Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 6, 2021
Title: RA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes Poster I: Cardiovascular Pulmonary Disease (0268–0295)
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Autoantibodies are hypothesized as one of the RA specific factors contributing to a heightened risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD) in this population. However, prior epidemiologic studies of RF and ACPAs with CVD risk in RA are conflicting, and the role of antibodies to other post-translationally modified peptides/proteins including malondialdehyde acetaldehyde (anti-MAA) are not well understood. We evaluated the associations of RF, ACPAs, and anti-MAA antibodies with major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) in RA.
Methods: We studied patients in a multicenter prospective cohort of U.S. veterans with RA. We measured RF by nephelometry, anti-CCP antibody by 2nd generation ELISA, and anti-MAA antibody (IgG, IgM, and IgA) by ELISA on banked serum from enrollment. In a subset of patients (n=1,422), 19 ACPA subspecificities were measured with a multiplex bead-based assay. Autoantibody concentrations were log-transformed and standardized (per 1 SD). RF and anti-CCP positivity were defined per assay cut-offs while anti-MAA was considered positive if in the upper two tertiles, yielding a similar frequency of positivity. MACE was defined as a composite of myocardial infarction, coronary revascularization, stroke, or CVD-related death identified from VA databases and the National Death Index using a previously validated administrative algorithm. Baseline covariates were obtained from registry and administrative data and included demographics, smoking status, BMI, LDL cholesterol, comorbidities (hypertension, diabetes, lung disease, prior MACE), medications (MTX, TNFi biologics, prednisone), and DAS28. We used multivariable Cox regression to examine the associations of autoantibodies with incident MACE and CVD death.
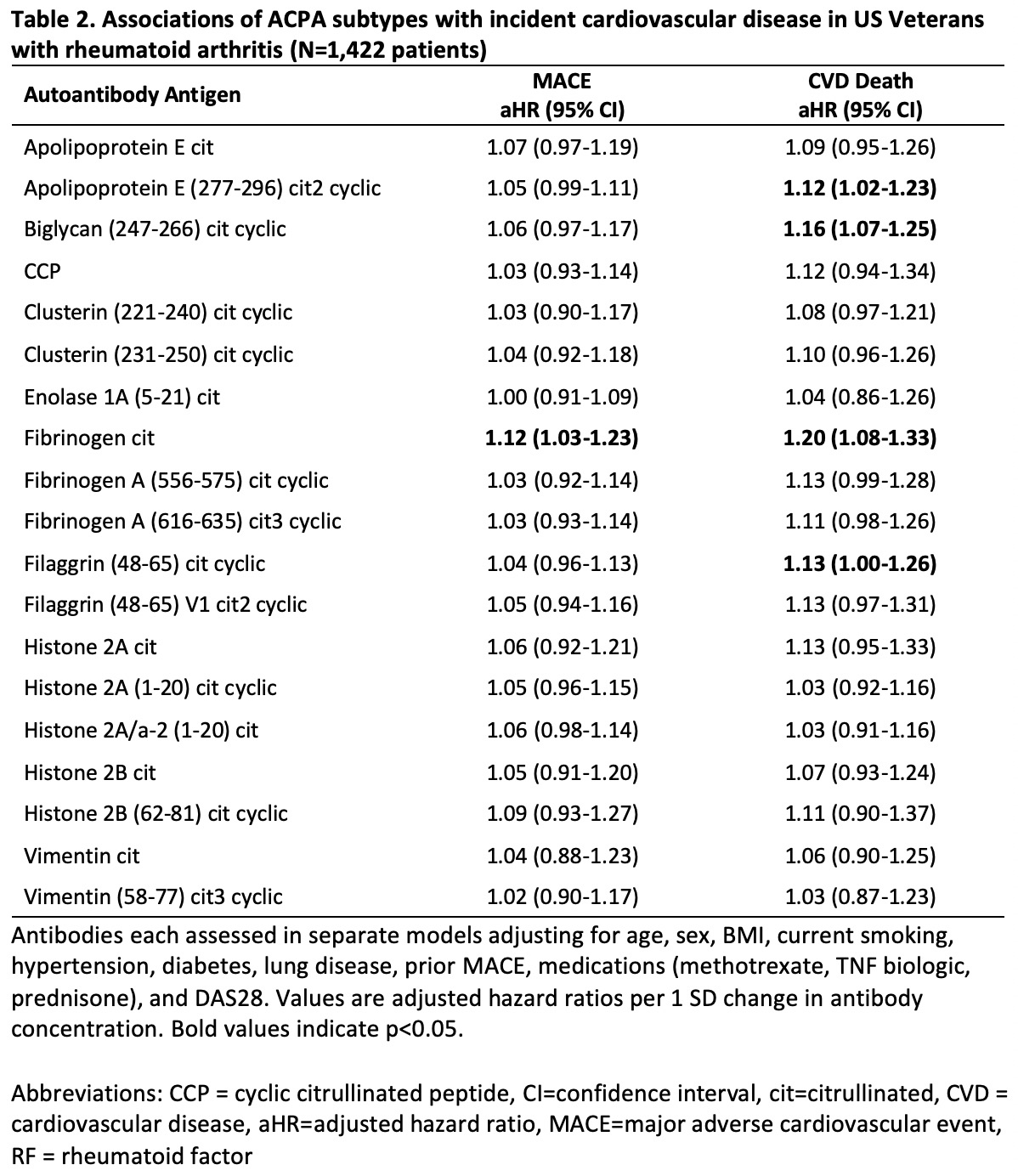
Results: Among 2,362 RA patients (90% male, mean age 72 years), there were 388 MACE outcomes over 19,868 person-years (PY) of follow-up and 220 CVD deaths. Higher concentrations of RF (aHR per 1 SD 1.15 [1.04-1.27]) and IgM anti-MAA (aHR 1.20 [1.03-1.39]) were associated with risk of MACE (Table 1). Effect sizes were similar for other autoantibodies, though not statistically significant. Similarly, higher concentrations of anti-CCP (aHR 1.27 [1.11-1.45]) and IgG (aHR 1.24 [1.06-1.43]) and IgM (aHR 1.22 [1.05-1.42]) anti-MAA were significantly associated with CVD-death, and non-significant associations were observed for other autoantibodies. When evaluated as seropositivity, estimates were less precise with only RF significantly associated with CVD-death (aHR 1.72 [95% CI 1.04-2.86]). Analyses of ACPA subtypes revealed associations between higher concentrations of anti-cit fibrinogen with MACE (aHR 1.12 [1.03-1.23]) and CVD death (aHR 1.20 [1.08-1.33]) as well as anti-cit apolipoprotein E, biglycan, and filaggrin with CVD death (aHR 1.12 [1.02-1.23], 1.16 [1.07-1.25], and 1.13 [1.00-1.26]).
Conclusion: Higher concentrations of several RA-related autoantibodies were associated with MACE and/or CVD-mortality, providing support to the hypothesis that autoantibodies may directly contribute to excess CVD risk in RA. Additional study is needed to elucidate pathophysiological mechanisms underpinning these epidemiologic associations.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Johnson T, Duryee M, Hunter C, Roul P, Yang Y, Sokolove J, Robinson W, Baker J, Thiele G, Mikuls T, England B. Autoantibodies and the Risk of Incident Cardiovascular Disease in US Veterans with Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/autoantibodies-and-the-risk-of-incident-cardiovascular-disease-in-us-veterans-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/autoantibodies-and-the-risk-of-incident-cardiovascular-disease-in-us-veterans-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/