Session Information
Date: Monday, November 9, 2020
Title: SLE – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes Poster III: Bench to Bedside
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Tubulointerstitial disease (TID), defined as tubulointerstitial inflammation (TII) or interstitial fibrosis/tubular atrophy (IFTA), is associated with progression to end stage renal disease (ESRD) in lupus nephritis. Early detection of TID via non-invasive methods is crucial to identifying those at highest risk for renal failure. A set of urine biomarkers of tubular damage has recently been developed to detect acute kidney injury.1 This study sought to determine whether these biomarkers of tubular injury collected around the time of clinically indicated biopsies for lupus nephritis were associated with the presence of IFTA/TII.
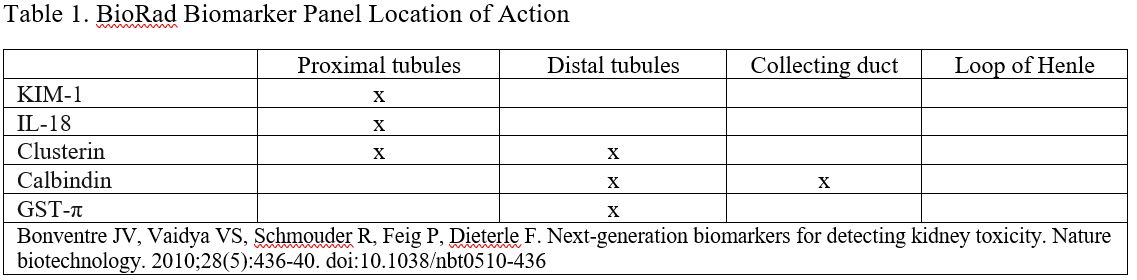
Methods: Urine samples from 29 adult and pediatric lupus patients with clinically indicated renal biopsies performed between 2010 and 2019 were included. Samples were evaluated for tubular injury markers KIM-1, interleukin-18 (IL-18), clusterin, calbindin, and glutathione S-transferase-π (GST- π) using the Bio-Plex ProTM kidney assay. Biomarkers (Table 1) were correlated with presence or absence of IFTA/TII on biopsies performed within 180 days prior to and 21 days after sampling. These biomarkers were normalized to urine creatinine excretion.
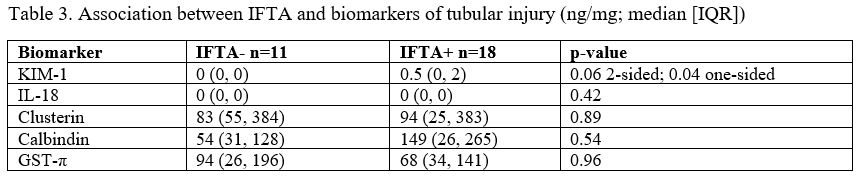
Results: Of 29 patients, 18 (62%) had evidence of IFTA on renal biopsy (Table 2). IFTA+ patients had a median age (IQR) of 36 (27, 50) vs. 20 (14, 59) in the IFTA group, p = 0.25. BMI was significantly higher in IFTA+ patients (median (IQR) 30 (24, 36) kg/m2 vs. 23 (20, 26) kg/m2, p < 0.001), as was blood pressure on day of biopsy. KIM-1 levels were higher when IFTA was present, median (IQR) 0.5 (0, 2) ng/mg vs. 0 (0, 0) ng/mg for IFTA+ and IFTA-, respectively, one sided p-value 0.04. KIM-1 was detectable ( > 0) in 9 (50%) of IFTA+ and in 2 (18%) IFTA-, p = 0.09. No association between KIM-1 and TII was observed. There was no association between the other 4 biomarkers and IFTA or TII (Table 3). KIM-1 levels did not differ by age, sex, race, ethnicity, or lupus nephritis class, and were not associated with serum C3, C4, or dsDNA at time of sample collection. KIM-1, calbindin, GST-π and clusterin were associated with proteinuria.
Conclusion: Though limited by sample size, these pilot results suggest that urinary KIM-1, a kidney injury marker secreted by the proximal tubules, in samples collected around the time of biopsies may serve as a non-invasive biomarker for the presence of IFTA in lupus nephritis.
Reference:
- Stephen L, et al. Profiling of Human, Canine, and Rat Urine Samples Using Bio-Plex ProTM RBM Kidney Toxicity Assays. Available from: http://www.bio-rad.com/webroot/web/pdf/lsr/literature/Bulletin_6400.pdf
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Lally B, Wang S, Chalmers S, Mowrey W, Rubinstein T, Goilav B, Broder A. Urine Biomarkers of Tubulointersitital Damage in Lupus Nephritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/urine-biomarkers-of-tubulointersitital-damage-in-lupus-nephritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/urine-biomarkers-of-tubulointersitital-damage-in-lupus-nephritis/