Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 13, 2022
Title: SLE – Diagnosis, Manifestations, and Outcomes Poster II: Manifestations
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 1:00PM-3:00PM
Background/Purpose: T cells play a critical role in the pathogenicity of SLE and lupus nephritis (LN). Hence, identifying T cell co-stimulatory pathways and mediators that correlate with disease activity may significantly aid in the development of biomarkers applicable for clinical use, and help identify novel therapeutic targets. We found that expression of CD6 (on T cells) and ALCAM (on antigen presenting cells and on tubular cells) is upregulated in the kidneys in LN mouse models and that blockade of the pathway using an anti-CD6 monoclonal antibody significantly reduced the severity of kidney involvement, implicating an important role for the CD6-ALCAM pathway in the development of LN. Furthermore, we found that soluble urine ALCAM is significantly elevated in patients with LN. Here, we expand upon the previous analyses by evaluating urine ALCAM as a predictor of nephritis progression and/or resolution.
Methods: Patient urine and serum samples were acquired through the Accelerating Medicines Partnership (AMP), a public-private partnership to accelerate discovery and development of therapeutics for autoimmune diseases. Samples were obtained from patients with biopsy proven LN and living kidney donor controls and longitudinal sampling (0, 3, 6, and 12 months) was available for 143 LN patients. Soluble levels of ALCAM were quantitated by ELISA, CD6 levels by a proprietary ECL assay, and urine creatinine from the same urine sample was measured by an improved Jaffe method. Urine ALCAM or CD6 levels were then normalized to urine creatinine levels on a pg (ALCAM or CD6) per mg creatinine basis. Responder status (complete response (CR), partial response (PR), no response (NR)) was as determined by AMP. In a separate analysis, responder and non-responder status was determined by change in UPCR where responders showed a decrease in UPCR of greater than 50% from the selected starting point.
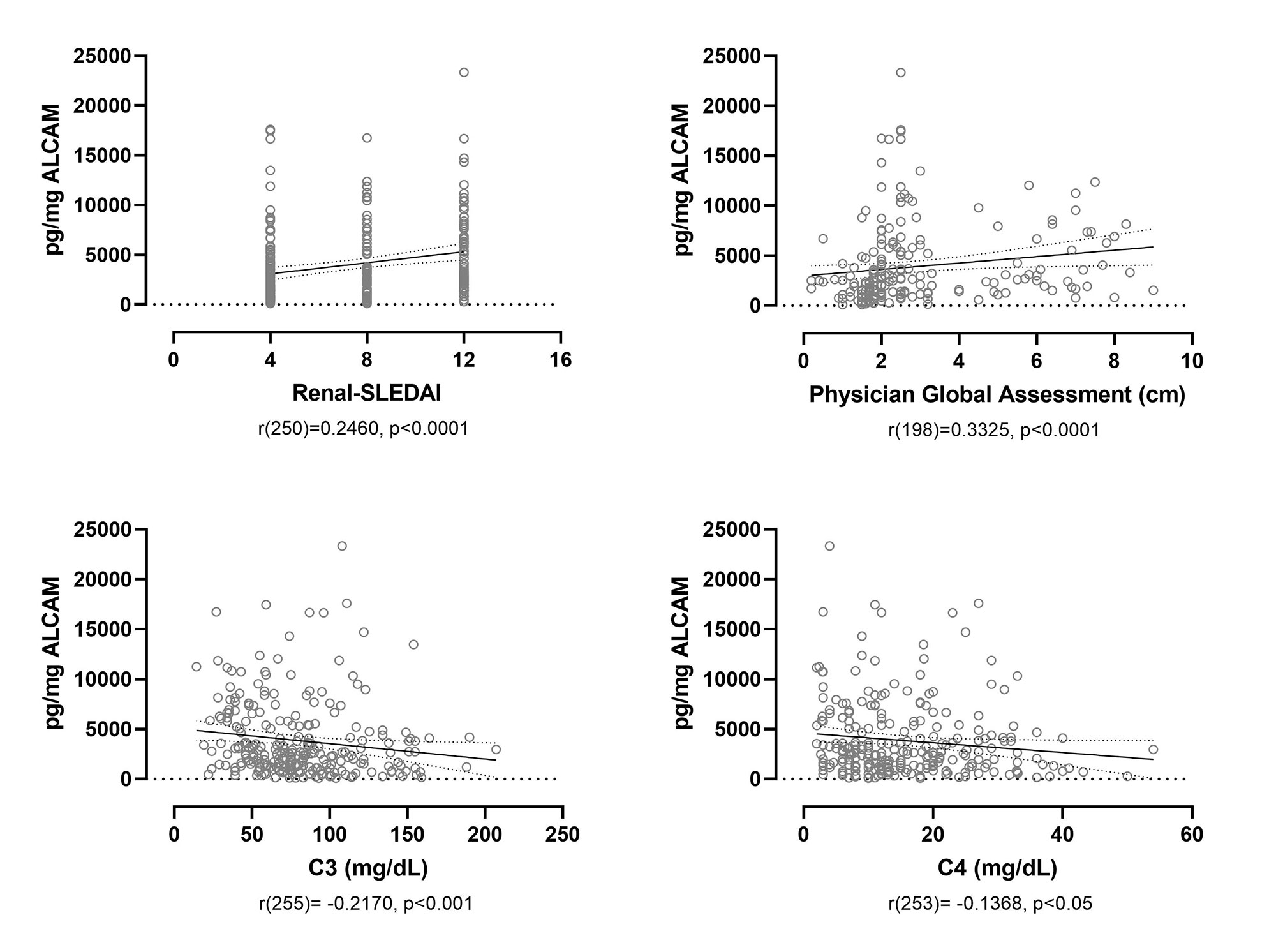
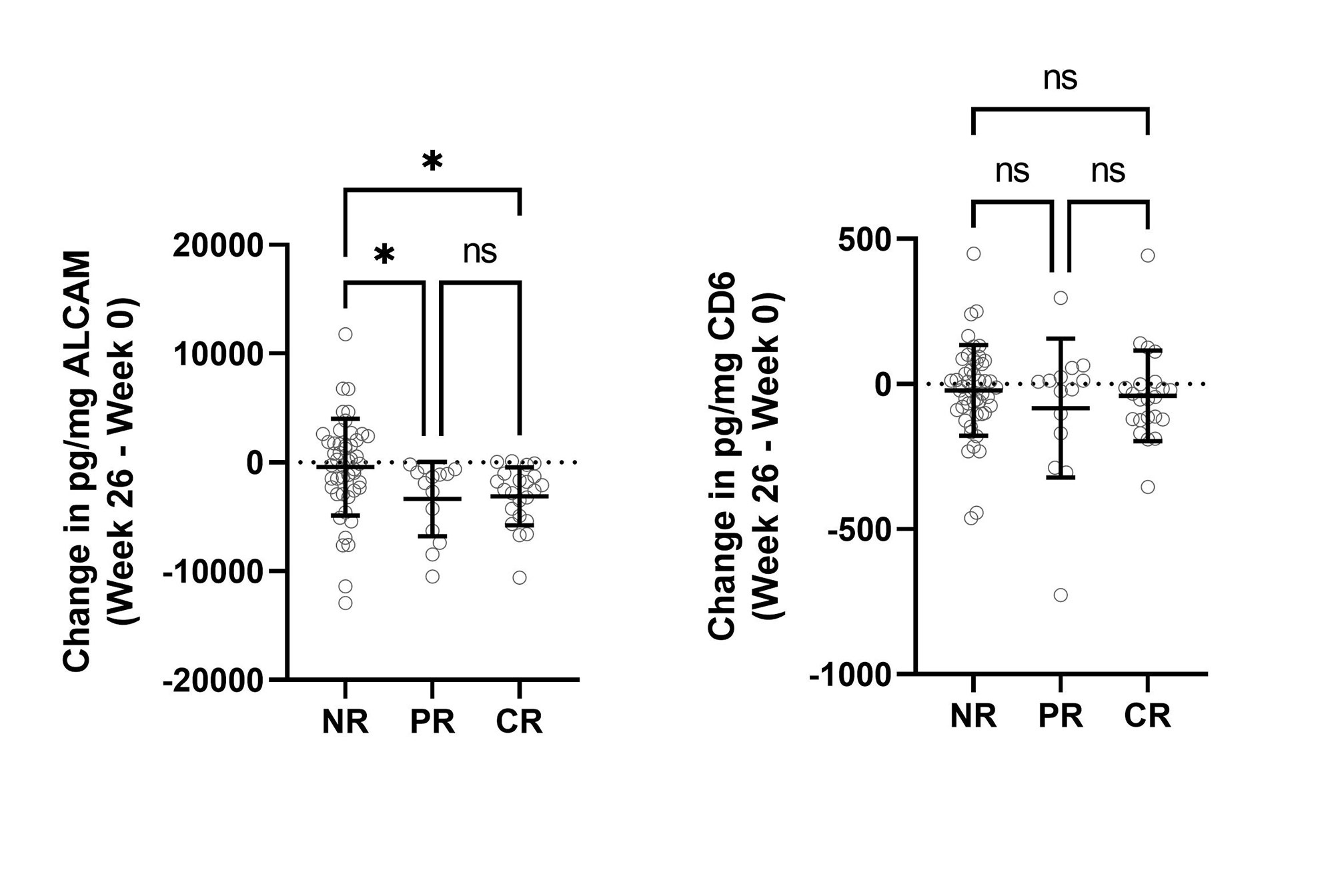
Results: Cross-sectional analysis at baseline/week 0 showed that urine ALCAM significantly correlated with renal-SLEDAI (r(250) = 0.2460, p< 0.0001), the Physician Global Assessment (PGA) score (r(198) = 0.3325, p< 0.0001), and negatively with serum C3 (r(255) = -0.2170, p< 0.001) and C4 (r(253) = -0.1368, p< 0.05) (Figure 1). A receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve was used to assess the sensitivity and specificity of urine ALCAM and CD6 as predictors of LN compared to healthy controls. Urine ALCAM is a strong predictor of active LN with an area under the curve (AUC) of 0.9781, compared to urine CD6 with an AUC of 0.7168. To evaluate longitudinal changes in urine ALCAM or CD6 and their associations with response status, the change between week 0 and week 26 was determined and related back to response status. Partial and complete responders experienced a significant reduction in urine ALCAM compared to non-responders, irrespective of the type of treatment, while urine CD6 did not distinguish between these groups (Figure 2).
Conclusion: Urinary ALCAM is a biomarker of disease severity in LN that could be indicative of a patient’s response to treatment. Analyses are in progress to evaluate ALCAM in combination with other measures of disease severity to predict longer term disease outcomes.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Chu D, Schwartz N, Ampudia J, Guthridge J, James J, Buyon J, Connelly S, Fung M, Ng C, consortium A, Petri M, Mohan C, Putterman C. Urine ALCAM Is a Strong Predictor of Lupus Nephritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/urine-alcam-is-a-strong-predictor-of-lupus-nephritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/urine-alcam-is-a-strong-predictor-of-lupus-nephritis/