Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: B cell activating factor (BAFF) and a proliferation-inducing ligand (APRIL) are cytokines that signal through transmembrane activator and CAML interactor (TACI), B cell maturation antigen (BCMA), and/or BAFF-Receptor (BAFF-R) and play important roles in B cell development, proliferation, function, and survival. Therapeutic agents targeting BAFF and/or APRIL have demonstrated promising clinical potential in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), lupus nephritis, and other B cell-related diseases, but have generally targeted only BAFF, only APRIL, or predominantly BAFF. Due to the overlapping and non-redundant roles of BAFF and APRIL, more potent and/or complete inhibition of both cytokines is likely required for optimal efficacy. Povetacicept is an Fc fusion protein of a variant TACI domain engineered to have enhanced affinity for BAFF and APRIL, providing more potent dual inhibition of both BAFF and APRIL than wild type (WT) TACI-Fc or BAFF- or APRIL-specific antibodies. In preclinical mouse lupus models povetacicept suppressed autoantibodies, renal IgG deposition, and nephritis.1
Methods: Publicly available RNA Sequencing (RNA-Seq) datasets from healthy donors and SLE subjects were utilized to assess APRIL and BAFF gene expression.2-4 Primary B cells isolated from healthy donor PBMCs were stimulated with CD40L for 72 hours, washed and then cultured for an additional 24 hours with 5 nM APRIL and 10 nM BAFF in the presence of either 100 nM of Fc control, povetacicept, anti-BAFF mAb (belimumab), or anti-APRIL mAb. Cultured B cells were then harvested for flow cytometry analysis or processed for bulk RNA-seq.
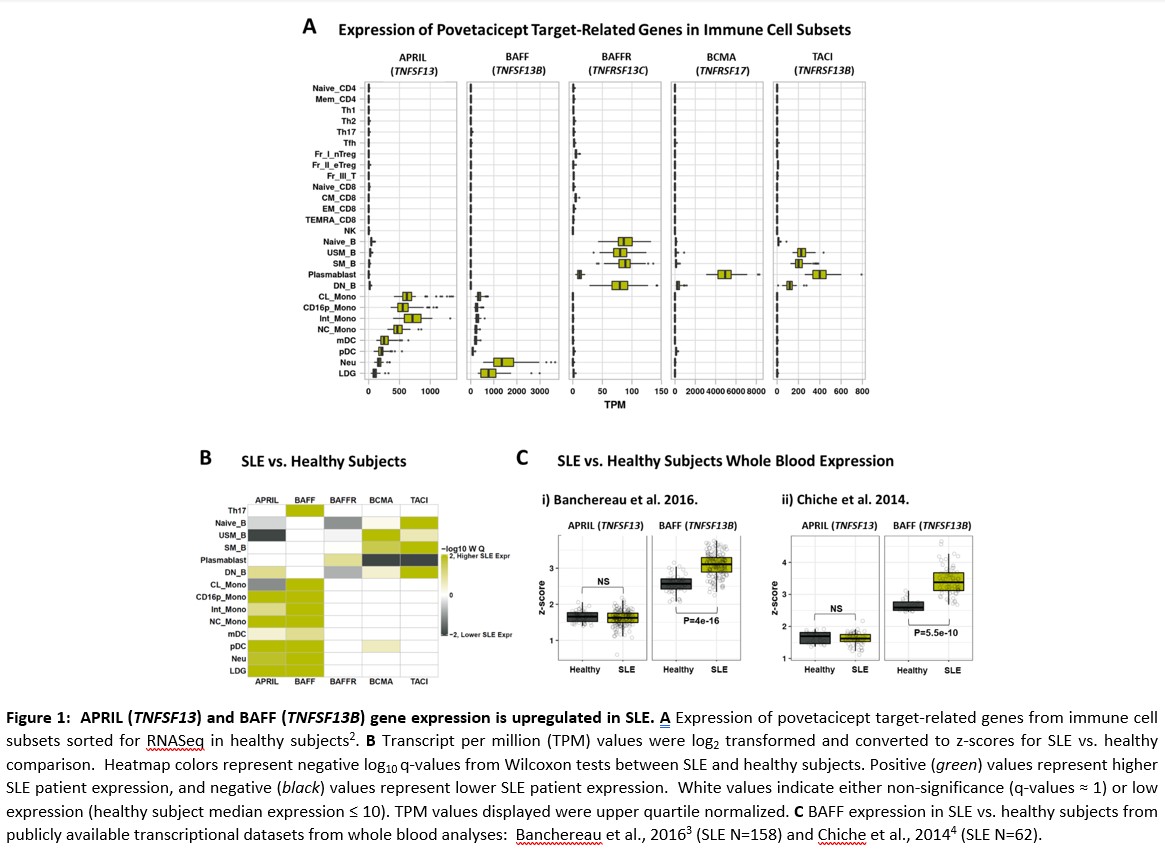
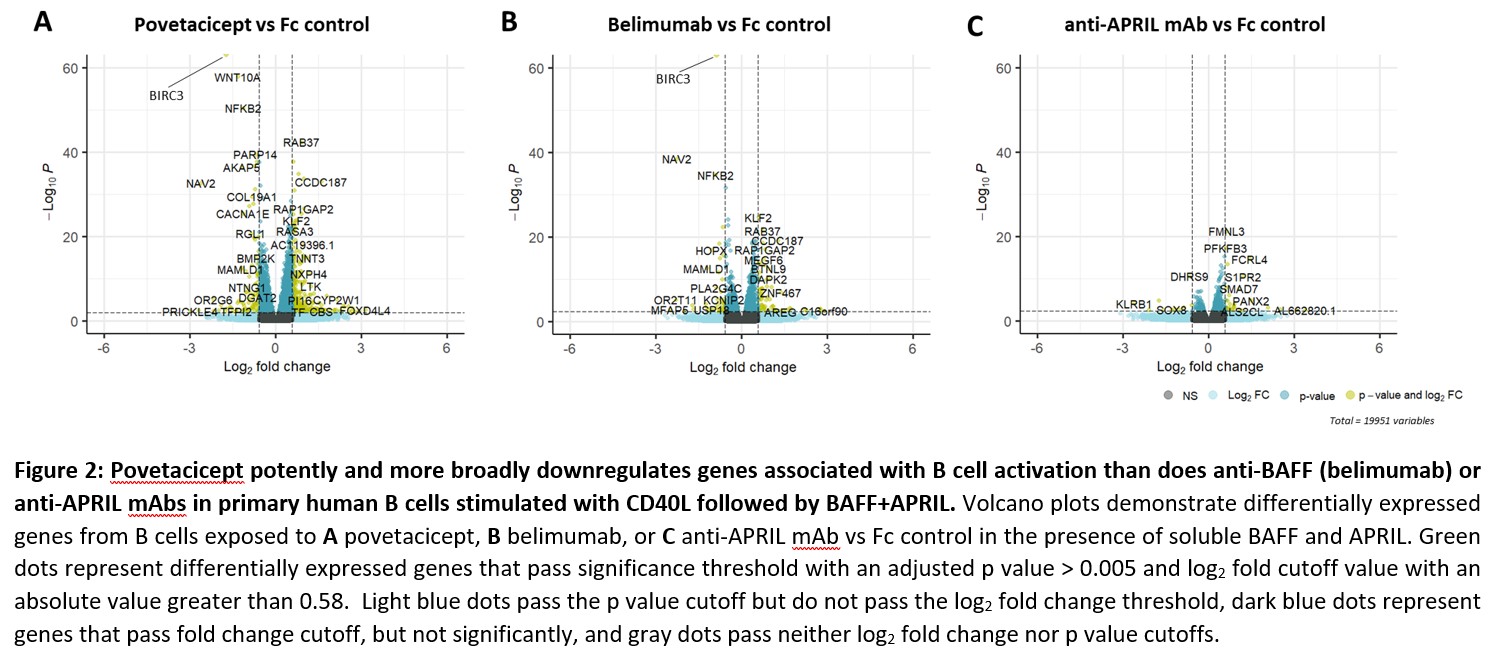
Results: In publicly available transcriptional datasets, SLE patients showed a significant elevation of only BAFF in whole blood compared to healthy adults, but specific analysis of cell types known to be associated with SLE pathogenesis revealed upregulation of both APRIL and BAFF (Fig 1). Genes associated with B cell activation, regulation of immunoglobulin production, and adaptive immunity were upregulated in primary B cells cultured with CD40L, BAFF, and APRIL. Povetacicept potently suppresses inflammatory pathways, significantly more broadly than mAbs targeting BAFF or APRIL alone (Fig 2).
Conclusion: Dual inhibition of both BAFF and APRIL may be required to achieve optimal suppression of pathogenic pathways associated with SLE and related diseases. When coupled with data from the literature, these results further support the clinical evaluation of dual BAFF/APRIL inhibitors such as povetacicept in SLE, as well as in other B cell- and/or autoantibody-related diseases. Clinical studies of povetacicept in autoimmune glomerulonephritis (NCT05732402) and cytopenias (NCT05757570) have been initiated; a study in SLE is in preparation.
1 Evans L, et al. 2023 Jan 27. Arthritis Rheumatol. Online ahead of print.
2 Ota M, et al. 2021. Cell. 184(11): 3006-21.
3 Banchereau R, et al. 2016. Cell. 165(6): 1548-1550.
4 Chiche L, et al. 2014. Arthritis Rheumatol. 66(6): 1583-95.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Blair T, Repash E, Bankhead A, Enstrom A, Evans L, Debrot S, Chunyk A, Mudri S, Peng S, Dillon S. Upregulation of Both APRIL and BAFF in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Suggests Non-Redundant Roles, Further Revealed by Dual Inhibition with Povetacicept (ALPN-303; TACI vTD-Fc) [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/upregulation-of-both-april-and-baff-in-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-suggests-non-redundant-roles-further-revealed-by-dual-inhibition-with-povetacicept-alpn-303-taci-vtd-fc/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/upregulation-of-both-april-and-baff-in-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-suggests-non-redundant-roles-further-revealed-by-dual-inhibition-with-povetacicept-alpn-303-taci-vtd-fc/