Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: To analyze for differences in quadriceps maximal isometric voluntary contraction (MVIC), muscle endurance (ME), muscle mass and fat mass (m. vastus lateralis, mid-thigh) in patients with recent onset PM/DM and established PM/DM.
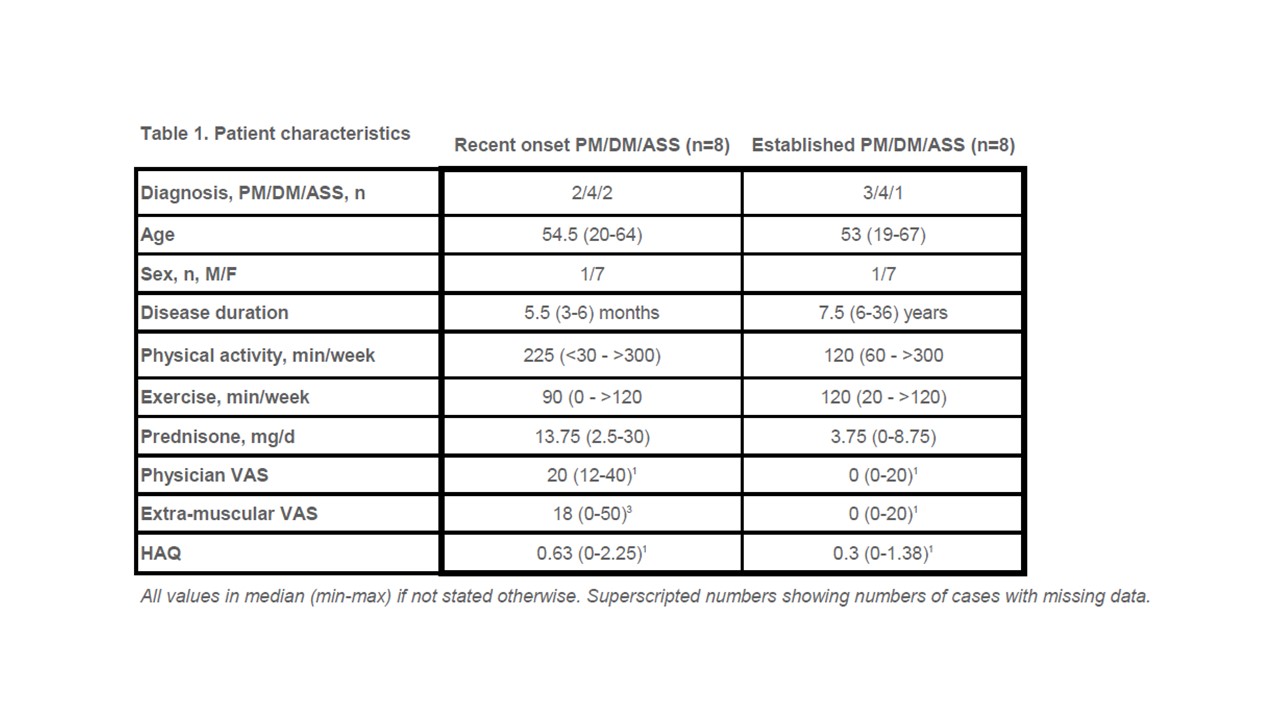
Methods: All patients diagnosed with PM, DM or ASS during September 2017 to January 2020 at Karolinska University Hospital or Akademiska Hospital who met the inclusion criteria were asked to participate (n=16). So far 8 patients with established PM/DM/ASS have been identified to match 8 of the patients with recent onset disease, by age and gender. A dynamometer from Biodex was used to assess MVIC and ME starting with three warm-up 4-sec. contractions followed by three maximal contractions, all with a 3-minute rest in-between. Thereafter six sets of twelve submaximal contractions, starting on 20 % of MVIC and increasing by 10 % for each set, finishing on 70 % of MVIC. Each set ended with a new maximal contraction registered as percentage of initial MVIC. Muscle and fat mass was assessed by MRI. A blinded, experienced radiologist analyzed the muscle mass in m. vastus medialis and lateralis (distance femur – outer edge of the muscle) and fat mass (outer edge of muscle – inner edge of skin) in millimeters (mm). Examinations of muscle function and MRI were conducted at most two weeks apart.
Results: Patients with recent onset PM/DM had a median MVIC of 73 (53-93) Nm and established PM/DM had 75 (41-118) Nm (p=0.65). Median ME was 85 (63-89) % and 90.5 (83-98) % for the 8 patients with recent onset disease and established disease, respectively (p=0.007). Median muscle mass for patients with recent onset PM/DM was 38.5 (26-47) mm and 33 (20-55) mm for patients with established disease (p=0.41). Patients with recent onset disease had a median fat mass of 13 (7-21) mm and patients with established PM/DM had 10 (7-23) mm (p=0.49).
Conclusion: Patients with recent onset, active PM/DM/ASS had a significantly reduced muscle endurance (ME) compared to matched patients with established disease. No significant differences were found between the groups regarding maximal voluntary isometric contraction (MVIC), muscle mass or fat mass. Further data collection is needed to reach statistical power.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Andreasson K, Alexanderson H. Patients with Recent Onset, Active Polymyositis (PM), Dermatomyositis (DM) and Antisynthetase Syndrome (ASS) Have Reduced Muscle Endurance but Not Reduced Muscle Strength Compared to Patients with Established, Low-active Disease [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/patients-with-recent-onset-active-polymyositis-pm-dermatomyositis-dm-and-antisynthetase-syndrome-ass-have-reduced-muscle-endurance-but-not-reduced-muscle-strength-compared-to-patients-with-est/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/patients-with-recent-onset-active-polymyositis-pm-dermatomyositis-dm-and-antisynthetase-syndrome-ass-have-reduced-muscle-endurance-but-not-reduced-muscle-strength-compared-to-patients-with-est/