Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: To address the reactivity and affinity against histidyl-transfer RNA synthetase (HisRS) autoantigen of anti-Jo1 autoantibodies from serum and bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) and associations with clinical data in patients with idiopathic inflammatory myopathies/anti-synthetase syndrome (IIM/ASS).
Methods: Samples and clinical data were obtained from: i) 25 anti-Jo1+ (19 sera and 6 BALF/matching sera at diagnosis, 16/19 sera at follow-up); ii) 29 anti-Jo1– (25 sera and 4 BALF/matching sera at diagnosis) patients; iii) 24 age/gender matched healthy controls. Reactivity towards HisRS full-length (HisRS-FL), two HisRS domains, and two HisRS splice variants (WHEP and SV) was tested. Anti-Jo1 IgG reactivity was evaluated by ELISA and western blot in IgG purified from serum by affinity chromatography. In paired serum-BALF, anti-Jo1 IgG and IgA reactivity was analyzed by ELISA. Autoantibodies affinity was measured by surface plasmon resonance. Correlations between autoantibody reactivity and clinical data were evaluated.
Results: Anti-Jo1 IgG from serum and BALF bound HisRS-FL, WHEP and SV with high reactivity, already at diagnosis and recognized both conformation-dependent and -independent HisRS epitopes (Figure 1). Levels of autoantibodies (against HisRS-FL, -domains and -splice variants) generally decreased over time (Figure 2). Individuals with interstitial lung disease, arthritis and less skin involvement presented higher autoantibody levels against HisRS-FL (Figure 3). IgG with anti-WHEP reactivity in BALF correlated with poor pulmonary function. Anti-HisRS-FL IgG displayed high affinity early in the disease.
Conclusion: High levels and high affinity of anti-Jo1 autoantibodies towards HisRS early in disease in sera and BALF support the hypothesis that autoimmunity against HisRS is most likely initiated before IIM/ASS diagnosis.
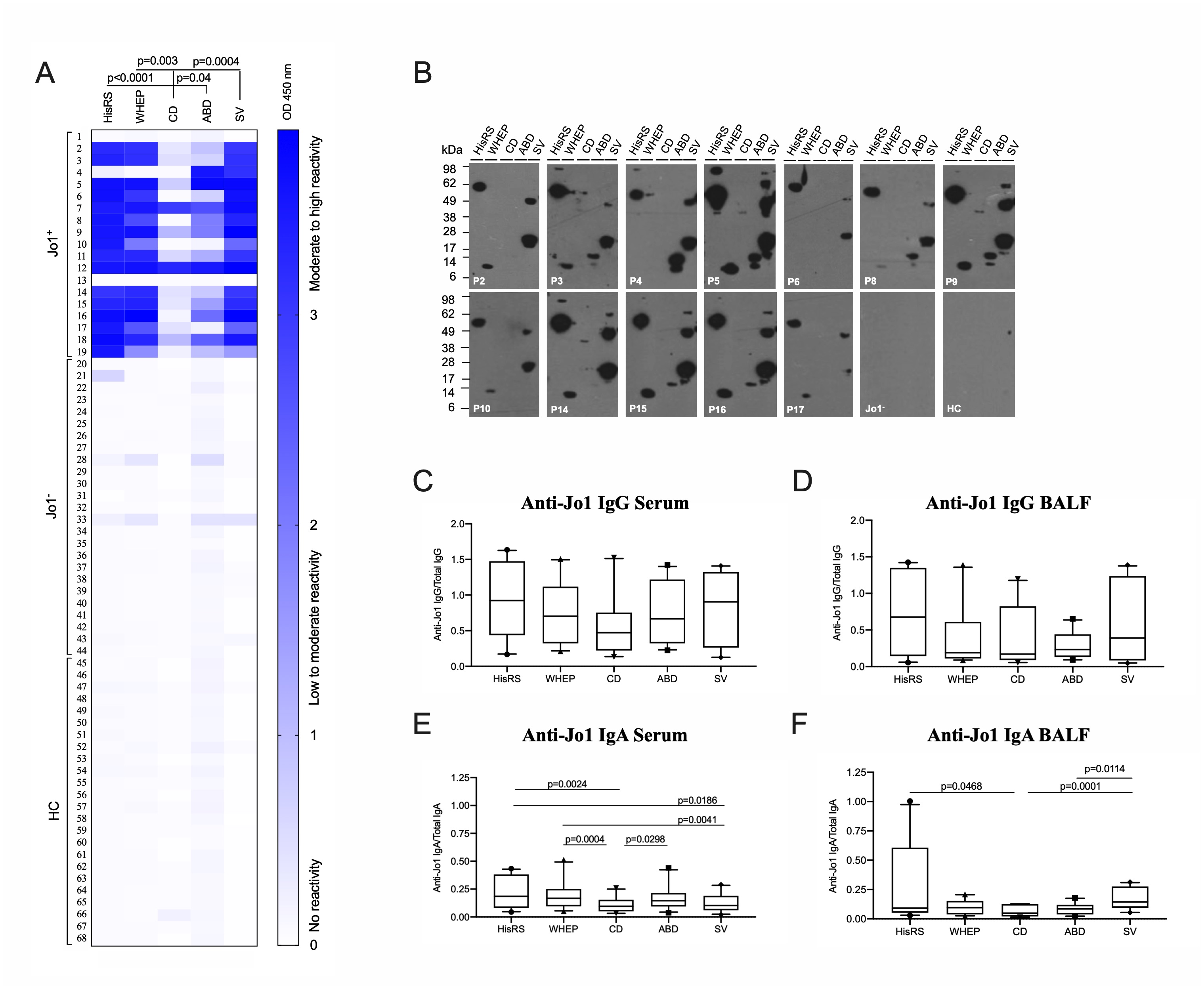 Serum and BALF-derived anti-Jo1 autoantibodies display high reactivity against HisRS variants/domains already at IIM/ASS diagnosis. (A) The reactivity towards HisRS-FL, WHEP, CD, ABD, and SV as conformational epitopes was measured by ELISA in IgG purified from serum of 19 anti-Jo1+, 25 anti-Jo1-, and 24 healthy controls (HC). Higher reactivity corresponds to stronger blue color. (B) Anti-Jo1 reactivity against linear HisRS antigens was addressed by WB in IgG purified from serum of 12 anti-Jo1+, 1 anti-Jo1-, and 1 HC. Stronger band intensity denotes higher anti-Jo1 reactivity. Some patients also showed an additional band, correspondent to HisRS dimer. (C-D-E-F) Anti-Jo1 IgG and IgA reactivity in BALF and paired serum was measured by ELISA in 6 anti-Jo1+. Autoantibody levels were normalized to total values of IgG and IgA (Y-axis). Kruskal-Wallis (A) and Friedman’s tests (C-D-E-F) corrected for multiple comparisons by Dunn’s test was applied. P < 0.05 was assumed as significantly different.
Serum and BALF-derived anti-Jo1 autoantibodies display high reactivity against HisRS variants/domains already at IIM/ASS diagnosis. (A) The reactivity towards HisRS-FL, WHEP, CD, ABD, and SV as conformational epitopes was measured by ELISA in IgG purified from serum of 19 anti-Jo1+, 25 anti-Jo1-, and 24 healthy controls (HC). Higher reactivity corresponds to stronger blue color. (B) Anti-Jo1 reactivity against linear HisRS antigens was addressed by WB in IgG purified from serum of 12 anti-Jo1+, 1 anti-Jo1-, and 1 HC. Stronger band intensity denotes higher anti-Jo1 reactivity. Some patients also showed an additional band, correspondent to HisRS dimer. (C-D-E-F) Anti-Jo1 IgG and IgA reactivity in BALF and paired serum was measured by ELISA in 6 anti-Jo1+. Autoantibody levels were normalized to total values of IgG and IgA (Y-axis). Kruskal-Wallis (A) and Friedman’s tests (C-D-E-F) corrected for multiple comparisons by Dunn’s test was applied. P < 0.05 was assumed as significantly different.
 Reactivity of anti-Jo1 autoantibodies towards HisRS variants decreases over time but remains high against HisRS-FL. (A-B) Reactivity against HisRS-FL, -splice variants (WHEP and SV), and -domains (CD and ABD) displayed by total IgG purified from the first available anti-Jo1+ sera close to diagnosis (T = -0.25 – 0 years) and 2.1 – 3 years after diagnosis. (C-D-E) Anti-Jo1 reactivity of 3 anti-Jo1+ patients (P7, P6, P11) displayed by total IgG purified from sera collected longitudinally. Y-axis represents anti-Jo1 antibody levels against HisRS, measured in the total IgG isolated from anti-Jo1+ IIM/ASS sera. X-axis represents disease duration in years. Dark grey sentences provide information on rituximab introduction and/or follow-up on interstitial lung disease/arthritis. Concentration (ng/mL) of anti-Jo1 antibodies was calculated based on a standard curve derived from anti-Jo1 IgG isolated from a sera pool of 38 anti-Jo1+ IIM/ASS individuals. Total anti-Jo1+ IgG from different patients present distinct binding capacity to HisRS proteins (note the different scale which goes from 100, 200, 400 up to 1200 ng/mL). The letter P (Patient) followed by a number in each graph represents an anti-Jo1+ IIM/ASS individual.
Reactivity of anti-Jo1 autoantibodies towards HisRS variants decreases over time but remains high against HisRS-FL. (A-B) Reactivity against HisRS-FL, -splice variants (WHEP and SV), and -domains (CD and ABD) displayed by total IgG purified from the first available anti-Jo1+ sera close to diagnosis (T = -0.25 – 0 years) and 2.1 – 3 years after diagnosis. (C-D-E) Anti-Jo1 reactivity of 3 anti-Jo1+ patients (P7, P6, P11) displayed by total IgG purified from sera collected longitudinally. Y-axis represents anti-Jo1 antibody levels against HisRS, measured in the total IgG isolated from anti-Jo1+ IIM/ASS sera. X-axis represents disease duration in years. Dark grey sentences provide information on rituximab introduction and/or follow-up on interstitial lung disease/arthritis. Concentration (ng/mL) of anti-Jo1 antibodies was calculated based on a standard curve derived from anti-Jo1 IgG isolated from a sera pool of 38 anti-Jo1+ IIM/ASS individuals. Total anti-Jo1+ IgG from different patients present distinct binding capacity to HisRS proteins (note the different scale which goes from 100, 200, 400 up to 1200 ng/mL). The letter P (Patient) followed by a number in each graph represents an anti-Jo1+ IIM/ASS individual.
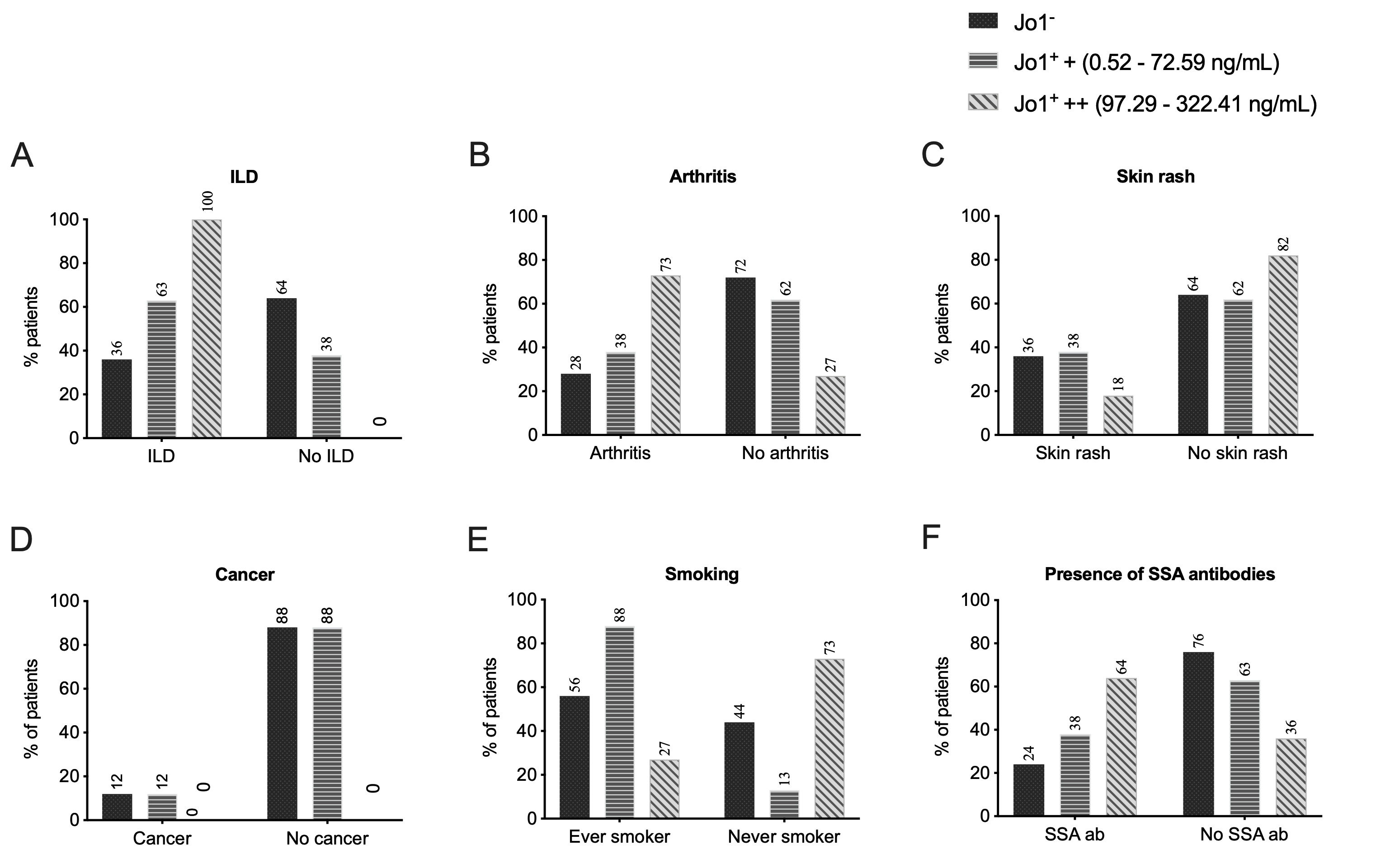 IIM/ASS patients diagnosed with ILD and arthritis and less skin involvement harbor more reactive anti-Jo1 autoantibodies. (A-B-C-D-E-F) Percentage of IIM/ASS patients distributed according to anti-HisRS full-length (HisRS-FL) reactivity levels, clinical diagnosis and clinical manifestations. The anti-HisRS-FL reactivity displayed was measured in total anti-Jo1+ IgG purified from serum. Numbers on top of the bars represent the percentage of patients in the group. Jo1-, anti-Jo1 IIM/ASS negative patients; Jo1+ +, anti-Jo1 IIM/ASS positive patients with low to moderate reactivity (0.52 – 72.59 ng/mL); Jo1+ ++, anti-Jo1 IIM/ASS positive patients with moderate to high HisRS reactivity (97.29 – 322.41 ng/mL). IIM, idiopathic inflammatory myopathies. ILD, interstitial lung disease; ASS, anti-synthetase syndrome.
IIM/ASS patients diagnosed with ILD and arthritis and less skin involvement harbor more reactive anti-Jo1 autoantibodies. (A-B-C-D-E-F) Percentage of IIM/ASS patients distributed according to anti-HisRS full-length (HisRS-FL) reactivity levels, clinical diagnosis and clinical manifestations. The anti-HisRS-FL reactivity displayed was measured in total anti-Jo1+ IgG purified from serum. Numbers on top of the bars represent the percentage of patients in the group. Jo1-, anti-Jo1 IIM/ASS negative patients; Jo1+ +, anti-Jo1 IIM/ASS positive patients with low to moderate reactivity (0.52 – 72.59 ng/mL); Jo1+ ++, anti-Jo1 IIM/ASS positive patients with moderate to high HisRS reactivity (97.29 – 322.41 ng/mL). IIM, idiopathic inflammatory myopathies. ILD, interstitial lung disease; ASS, anti-synthetase syndrome.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Notarnicola A, Preger C, Lundström S, Renard N, Wigren E, Van Gompel E, Galindo-Feria A, Persson H, Fathi M, Grunewald J, Jakobsson P, Gräslund S, Lundberg I, Fernandes-Cerqueira C. Highly Reactive anti-Jo1 Autoantibodies to Distinct HisRS Variants and Domains Associate with Lung and Joint Involvement in Patients with Myositis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/highly-reactive-anti-jo1-autoantibodies-to-distinct-hisrs-variants-and-domains-associate-with-lung-and-joint-involvement-in-patients-with-myositis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/highly-reactive-anti-jo1-autoantibodies-to-distinct-hisrs-variants-and-domains-associate-with-lung-and-joint-involvement-in-patients-with-myositis/
