Session Information
Date: Monday, November 8, 2021
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: During the COVID pandemic assessments of RA disease activity (DA) have relied on virtual assessments by patient report. It is unknown whether non-articular pain might influence these. We sought to determine if patient reported Non-Articular Pain (NAP) by body pain diagram (BPD) influences the agreement of change in clinical disease activity index (CDAI) scores over 3 months as rated by rheumatologist (MD) and patient (PT), comparing a previously validated PT CDAI and the standard MD CDAI. We hypothesized agreement would be similar for PT- and MD- CDAI ratings in patients without NAP or regional NAP (RP) but would be worse in patients with widespread NAP (WSP).
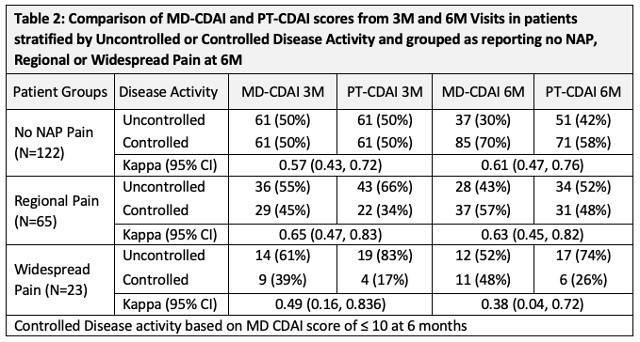
Methods: Data were from patients with early RA (Symptoms < 1 year) who were enrolled in CATCH between Mar 2017 and Mar 2021. All had complete data at 3- and 6- month (M) visits to calculate MD- and PT- CDAI scores. Patients had to have completed a BPD at each visit. Patients were classified as having regional RP (1 or 2 regions of pain on BPD), or WSP (3 or more regions of pain on BPD) at their 6M Visit. In CATCH MDs and patients separately identify tender/painful and swollen joints using a 28-joint count homunculus, and both report global assessments (GA) (NRS 0-10) at each visit. The PTCDAI score was the sum of PT-rated TJC28, SJC28, MDGA and PTGA (0-76). We compared PT and MD CDAI scores at 3M and 6M visits in all patients and in subgroups based on presence of and type of NAP. We then compared change in MD and PT CDAI scores between 3M to 6M visits stratified by NAP report and further stratified by disease activity control between 3M and 6M defining controlled as low disease activity or remission (LDA/REM) using a standard cut point of ≤ 10 by MD CDAI at 6M and active uncontrolled disease activity (high or moderate disease activity (HDA/MDA)). Simple Kappa and one way ICC were used to assess agreement for categorical and continuous measures.
Results: The sample included 210 participants with a mean (SD) age of 57 (13), symptom duration of 5.3 (2.8); 80% met RA criteria, 81% were white, 65%/60% were ACPA/RF positive. At 6 months 58% reported no NAP, 31% Regional Pain and 12% Widespread Pain. Patients with any NAP were older, mostly female, with more comorbidities, and higher PT CDAI scores compared to MD CDAI scores. More pts with WSP smoked and received glucocorticoids (Table 1). Agreement between PT and MD CDAI scores at 3M and 6M single time points, regardless of DA control was high for patients without NAP and with RP, but lower for patients reporting WSP (Table 2). Agreement for the change in MD and PT CDAI scores between 3M and 6M visits was high-moderate to high for pts without NAP, and RP but low for pts with WSP (Table 3).
Conclusion: PT CDAI scores at single time points, and the difference in scores between 3- and 6- month visits, were similar to MD CDAI scores for patients without NAP or with regional pain with good agreement, but agreement was poor for patients with WSP. These data suggest using caution in interpreting a PTCDAI in patients with a competing widespread pain disorder. It is possible regional NAP may represent RA-related inflammation such as tendinitis and may explain why agreement is still high in PT- and MD- CDAI scores.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Bykerk V, Schieir O, Valois M, Hazlewood G, Boire G, Hitchon C, Bessette L, Tin D, Keystone E, Thorne C, Pope J, Bartlett S. Widespread but Not Regional Non-articular Pain Influences Patient and Rheumatologist Reported Change in Clinical Disease Activity Index Scores over Time – Implications for Using Patient Ratings in Telehealth – a Study from the Canadian Early Arthritis Cohort [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/widespread-but-not-regional-non-articular-pain-influences-patient-and-rheumatologist-reported-change-in-clinical-disease-activity-index-scores-over-time-implications-for-using-patient-ratings-in-tel/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/widespread-but-not-regional-non-articular-pain-influences-patient-and-rheumatologist-reported-change-in-clinical-disease-activity-index-scores-over-time-implications-for-using-patient-ratings-in-tel/