Session Information
Date: Friday, November 6, 2020
Title: Innate Immunity Poster
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
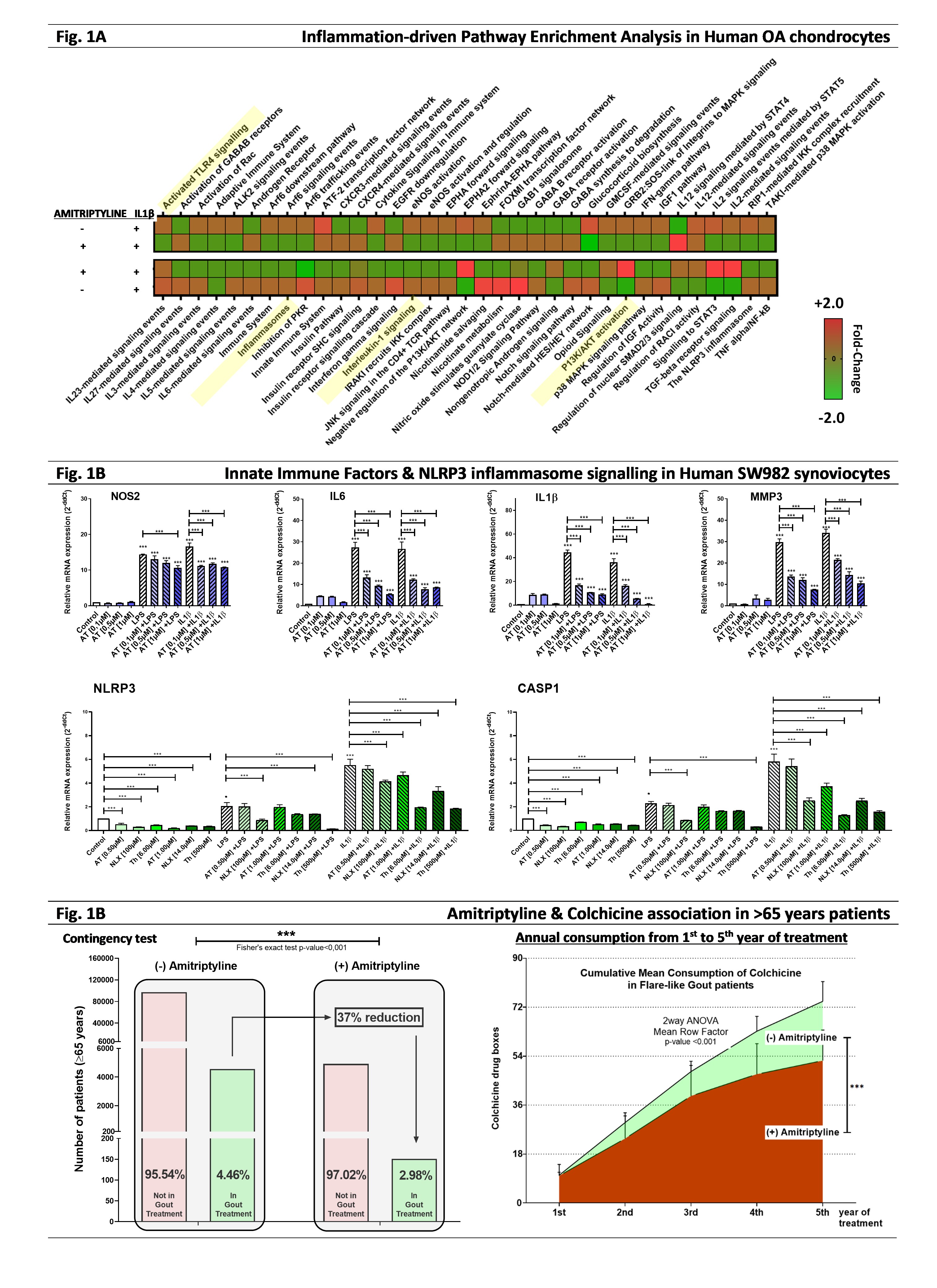
Background/Purpose: Joint inflammation is a common feature across multiple rheumatic diseases. To deal with the induction of innate immune factors, targeting therapeutic targets such as TLR4 and IL1R is required. We have recently reported the use of amitriptyline (AT), thalidomide (Th), and naloxone (NLX) to block TLR4 & IL1R-mediated innate immune responses in OA cartilage. Now we explore their use in synovia and gout inflammation.
Methods: The ethics committee approved (CAEIG 2016/258) the use of human samples and aggregated and dissociated clinical data from 440.000 citizens.
The activity and expression of TLR4, IL1R, and NLRP3 signaling pathways were determined by docking analysis (Autodocks-Vina), MTT cell viability assay, RT-PCR, and Western Blot, ELISA or MALDI-TOFF in human OA chondrocytes and synoviocytes (SW982 cell line). Statistics were performed using GraphPad Prism 9.0.
Results: The docking of AT, Th, and NLX towards TLR4 was confirmed by in silico binding affinity analysis. In human synoviocytes, the use of therapeutic doses of AT [0.1-1µM], NLX [1.4-100µM], and Th [3-500µM]) prevented the induction of several factors including NOS2, IL6, IL1B and MMP9 at the mRNA and protein level (up to -97%). The inhibition of the NLRP3 inflammasome pathway, which is linked to both synovitis and gout-associated inflammation, was verified by RT-PCR & MALDI-TOFF in OA chondrocytes and synoviocytes. Considering this link, we requested access to clinical data and found that amitriptyline consumers are less prone to require colchicine drug for gout treatment.
Conclusion: Amitriptyline, naloxone, and thalidomide prevent the induction of TLR4 & IL1R-mediated innate immune factors in OA chondrocytes and synoviocytes. Moreover, amitriptyline consumption reduced the dose of colchicine needed for gout treatment.
Considering that these drugs are being used in other indications, their repurpose might be a novel tool to manage inflammation across diverse rheumatic diseases.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Franco-Trepat E, Alonso-Pérez A, Guillán-Fresco M, López-Fagundez M, Pazos-Pérez A, Lois Iglesias A, Bravo S, Jorge-Mora A, Gómez-Reino J, Gómez R. Novel Repurposed Drugs Against Joint Inflammation Reveal Potential Use for Gout Treatment: An In Silico, In Vitro and Clinical Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/novel-repurposed-drugs-against-joint-inflammation-reveal-potential-use-for-gout-treatment-an-in-silico-in-vitro-and-clinical-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/novel-repurposed-drugs-against-joint-inflammation-reveal-potential-use-for-gout-treatment-an-in-silico-in-vitro-and-clinical-study/