Session Information
Date: Monday, November 9, 2020
Title: RA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes Poster IV: Lifespan of a Disease
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Disease presentation and progression in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is highly heterogeneous and requires careful consideration of outcome measurements to be used for individual patients. Here we explore the relationship between disease activity as measured by a standard patient report outcome measure (RAPID3) and multi-biomarker disease activity score (MBDA) across patient phenotypes and therapy regimens within a single community rheumatology practice.
Methods: Unstructured and structured de-identified data from 2019 of patients who satisfied ACR classification criteria for rheumatoid arthritis, were extracted from the electronic health record, including patient demographics, medication history, comorbidities, laboratory values, patient-reported outcomes, swollen joint counts (SJC), and ultrasound evaluation findings (US). The last available disease activity measures were recorded for each patient in 2019, and stable RA patients were defined as those with no change of DMARD therapy for at least 6 months prior to their last visit in 2019. Differences in patient outcomes and laboratory values were determined based on standard correlation analysis.
Results: Out of 757 RA patients with at least one medication script in 2019, 516 (68%) patients with stable RA were identified. Baseline demographics (Table 1) include mean [SD] age, 61.8 [14.7] years; 80% female; and mean [SD] BMI 28.1 [6.5]. Patient demographics, comorbidities, and outcome measurements based on medication regimens are summarized in Table 1. As shown in Figure 1, patients routinely displayed higher disease activity when measured using RAPID3 as compared to MBDA, and this effect was more pronounced in seronegative patients. While highly significant (p=0.006), the Pearson’s correlation coefficient between RAPID3 and MBDA was 0.14 among all patients, and 0.30 among seropositive patients (p=0.0004). There was no significant correlation between RAPID3 and MBDA (p=0.18) among seronegative patients. In the subset of patients maintained on methotrexate or hydroxychloroquine monotherapy, there was also no significant correlation between RAPID3 and MBDA in either MTX or HCQ monotherapy groups (MTX: r = -0.07, p = 0.68; HCQ: r = -0.27, p = 0.18). For patients maintained on bDMARD therapy, there was a significant but weak correlation between RAPID3 and MBDA (r = 0.15; p=0.01). These findings are summarized in Table 2.
Conclusion: Here we characterize the rheumatoid arthritis patient panel in a community rheumatology practice and demonstrate a significant difference between patient reported outcomes (as measured by RAPID3) and serum inflammatory markers (MBDA). Patients frequently had a higher RAPID3 disease activity level compared to their MBDA disease activity level, suggesting the need for a multi-faceted approach to measuring RA disease activity in individual patients. Further studies exploring optimal outcome metrics for different patient phenotypes within rheumatoid arthritis are indicated.
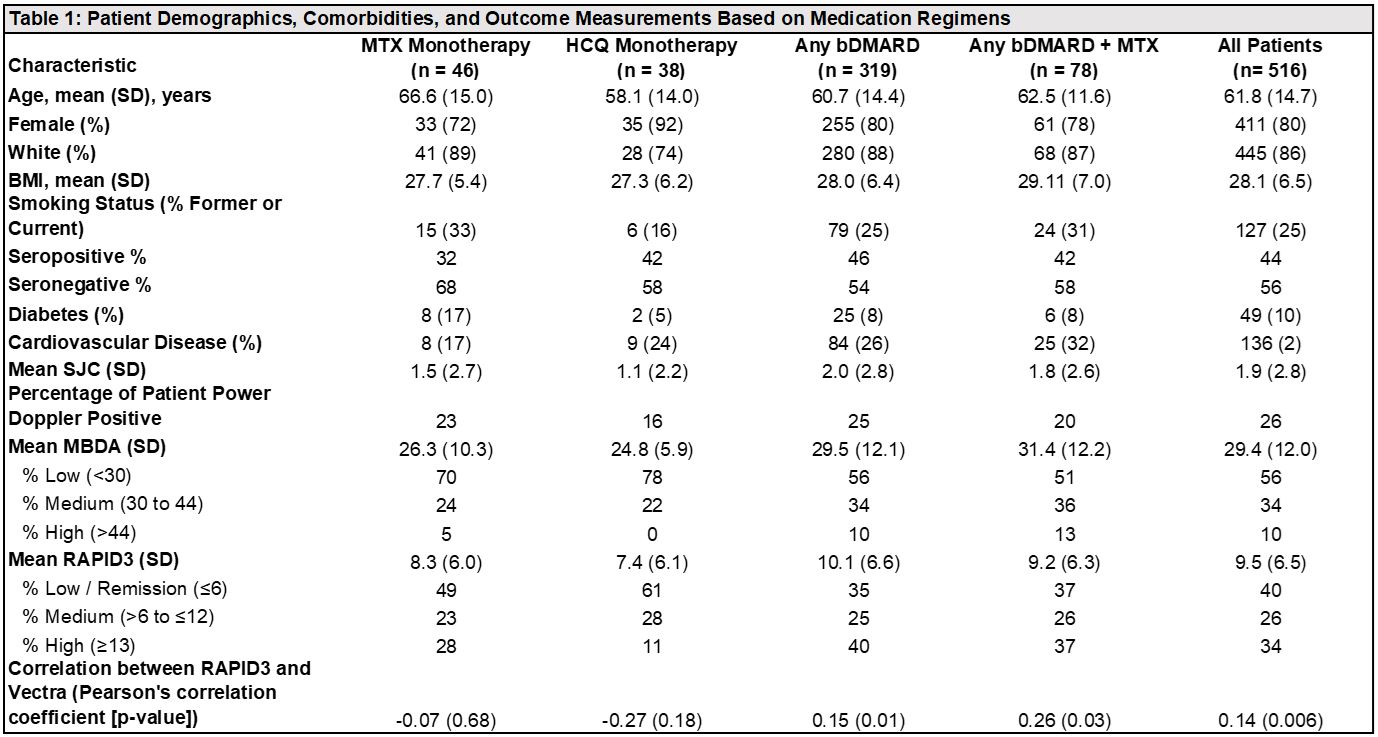 Table 1: Patient Demographics, Comorbidities, and Outcome Measurements Based on Medication Regimens
Table 1: Patient Demographics, Comorbidities, and Outcome Measurements Based on Medication Regimens
 Table 2 – Characteristics and Disease Activity Measurement Relationships by Serology Finding
Table 2 – Characteristics and Disease Activity Measurement Relationships by Serology Finding
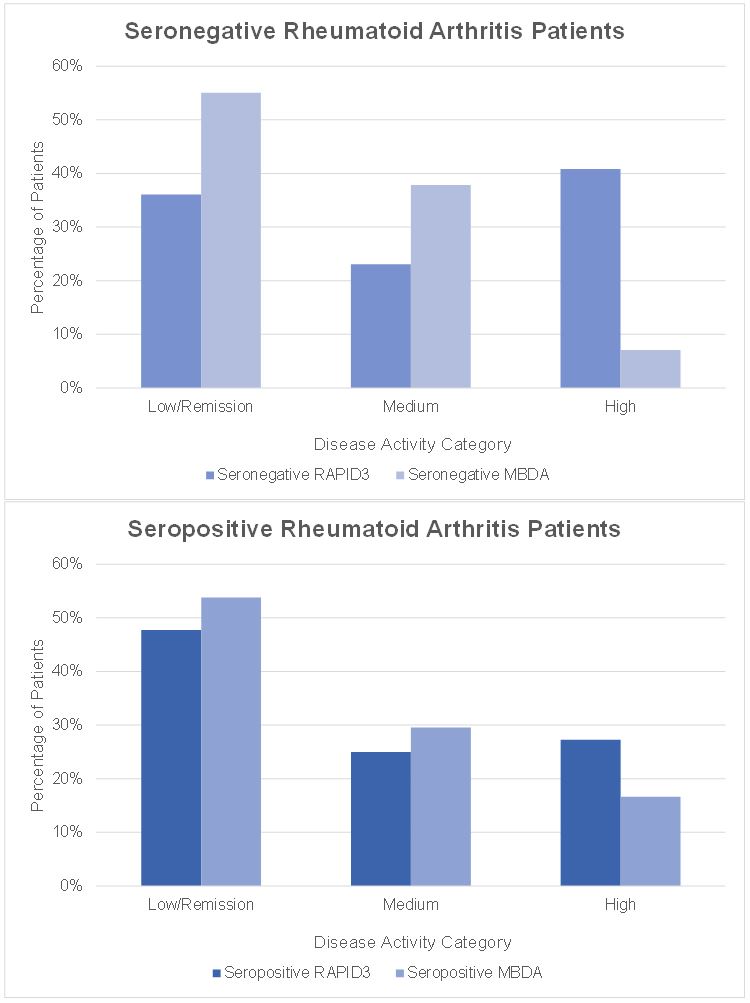 Percentages of Seropositive and Seronegative Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients Grouped by Disease Activity Category in RAPID3 and MBDA
Percentages of Seropositive and Seronegative Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients Grouped by Disease Activity Category in RAPID3 and MBDA
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
He E, Yalamanchi P, Arnold W, Arnold E. An Investigation of the Relationship Between Patient Reported Outcomes and Biomarkers in a Community Rheumatology Practice [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/an-investigation-of-the-relationship-between-patient-reported-outcomes-and-biomarkers-in-a-community-rheumatology-practice/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/an-investigation-of-the-relationship-between-patient-reported-outcomes-and-biomarkers-in-a-community-rheumatology-practice/
