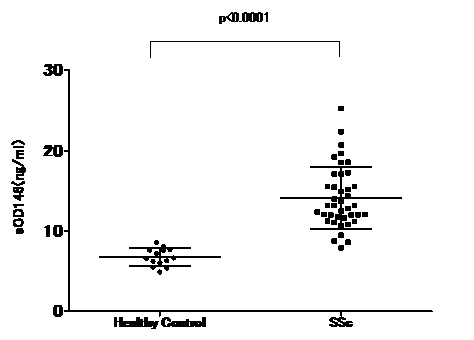Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 8, 2015
Title: Systemic Sclerosis, Fibrosing Syndromes and Raynaud's - Clinical Aspects and Therapeutics Poster I
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: CD146 is a transmembrane
glycoprotein belonging to Ig-superfamily. Human
endothelial cells, activated fibroblasts and Th17 cells express CD146 that
involved in angiogenesis, fibrosis and inflammation. CD146+ T cells secrete IL-17,
IFN-g, and TNF-a. CD146 also exists as a soluble form (sCD146) that has
biological activity. The aim of this study is to establish an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for detecting sCD146 , and to determine the serum levels of sCD146 in patients
with systemic sclerosis (SSc), and examine the
relationship with the clinical manifestations.
Methods: We used two non-cross-blocking CD146 mAbs to develop a sandwich ELISA for measuring serum
sCD146. Recombinant sCD146 was used to obtain the standard curve. IRB approved
blood sampling and measuring protocol was established at the Juntendo
University School of Medicine and Toyo University and enrolled healthy
controls. Blood samples were drawn from patients fulfilling criteria for SSc proposed by the 2013 classification criteria for SSc (ACR/EULAR). Levels of sCD146 were quantified in 40
serum samples from patients with SSc by the ELISA and
compared with those of 14 healthy controls. The clinical manifestation and
laboratory data of the patients were also examined.
Results: We established a sensitive and specific ELISA system
for testing sCD146. Systemic sclerosis was focused from the result of screening
various SCTDs for serum sCD146. The levels of sCD146 were significantly higher
in 40 patients with SSc (14.12 ng/ml)
than those in 14 healthy controls (6.73 ng/ml;
p<0.001) [Figure]. However, there was no statistical correlation between
sCD146 and the clinical manifestations, such as lung fibrosis and area of skin
fibrosis. But the level of sCD146 was significantly correlated with the level
of E-selectin, a marker of vascular damage. In addition,serum levels of sCD146
were decreased in SSc patients treated with
glucocorticoid.
Conclusion: We identified the presence of sCD146 in SSc serum. It is suggested that sCD146 is involved in
inflammation through vascular endothelial cells as well as E-selectin. The pathogenic and clinical significance of
sCD146 in SSc should be further examined.
Figure.Serum sCD146 in SSc
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kato K, Ito T, Tamura N, Okuda S, Matsushita M, Tada K, Yamaji K, Takasaki Y. Elevated Serum Levels of Soluble CD146 in Patients with Systemic Sclerosis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015; 67 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/elevated-serum-levels-of-soluble-cd146-in-patients-with-systemic-sclerosis/. Accessed .« Back to 2015 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/elevated-serum-levels-of-soluble-cd146-in-patients-with-systemic-sclerosis/