Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 7, 2021
Title: Patient Outcomes, Preferences, & Attitudes Poster II: Measurements (0739–0763)
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: The patient global assessment (PGA), typically assessed as ‘Considering all of the ways your arthritis has affected you, how do you feel your arthritis is today?‘ should reflect the patient’s perception of disease activity. It is incorporated as core set measure of disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) but has been criticized to not adequately fulfill its construct validity.
We explore different versions of the PGA and assess agreement, factors of variance, change over time and effect on disease activity classification.
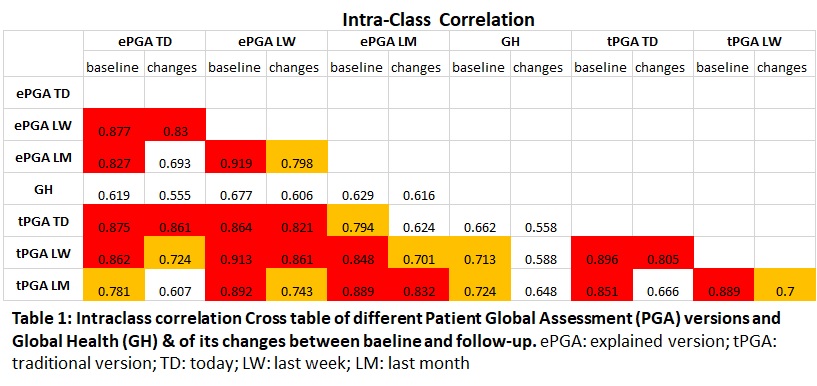
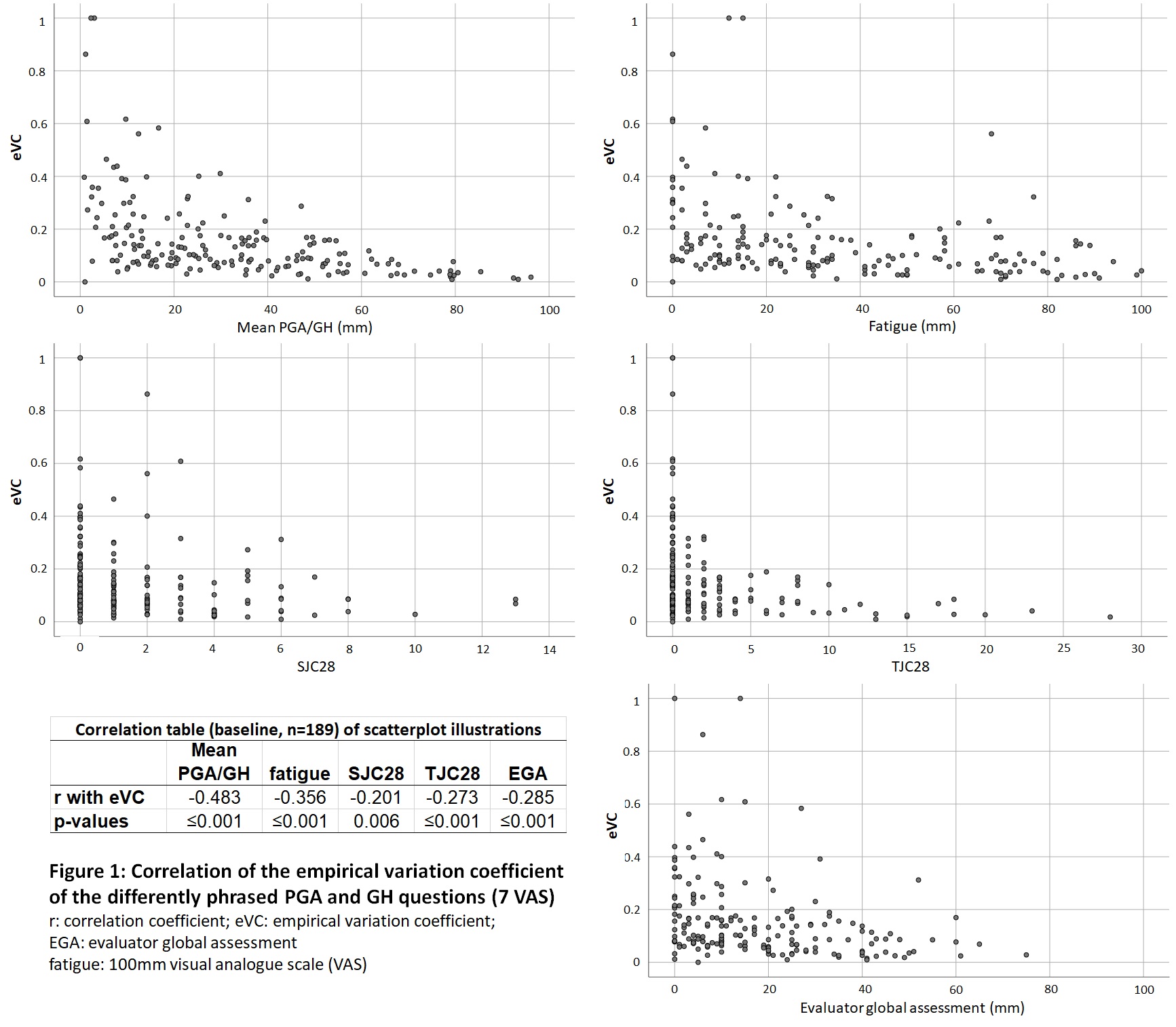
Methods: In a multicenter study (4 centers in US & Europe), RA patients were asked to score on global health (GH) and 6 differently phrased PGA questions using visual analogue scale covering 2 aspects: (1) providing more detailed explanation on disease activity (“Active arthritis can cause joint swelling OR stiffness, pain OR discomfort in your joints. WITH ACTIVE ARTHRITIS, You CAN BE tired during the day, even when you’ve slept well“ (ePGA) compared to traditional phrasing (tPGA); and (2) reference to 3 time periods: today (TD), last week (LW) or last month (LM). This generated 3 tPGA versions (TD/LW/LM) and 3 ePGA versions (TD/LW/LM). Agreement was calculated with intra-class correlation (ICC) and comparisons between PGA were done with paired-analyses. The empirical variation coefficient (eVC: (SD/mean)/SQRT(n)) was calculated per patient. The influence of disease duration, HAQ >0.5 or ≤0.5, SJC28, TJC28, fatigue and evaluator global assessment (EGA) on scoring of PGA versions were assessed and the resulting variations in disease activity classification.
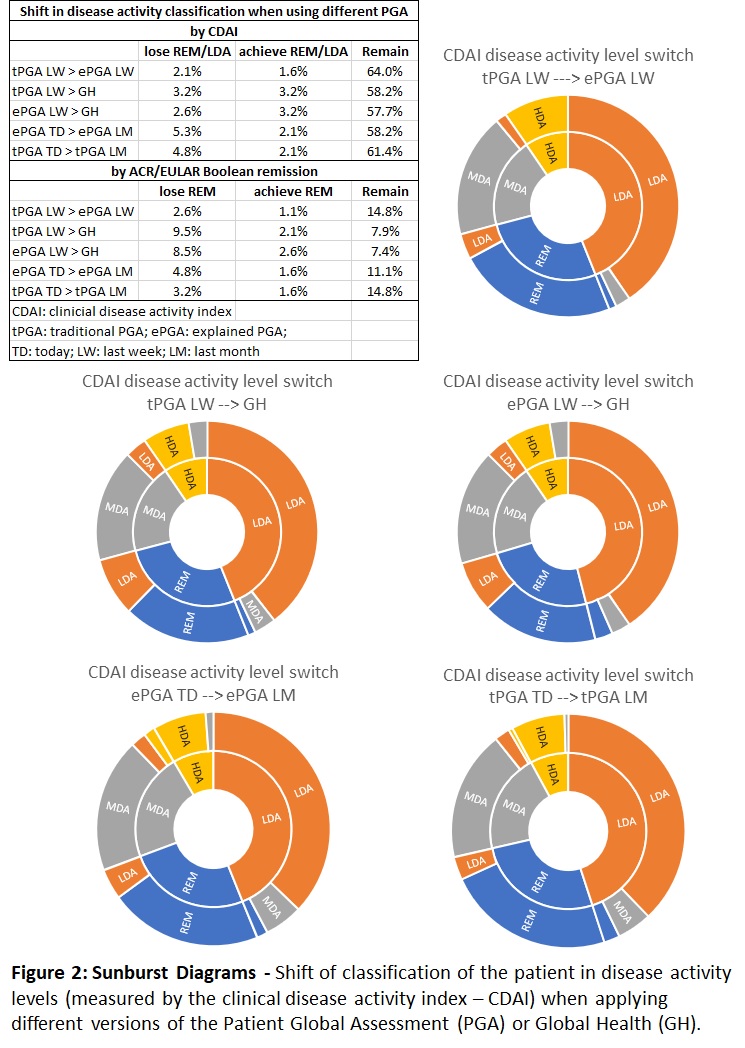
Results: At baseline (BL) 189 patients (82% female, 45%≥1 comorbidity, mean disease duration ±SD: 16.6±10.8, mean PGA: 31.8±22.7, mean eVC 0.15±0.15, mean SJC28: 1.6±2.3) and 138 with follow-up (FU) were subjected to analyses. In paired analyses ePGA were scored higher than tPGA (p≤0.001) and in both, scores were higher in longer reference periods. When comparing in between reference periods (Table 1), ICCs were all ranging >0.8. Changes in PGA between BL and FU reached high agreement, except for TD versus LM. Poor to moderate agreement both for BL, as well as change scores, were found between versions of PGA and GH (Table 1). BL to FU PGA changes correlated highly with changes in pain and moderately with changes in EGA. The difference between PGA and GH (LW, LM versions) increases with more swollen joints. Differences between phrasings were less pronounced in patients with HAQ >0.5 or with comorbidities. The variance in scores between questions was lower in people with higher disease activity. Higher mean PGA, fatigue, TJC, SJC and EGA correlated moderately with smaller eVC (Figure 1). The rate of patients switching CDAI disease activity level is around 8% when comparing tPGA with ePGA, but between 15% to 20% in PGA/GH and around 14% in TD/LM (Figure 2). Only up to 3% less achieve REM/LDA CDAI when switching to ePGA, however GH use instead of PGA coincides with 5 to 7% of patients less in Boolean remission.
Conclusion: Different versions of the PGA show high correlation, implicating that a more detailed phrasing would not increase construct validity. GH performs differently than PGA and may not be used interchangeably.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Studenic P, Baranskaya A, Cohen S, Shadick N, Iannaccone C, Mjaavatten M, Lie E, Kvien T, Smolen J, Aletaha D, Radner H. Different Versions of the Patient Global Question in Rheumatoid Arthritis – Does It Really Matter? – Results of a Multi-center Observational Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/different-versions-of-the-patient-global-question-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-does-it-really-matter-results-of-a-multi-center-observational-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/different-versions-of-the-patient-global-question-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-does-it-really-matter-results-of-a-multi-center-observational-study/