Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 16, 2024
Title: SLE – Treatment Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Zetomipzomib is a selective inhibitor of the immunoproteasome with anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory potential without evidence of immunosuppression to date. The MISSION study (NCT03393013), a Phase 1b/2, open-label study of zetomipzomib in patients with SLE ± LN, demonstrated both clinically meaningful renal responses in LN patients who had not previously responded to standard of care therapy and improvement across multiple exploratory SLE disease activity measures and biomarkers. Additional analyses of patients with highly active SLE and patients with nephrotic range proteinuria are presented here.
Methods: Patients who completed 13 weeks of zetomipzomib treatment at the target dose of 60 mg once weekly in Phase 1b (cohorts 2a, 2b, and 2c) and 24 weeks of zetomipzomib in Phase 2 were included in this analysis. Highly active SLE was defined as SLE patients with non-renal (nr) SLEDAI ≥10 (Phase 1b); nephrotic range proteinuria was defined as 24-hour urine protein to creatinine ratio (UPCR) ≥3 at baseline (Phase 1b and 2). SLE and LN disease measures, including BILAG (Phase 1b), UPCR, and a modified SLE Responder Index-4 (mSRI-4) defined as nrSLEDAI improved by ≥4 (exclusive of the 4 kidney domains), no worsening of Physician Global Assessment (PGA) ≥ 0.30 points (0-3 Likert scale) and no new BILAG A or 2 BILAG B organ domain scores, were evaluated. Biomarker analyses were performed on samples, including whole blood, cryopreserved peripheral blood mononuclear cells, plasma, and urine.
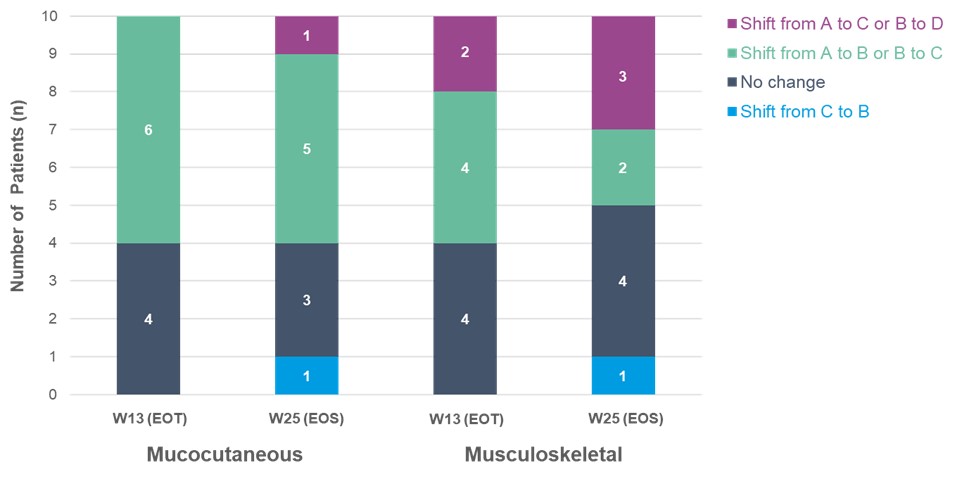
Results: Ten evaluable patients in Phase 1b were classified as highly active SLE at baseline (mean nrSLEDAI: 10.4). Six of the 10 patients had mSRI-4 responses at Week (W) 13 (end of treatment [EOT]), and 4 of those 6 patients maintained their responses at W25 (end of study [EOS]). At baseline, patients with highly active SLE largely displayed mucocutaneous or musculoskeletal manifestations, and mucocutaneous and musculoskeletal BILAG domains improved with zetomipzomib treatment in Phase 1b; Figure 1.
One patient in Phase 1b and 4 patients in Phase 2 had nephrotic range proteinuria at baseline (mean UPCR: 5.4). After 24 weeks of zetomipzomib treatment, 3 of the 4 patients in Phase 2 achieved a ≥50% reduction in UPCR at W25 (EOT) and at W37 (EOS); the one patient in Phase 1b also achieved a ≥50% reduction in UPCR by W25 (EOS). In addition, 2 of the 4 patients in Phase 2 improved in SLEDAI domains beyond the renal domains with nrSLEDAI improvement by ≥4 without worsening of PGA ≥ 0.30 points at W25 (EOT), and the Phase 1b patient had a mSRI-4 response at W25 (EOS).
Zetomipzomib administration was associated with a shift in the gene expression profile observed in highly active SLE patients towards the baseline profile of non-highly active SLE patients. Gene modules and immunophenotyping revealed changes in B and T lymphocyte populations compared to baseline. Numerous immune-related urine biomarkers, including CD163 and MCP-1, decreased in Phase 2 nephrotic patients over the course of treatment.
Conclusion: Results from this subgroup analysis suggest that treatment with zetomipzomib 60 mg once weekly is effective across multiple organ systems in patients with highly active SLE as well as in those with nephrotic range proteinuria (UPCR ≥3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Furie R, Saxena A, Parikh S, Leff R, Bohnett L, Ray K, Tuch B, Anderl J, Whang J, Palaniswamy K. Zetomipzomib (KZR-616), a First-in-Class Selective Immunoproteasome Inhibitor, Demonstrated Improvements in SLE/LN Disease Measures and Biomarkers in Patients with Highly Active SLE or Nephrotic Range Proteinuria in the Open-label Phase 1b/2 MISSION Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/zetomipzomib-kzr-616-a-first-in-class-selective-immunoproteasome-inhibitor-demonstrated-improvements-in-sle-ln-disease-measures-and-biomarkers-in-patients-with-highly-active-sle-or-nephrotic-range/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/zetomipzomib-kzr-616-a-first-in-class-selective-immunoproteasome-inhibitor-demonstrated-improvements-in-sle-ln-disease-measures-and-biomarkers-in-patients-with-highly-active-sle-or-nephrotic-range/