Session Information
Date: Sunday, October 26, 2025
Title: (0280–0305) Muscle Biology, Myositis & Myopathies – Basic & Clinical Science Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Juvenile dermatomyositis (JDM) is an autoimmune vasculopathy affecting muscle, skin, and vasculature. Core set measures (CSM) assess disease activity and damage, and guide treatment. However, CSMs can be time consuming and provider dependent. Type I and II interferon (IFN) signatures correlate with disease activity. Some metabolites in the urine of children with rheumatic diseases reflect IFN activity. We aim to assess correlations between CSMs of disease activity and damage and urinary metabolites reflective of IFN activity kynurenine pathway, oxidative stress, intracellular micronutrient status, or neurotransmitter production in JDM. We hypothesize that urine metabolite concentrations correlate with JDM clinical disease.
Methods: This was a cohort study at the National Institutes of Health in collaboration with Cincinnati Children’s. Inclusion criteria: a) definite or probable JDM per Bohan and Peter criteria in patients ≤18 yrs; and b) disease activity and damage CSMs performed within 3 days of urine and blood collection. Ethos R&D measured concentrations of 10 urine metabolites via mass spectrometry, normalized by urine creatinine. Absolute values of Spearman’s rank correlation coefficient were calculated for each urine biomarker-CSM pair and each serum/plasma biomarker-CSM pair then sorted by the root mean square (RMS) to determine individual strongest disease predictors. Activity and damage CSMs were separated, and RMS calculated to determine predictors for activity and damage.For each CSM, we performed linear regression with independent coefficients for each urine metabolite. CSM values were plotted against predicted CSM values and R2 was calculated. We excluded patients with urine metabolite concentrations with a Z-score >5 (n=1).
Results: Demographics and clinical characteristics of 33 patients are shown in Table. Figure 1 shows urine metabolites and plasma biomarkers predictive of disease activity and damage across the CSMs. Quinolinate (QA) (RMS=0.42), homocysteine (HYCS) (RMS=0.35) kynurenate (KYNA) (RMS=0.34), and 5-HIAA (RMS=0.31) are most predictive of disease activity and damage. QA (RMS=0.44,0.38), KYNA (RMS=0.36. 0.28), HYCS (RMS=0.34, 0.33), 5-HIAA (RMS=0.32, 0.27), and vanilmandelate (VMA) (RMS=0.31, 0.25) correlate best with activity and damage measures, respectively.Creatinine (RMS=0.44, 0.33), von Willebrand Factor Antigen (VWF Ag) (RMS=0.35, 0.32), and total protein (RMS=0.31, 0.39) correlate best with disease activity and damage measures, respectively. Urine biomarkers outperform serum/plasma biomarkers, namely total protein (RMS=0.36) and VWF Ag (RMS=0.31). Urine biomarkers showed strong correlations with CSMs in linear regression models (Figure 2), highest for MMT26 (R2=0.74), DAS (R2=0.70), MMT15 (R2=0.67), and Physician Global Activity (R2=0.65).
Conclusion: We report strong correlations between clinical measures of JDM disease activity and damage and 10 urine metabolites, many in the kynurenine pathway. 5 of these reflect disease status individually. This first step toward identifying urine biomarkers of disease activity and damage in JDM may facilitate non-invasive methods for disease monitoring and clinical decision-making.
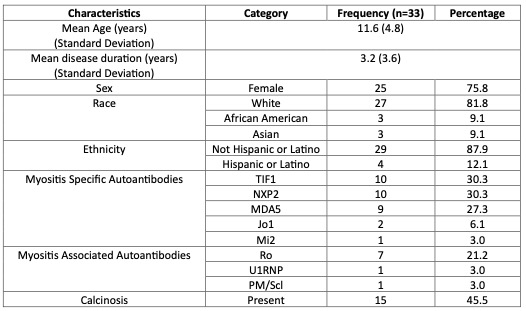 Table. Patient demographics and clinical characteristics at time of sample collection. Patients were in varying stages of their disease course.
Table. Patient demographics and clinical characteristics at time of sample collection. Patients were in varying stages of their disease course.
.jpg) Figure 1. Heatmap of the absolute value of Spearman’s rank correlation coefficient calculated for each urine biomarker-core set measure (CSM) pair (top block), and each serum or plasma biomarker-CSM pair (bottom block) for comparison. Urine metabolites are sorted from top to bottom by the root mean square (RMS) of Spearman’s rank correlation coefficient to demonstrate the individually strongest predictors of disease activity and damage. VWF = von Willebrand Factor; LDH = lactate dehydrogenase. CDASI = Cutaneous Dermatomyositis Disease Area and Severity Index; CHAQ = Childhood Health Assessment Questionnaire; CMAS = Childhood Myositis Assessment Scale; DAS = Disease Activity Score; MDI = Myositis Damage Index; MMT = Manual Muscle Testing.
Figure 1. Heatmap of the absolute value of Spearman’s rank correlation coefficient calculated for each urine biomarker-core set measure (CSM) pair (top block), and each serum or plasma biomarker-CSM pair (bottom block) for comparison. Urine metabolites are sorted from top to bottom by the root mean square (RMS) of Spearman’s rank correlation coefficient to demonstrate the individually strongest predictors of disease activity and damage. VWF = von Willebrand Factor; LDH = lactate dehydrogenase. CDASI = Cutaneous Dermatomyositis Disease Area and Severity Index; CHAQ = Childhood Health Assessment Questionnaire; CMAS = Childhood Myositis Assessment Scale; DAS = Disease Activity Score; MDI = Myositis Damage Index; MMT = Manual Muscle Testing.
.jpg) Figure 2. For each core set measure (CSM), linear regression models were calculated with independent coefficients for each of the urine biomarkers, normalized by urine creatinine. Measured CSM values on the x axes were plotted against model-predicted CSM values on the y axes, and an R2 was calculated based on goodness of fit to the ideal model y=x (dotted line). CDASI = Cutaneous Dermatomyositis Disease Area and Severity Index; CHAQ = Childhood Health Assessment Questionnaire; CMAS = Childhood Myositis Assessment Scale; DAS = Disease Activity Score; MDI = Myositis Damage Index; MMT = Manual Muscle Testing.
Figure 2. For each core set measure (CSM), linear regression models were calculated with independent coefficients for each of the urine biomarkers, normalized by urine creatinine. Measured CSM values on the x axes were plotted against model-predicted CSM values on the y axes, and an R2 was calculated based on goodness of fit to the ideal model y=x (dotted line). CDASI = Cutaneous Dermatomyositis Disease Area and Severity Index; CHAQ = Childhood Health Assessment Questionnaire; CMAS = Childhood Myositis Assessment Scale; DAS = Disease Activity Score; MDI = Myositis Damage Index; MMT = Manual Muscle Testing.
A. Disease Activity CSMs: Physician Global Activity, Patient Global Activity, DAS, CDASI Total Activity.
B. Muscle Strength and Function CSMs: MMT15, MMT26, CMAS, CHAQ Disability Index, CHAQ Pain.
C. Disease Damage CSMs: Physician Global Damage, MDI Total Extent, MDI Total Severity, CDASI Total Damage.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
O'Connor S, Brunner H, Gunn J, Farhadi P, Phillips C, Rider L, Grom A, Angeles-Han S. Urine Kynurenine Pathway Biomarkers Correlate with Disease Activity and Damage Core Set Measures in JDM [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/urine-kynurenine-pathway-biomarkers-correlate-with-disease-activity-and-damage-core-set-measures-in-jdm/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/urine-kynurenine-pathway-biomarkers-correlate-with-disease-activity-and-damage-core-set-measures-in-jdm/
