Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 17, 2024
Title: Abstracts: SLE – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes II: Biomarkers
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 1:00PM-2:30PM
Background/Purpose: Lupus nephritis (LN) is a pathologically diverse autoimmune disease that can lead to end-stage kidney disease and mortality. Although Class II LN is considered as a milder form of LN which often requires no or minimal treatment, a growing body of clinical evidence suggests Class II LN may be more severe than previously thought. Urine proteomics previously demonstrated monocyte/neutrophil degranulation, macrophage activation, and wound healing/matrix degradation were enriched in class III and IV LN. We hypothesized that urine proteomics on Class II LN will capture the extent of kidney inflammation, revealing both similarities with more advanced stages of disease as well as proteomic signatures specific Class II.
Methods: We quantified 1200 biomarkers (Kiloplex, RayBiotech) in urine samples collected before a clinically indicated kidney biopsy that showed ISN Class II LN as part of the Accelerating Medicines Partnership in RA/SLE (AMP). Single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNAseq) of 16 Class II renal biopsies was utilized to corroborate urinary signatures with renal tissue. Over 35 thousand cells were captured across tubular, stromal and immune compartments. Leveraging the AMP scRNA-seq dataset, we included 30 control, 46 membranous, 51 mixed and 58 proliferative samples with over 600 thousand cells captured in total.
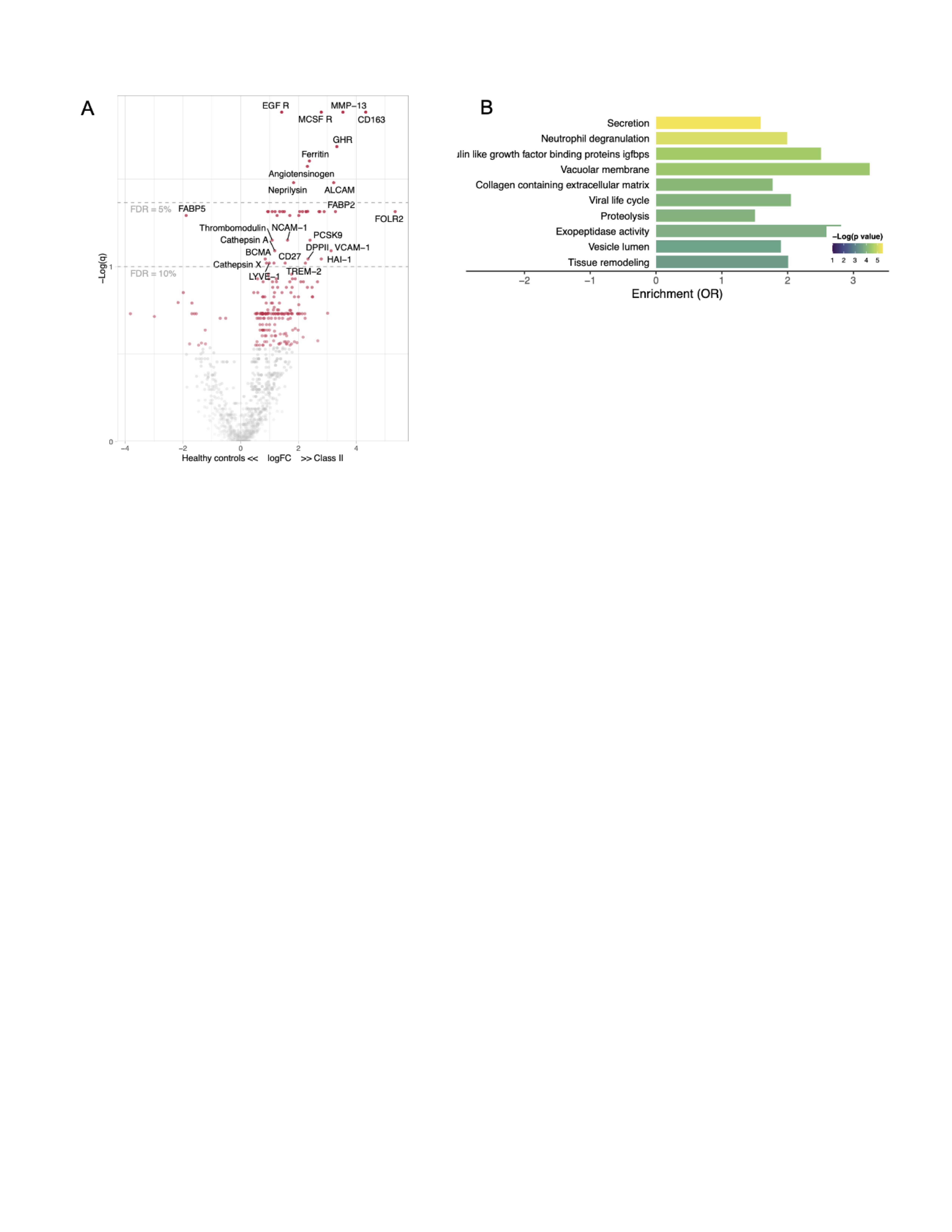
Results: Urine proteomic profiles were compared in 16 Class II LN patients and 10 healthy controls, revealing an inflammatory and profibrotic signature in Class II. For example, patients with class II LN demonstrated an elevation of MMP-13, M-CSF receptor, CD163, ALCAM, and FOLR2 (Figure 1A). Pathway analysis showed enrichment of neutrophil degranulation, collagen containing extracellular matrix and tissue remodeling pathways (Figure 1B).
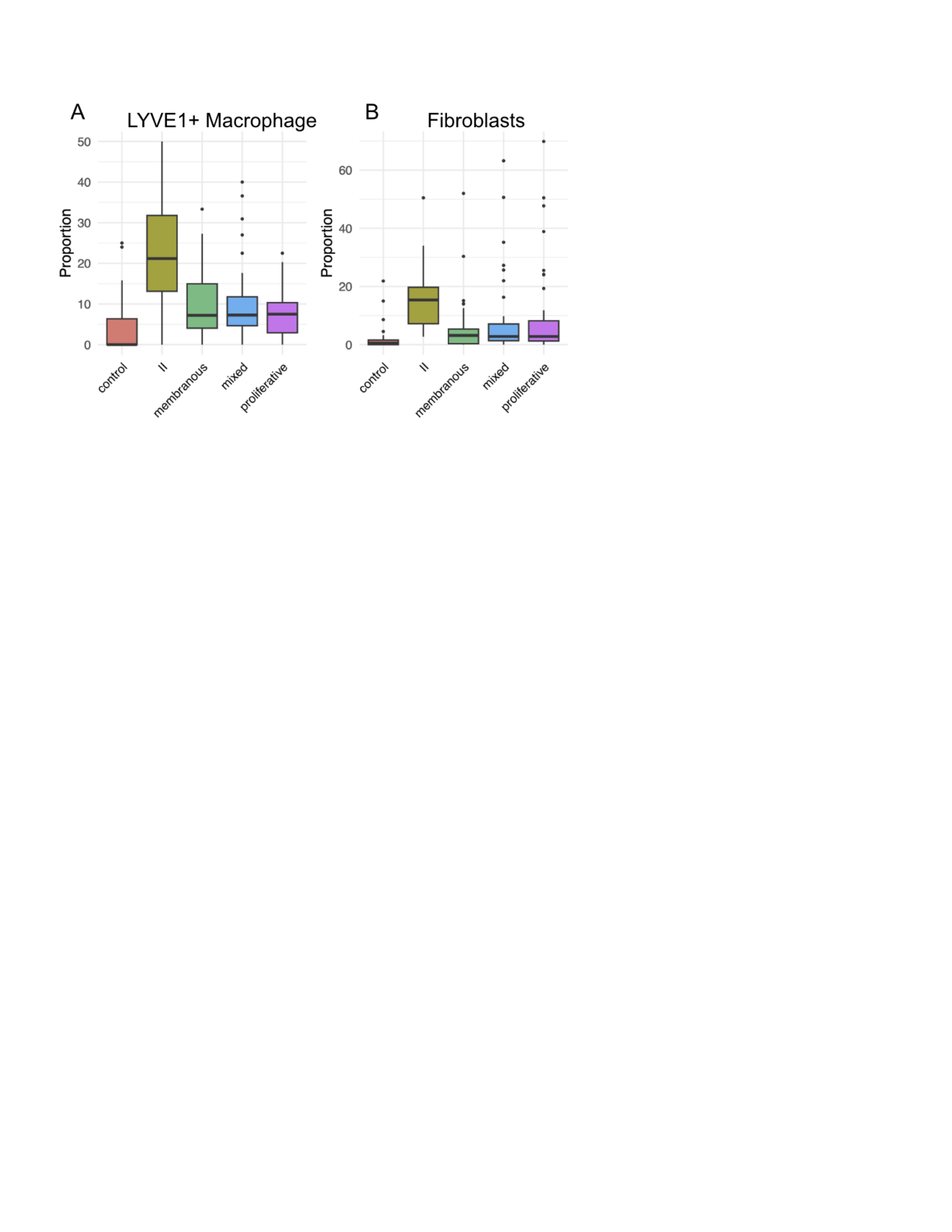
Kidney scRNA-seq confirmed an anti-inflammatory macrophage population expanded in Class II LN with high expression of FOLR2 and LYVE1 (Figure 2A). In addition, there was an expansion of fibroblasts in Class II with an activated phenotype (Figure 2B), possibly contributing to the enrichment of pathways involving tissue remodeling and collagen containing extracellular matrix in Figure 1B.
Conclusion: Although Class II LN is generally considered mild, proteomic and kidney transcriptional analyses demonstrated immune activation and tissue remodeling signatures. These signatures are similar to those previously identified in the more aggressive proliferative LN suggesting that Class II LN, or at least a subset, exists on a spectrum with class III and IV LN.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Shwetar J, Buyon J, Petri M, Ruggles K, Fava A. Urine Proteomics in Class II Lupus Nephritis Reveals Immune Activation and Pro-Fibrotic Signatures [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/urine-proteomics-in-class-ii-lupus-nephritis-reveals-immune-activation-and-pro-fibrotic-signatures/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/urine-proteomics-in-class-ii-lupus-nephritis-reveals-immune-activation-and-pro-fibrotic-signatures/