Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 7, 2021
Title: Patient Outcomes, Preferences, & Attitudes Poster II: Measurements (0739–0763)
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Changing landscape of patient care from in-person to virtual telemedicine-based consultation in times of a global pandemic has necessitated a wider use of patient-centered outcomes measures (PCOMs) and device-based measures for objective disease assessment. We prospectively validated 2 novel task based PCOMs for physical function, namely Arm Lift test (AL) & Two-Minute Walk Distance (2MWD) in idiopathic myositis (IIM) patients.
Methods: This was a prospective observational study with enrolment of adult patients with IIM in the MyoCite cohort (2017 ACR/EULAR criteria). Both active and inactive disease patients were enrolled. Active disease was defined as escalation of immunosuppression within 3 months, elevated muscle enzymes, physician VAS >2, skin disease worsening or fall in MMT8< 76 (any 2).
Two novel tests were performed at baseline; AL: Time taken for arm abduction ten times & 2MWD: distance walked in 2 minutes. We also evaluated all myositis core set measures [MMT 8, patient and physician global disease activity (PtGA and PhGA), HAQ-DI, extra-muscular disease activity as well as MDAAT & MDI]. Test-discriminant validity was tested between active and inactive myositis.
The results were validated in a larger Teleconsultation-based cohort to differentiate active vs. inactive disease. All values are in median(IQR).
Results: Observation cohort
22 adult IIM patients (68% female) of age 30.5 (19-62) years were enrolled. Median AL time, 2MWD and MMT-8 were 11.9 (10.5-14) seconds, 198 (167-225) metres and 79 (74-80) respectively.
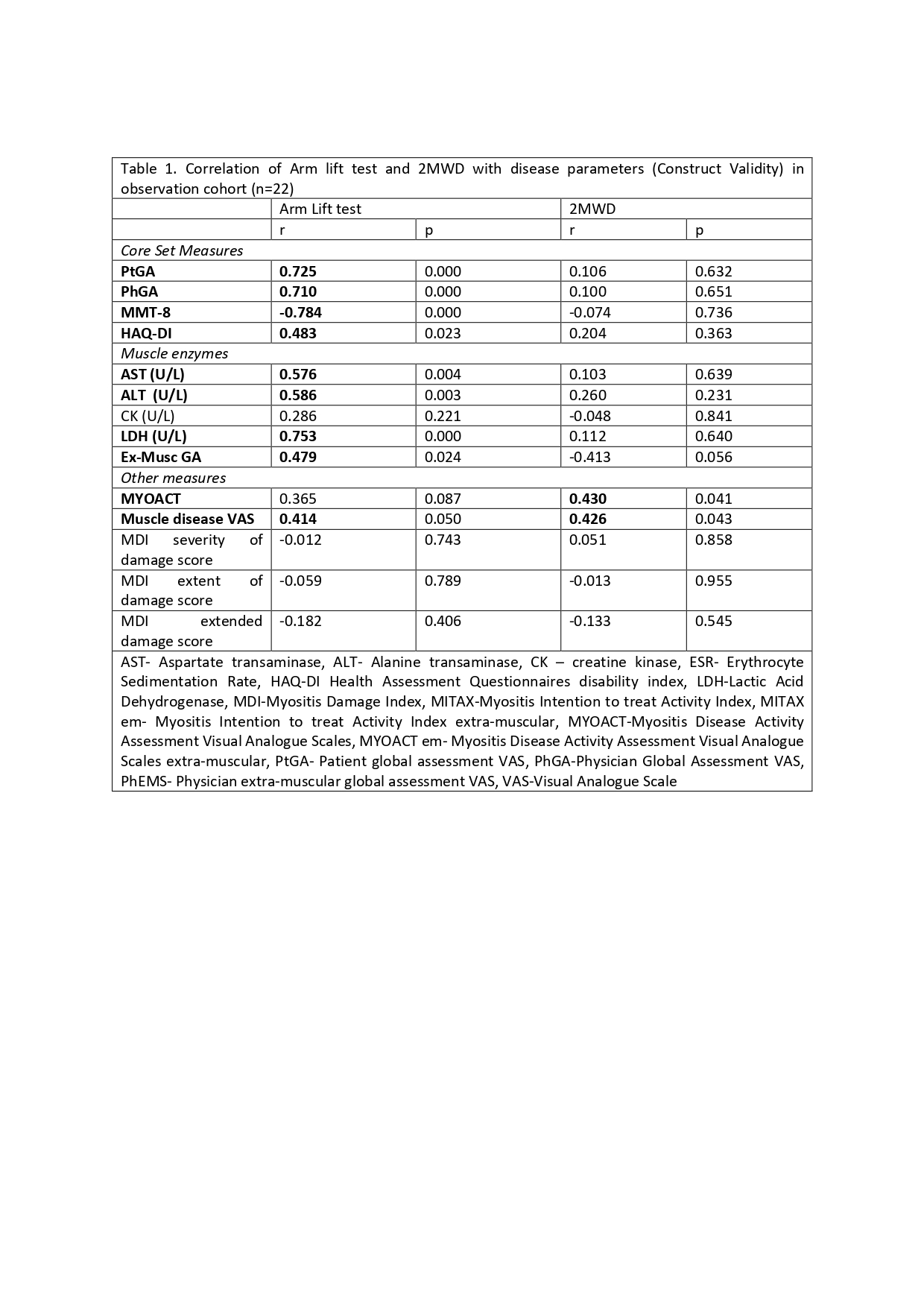
AL and 2MWD showed excellent test-retest reliability (Cronbach’s alpha 0.987 & 0.99 respectively, n=12). AL test had moderate to strong correlation all myositis core set measures including MMT8, PtGA, PhGA, HAQ-DI, Extra-muscular global (Ex-MuscGA), muscle enzyme (LDH, AST, ALT) and MYOACT (trend), but not with CK levels and MDI (table 1). In addition it showed moderately strong association with muscle disease VAS and muscle disease remission. In contrast, 2MWD had huge variability and no significant association with any of the core set or other measures except a moderate correlation with muscle VAS.
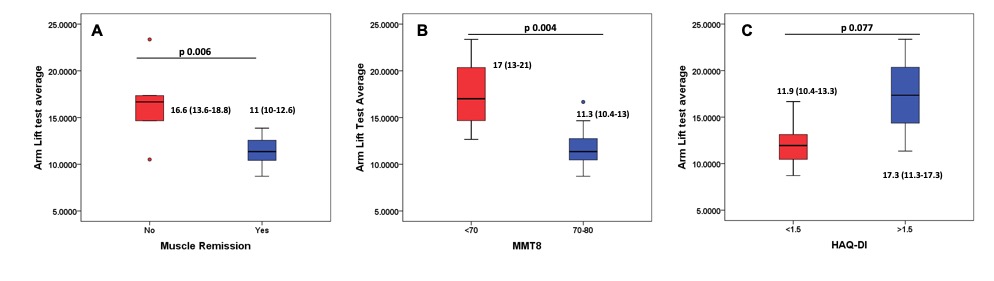
A higher AL time discriminated active and inactive myositis (16.6 vs 11 seconds, p=0.006) and discriminated between patients with and without muscle weakness (significant) and HAQ (non-significant trend) (Figure 1 A-C). However, 2MWD didn’t discriminate based on muscle disease activity or other measures.
AUC for active versus inactive disease was 0.882 (p 0.006) with AL test. A cut-off of 12.8 seconds had 94% negative predictive values for active muscle disease (83% sensitivity, 83% specificity).
Validation cohort
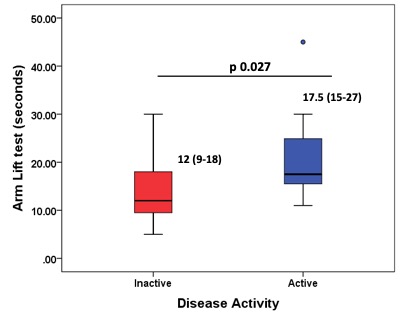
In 47 patient visits among 26 patients (81% female, 33 years median age), AL significantly differentiated between active vs. inactive patients (Figure 2).
Conclusion: AL correlated well with myositis disease activity measures including muscle weakness providing preliminary evidence for its role as PCOM in IIM especially in clinical trials and telemedicine consultation. 2MWD was not a good test for outcome evaluation of IIM patients. Larger longitudinal studies are needed to further validate these findings.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Naveen R, R Thakare D, Agarwal V, Aggarwal R, Gupta L. Validation of Two Simple Patient-centered Outcome Measures for Virtual Monitoring of Patients with Idiopathic Inflammatory Myositis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/validation-of-two-simple-patient-centered-outcome-measures-for-virtual-monitoring-of-patients-with-idiopathic-inflammatory-myositis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/validation-of-two-simple-patient-centered-outcome-measures-for-virtual-monitoring-of-patients-with-idiopathic-inflammatory-myositis/