Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Individuals with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) are at higher risk of herpes zoster (HZ) compared to the general population. This interim analysis evaluated the vaccine effectiveness (VE) of recombinant zoster vaccine (RZV) against HZ and postherpetic neuralgia (PHN) and risk of flares in adults ≥50 years of age (YoA) with RA.
Methods: We conducted a retrospective matched cohort analysis to evaluate VE of RZV in a large healthcare system. We included adults ≥50 YoA with RA (≥2 encounters with ICD-10 codes for RA) who received 2 doses of RZV ≥28 days apart during 04/01/2018 – 12/31/2021 and matched up to 1:3 to RZV unvaccinated individuals on age, sex, race/ethnicity, RA medication category, and index date (date of second dose among vaccinated; unvaccinated match assigned same date), with follow-up until 12/31/2022. Stratified Cox proportional hazards regression was used to estimate adjusted hazard ratios and VE. Since RZV is licensed as 2 doses given 2–6 months apart with flexibility of 1–2 months between doses for those who are or will be immunocompromised, VE against HZ was also assessed in adults who received 2 doses 4 weeks–6 months apart. HZ diagnosis was identified by ICD-10 codes plus antiviral medications prescribed within 7 days. All HZ cases with healthcare encounters 3–6 months after HZ diagnosis were chart reviewed for occurrence of PHN (persistent HZ-related pain which could not be explained by other obvious causes).
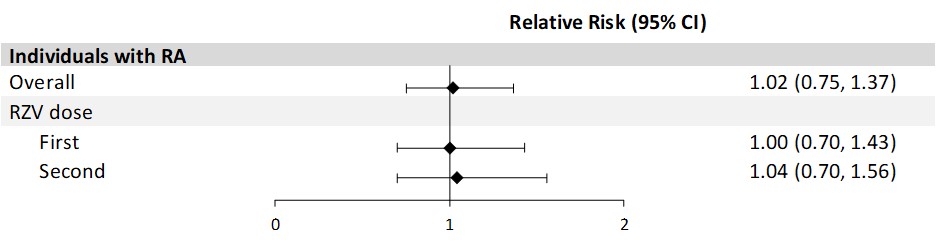
Among adults who received ≥1 dose of RZV, we conducted a self-controlled case series analysis to assess the risk of RA flare, defined as new-onset flare or disease worsening. Flares were identified through chart review of risk periods 30 days following each vaccine dose and comparison periods of –90 to –61 days and 31 to 60 days relative to each dose. The incidence of flares within 30 days after each dose of RZV was compared to that in the pre- and post-vaccination comparison periods. The relative risk (RR) of RA flare was estimated using conditional Poisson regression.
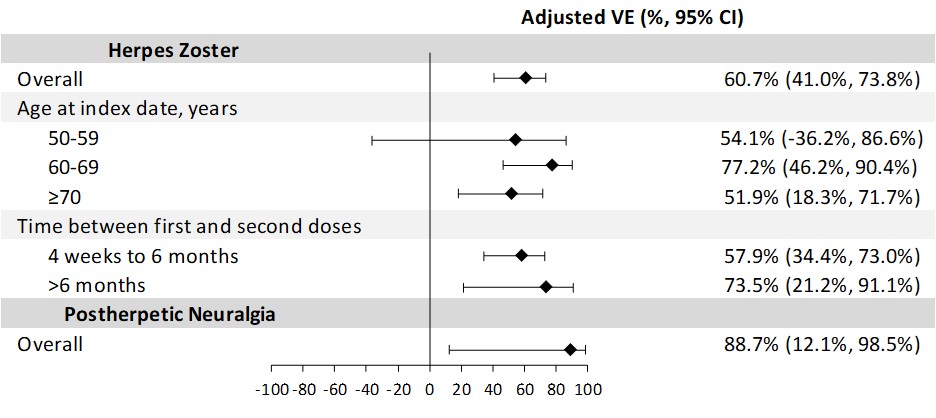
Results: For the VE analysis of adults ≥50 YoA with RA (n=1926 vaccinated, 5746 matched unvaccinated), 79.1% were female, 47.5% were non-Hispanic White, and the mean age was 69.4 years (standard deviation [SD] 9.4). Among adults with RA who received 2 RZV doses, the incidence rate of HZ was 8.0 (95% confidence interval [CI]: 5.7, 11.2) per 1000 person-years compared to an HZ incidence of 19.1 (95% CI: 16.6, 21.9) in the unvaccinated group. The overall adjusted VE of 2 doses of RZV against HZ was 60.7% (95% CI: 41.0%, 73.8%; Fig 1). The adjusted 2-dose VE against HZ for 4 weeks–6 months between doses was similar (VE: 57.9% [95% CI: 34.4%, 73.0%]). Adults with RA who received 2 doses of RZV had a PHN incidence of 0.2 (95% CI: 0.0, 1.7) per 1000 person-years compared to 1.9 (95% CI: 1.2, 3.0) in the unvaccinated group, with an adjusted VE of 88.7% (95% CI: 12.1%, 98.5%). Among 2606 adults ≥50 YoA with RA who received ≥1 dose of RZV (78.9% female, 45.0% non-Hispanic White, mean age 68.7 years [SD 9.2]), there was no increased risk of RA flares during 30 days after RZV vaccination (RR 1.0 [95% CI: 0.8, 1.4]; Fig 2).
Conclusion: Among adults ≥50 YoA with RA, 2 doses of RZV were effective in preventing HZ and PHN with no new safety concerns.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Rayens E, Sy L, Qian L, Wu J, Ackerson B, Luo Y, Cheng Y, Lin A, Solano Z, De Jesus J, Amundsen B, Florea A, Ku J, Chmielewski-Yee E, Oraichi D, Seifert H, Yun H, Tseng H. Vaccine Effectiveness and Safety of Recombinant Zoster Vaccine (RZV) in Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) Patient Populations Aged 50 Years and Older [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/vaccine-effectiveness-and-safety-of-recombinant-zoster-vaccine-rzv-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-ra-patient-populations-aged-50-years-and-older/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/vaccine-effectiveness-and-safety-of-recombinant-zoster-vaccine-rzv-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-ra-patient-populations-aged-50-years-and-older/