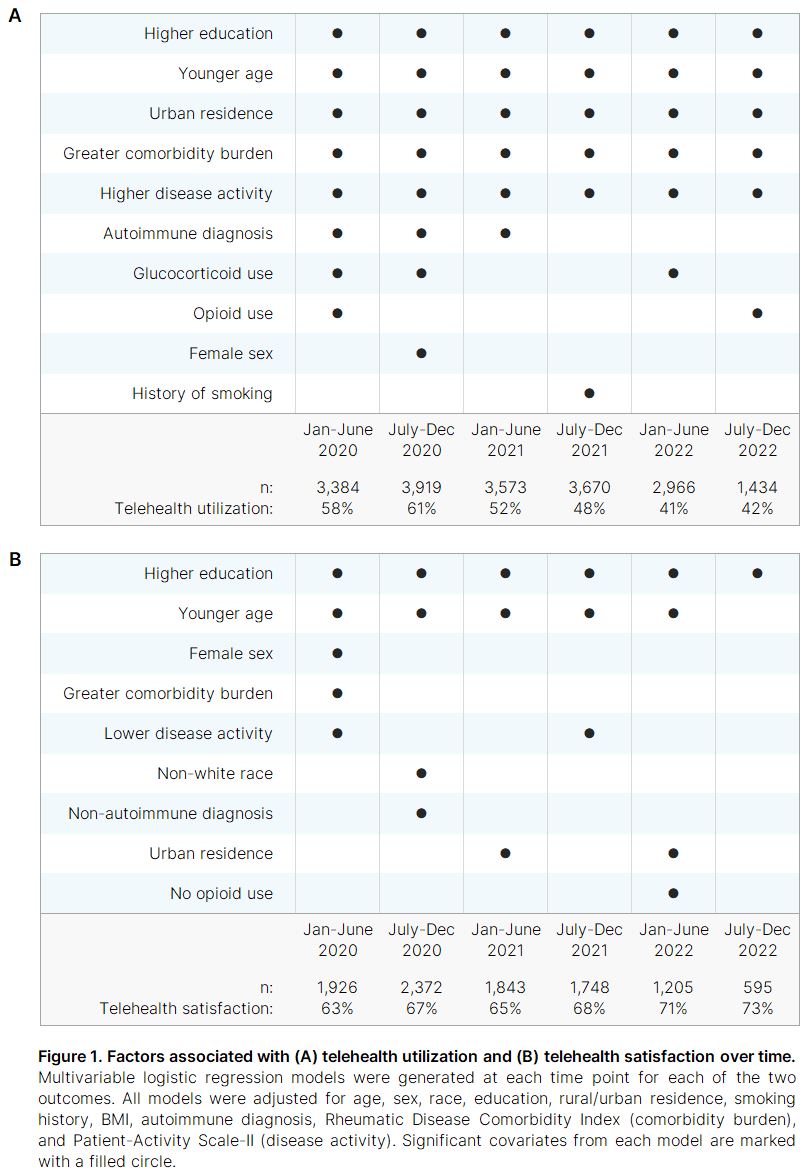
Results: Of 5,287 unique respondents, 3,846 (73%) reported telehealth utilization between January 2020 and December 2022. Respondent characteristics are presented in Table 1, and temporal trends are presented in Figure 1. Telehealth utilization peaked at 61% in the second half of 2020 and stabilized at approximately 40% throughout 2022. Higher education, younger age, urban residence, greater comorbidity burden, and worse disease activity were consistently associated with telehealth use throughout the pandemic thus far. Telehealth users earlier in the pandemic had significantly higher odds of having an autoimmune diagnosis, but since July 2021 this was not statistically significant. Telehealth satisfaction demonstrated a steady increase over time, rising from 63% to 73%. Higher education and younger age were consistently associated with greater telehealth satisfaction.
Conclusion: Rates of telehealth utilization among individuals with RDs has remained substantial throughout the COVID-19 pandemic, although rates have decreased since 2020. Improved telehealth infrastructure and growing familiarity with the technology may have contributed to increased satisfaction over time, but individuals who are younger and more highly educated continue to have higher odds of telehealth satisfaction. Those with greater comorbidity burdens and higher disease activity have very consistently been the most likely to utilize telehealth services. Ensuring quality of care for these higher risk populations remains essential as telehealth continues to become a more integral part of rheumatology practice.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Wipfler K, Michaud K. Telehealth Utilization and Satisfaction Among Patients with Rheumatic Diseases: Trends Since the Onset of the COVID-19 Pandemic [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/telehealth-utilization-and-satisfaction-among-patients-with-rheumatic-diseases-trends-since-the-onset-of-the-covid-19-pandemic/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/telehealth-utilization-and-satisfaction-among-patients-with-rheumatic-diseases-trends-since-the-onset-of-the-covid-19-pandemic/