Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: A risk stratification model proposed a simple score using 4 biomarkers to identify those at high risk of developing inflammatory arthritis (IA) in primary care (1). Meanwhile the pre-clinical phase of IA is a continuum where biomarkers evolve. Identifying those indicating imminent (6 months) progression would be of value.
Objectives were to describe sequential changes in biomarkers prior IA development according to risk stratification and to identify predictive value of biomarkers for imminent IA.
(1) Duquenne et Al, Ann Intern Med 2023
Methods: In a single centre prospective observational cohort, 543 anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody (anti CCP) positive persons at risk of IA with a new non specific musculoskeletal symptom and no IA were recruited. Outcome was clinical IA. Risk score used anti CCP, rheumatoid factor (RF), early morning stiffness duration (EMS), and erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), defining 4 groups: those at high or low risk who subsequently developed IA or not. Collected data was gathered into 4 time periods prior IA: >2 years ( >2Y), 2 to 1 year (2-1Y), 12 to 6 months (12-6M), and < 6 months (< 6M), and equivalent time since first visit for those not developing IA. 1. Descriptive analyses: independent/paired analysis were done between/ within groups. 2. Predictive analyses: multivariable predictive analysis for imminent IA used panel data analysis on dichotomised biomarkers with a random intercept and robust error estimation.
Results: Of the 242/543 (45%) persons identified at high risk, 57% (139/242) developed IA in a median of 12 (3-33) months. In the low risk group 12% (37/301) did in 21 (9-55) months.
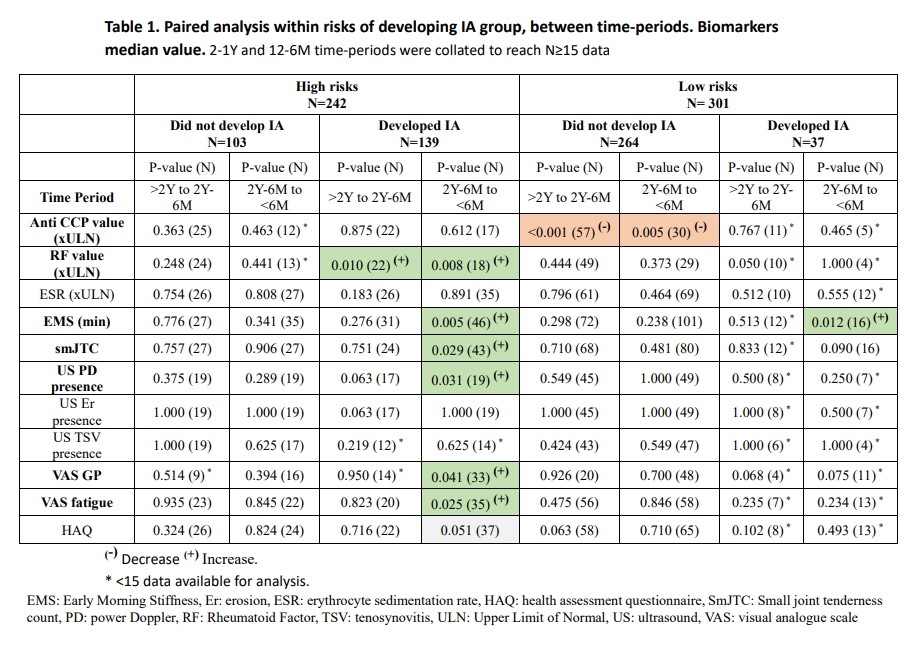
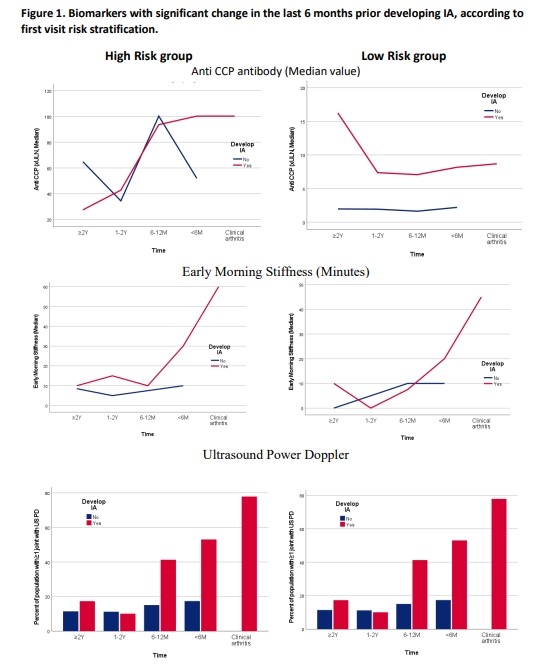
1. Descriptive analyses: In the high risk group, those developing IA (Dev IA) showed a significant increase in RF value, EMS, small joints tenderness count (SmJTC), US power Doppler (PD), fatigue and pain < 6M prior IA (Table 1). Compared to those who would not develop IA (No dev IA), they showed similar anti CCP value but higher RF value throughout follow up, then sequential differences with higher number of joints with US PD presence (2-1Y), ESR, US erosions and tenosynovitis (12-6M), and finally higher smJTC and EMS < 6M prior IA.
In the low risk group, analysis within Dev IA group showed a significant increase in EMS and a decrease in anti CCP value < 6M prior IA. Compared No dev IA, in < 6M prior IA, they showed higher US features, EMS, small joints tenderness count (SmJTC), and PROs (P< 0.05). Anti CCP and RF values were higher throughout follow up.
2. Predictive analyses: In the high risk group, the best predictors for progression to IA within 6 months were RF + (OR 6 [CI 1-33]), EMS ≥30min (OR 11 [CI 2-62]), US PD presence (OR 5 [CI 1-21]), and smJTC ≥1 (OR 5 [CI 1-23]). In the low risk group, it is anti CCP >3xULN (OR7 CI 2-25), RF + (OR 8 [CI 2-32]) that were the most predictive for imminent IA.
Conclusion: In persons at high risk of developing IA, many biomarkers increased < 6M prior but the best predictors for imminent IA were morning stiffness duration, tenderness of the small joints, and US PD presence, therefore should be followed closely. In the low risk group, although EMS showed significant late increase, it is those with high anti CCP value and RF positive that showed the best predictive value for imminent progression.
* <15 data available for analysis.
EMS: Early Morning Stiffness, Er: erosion, ESR: erythrocyte sedimentation rate, HAQ: health assessment questionnaire, SmJTC: Small joint tenderness count, PD: power Doppler, RF: Rheumatoid Factor, TSV: tenosynovitis, ULN: Upper Limit of Normal, US: ultrasound, VAS: visual analogue scale.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Duquenne L, Sahin Eroglu D, Wu J, Harnden K, Di Matteo A, Thornton L, Chowdhury R, Garcia-Montoya L, Mankia K, Emery P. Which Biomarkers Indicate Imminent Progression to Inflammatory Arthritis in High Risk CCP Positive Persons? [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/which-biomarkers-indicate-imminent-progression-to-inflammatory-arthritis-in-high-risk-ccp-positive-persons/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/which-biomarkers-indicate-imminent-progression-to-inflammatory-arthritis-in-high-risk-ccp-positive-persons/