Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 6:00PM-7:00PM
Background/Purpose: Systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis (SJIA) associated lung disease (SJIA-LD) is an emerging and life-threatening clinical problem. Despite recent advances, there remain key unanswered questions regarding prevalence, pathogenesis, influence of biologics, and outcomes, and prospective clinical and laboratory characterization of SJIA-LD is needed.
The objective is to define baseline clinical and laboratory features of patients with SJIA-LD enrolled in the CARRA Registry SJIA-LD cohort.
Methods: Existing or newly enrolled CARRA Registry patients with SJIA and suspected, probable, or definite SJIA-LD were included in the cohort. In addition to standard Registry data, lung disease specific data was obtained at baseline and at 6-month follow-up visits using a standardized case report form through REDCap Cloud. This study was approved by the DCRI Reliant IRB and/or IRB of all Registry sites.
Results: As of January 2023, 36 patients were enrolled in the cohort from 16 CARRA Registry sites. 46% had definite (biopsy-proven), 36% probable, and 18% suspected SJIA-LD. 22 patients had LD data available. Of those, 23% underwent lung biopsy: all had pulmonary alveolar proteinosis (PAP) and interstitial inflammation, and 40% had collagenous fibrosis. 77% had at least one definite episode of macrophage activation syndrome (MAS) (including 64% which met the 2016-SJIA-MAS criteria), 73% had more than one MAS episode, and 32% had subclinical MAS. MAS occurred prior to SJIA-LD diagnosis in 68% and coincided with it in 18%. The demographic and clinical features at the baseline CARRA Registry visit are shown in Table 1. Median (IQR) values of selected labs at the baseline visit were as follows: AST: 42 U/L (34-62), CRP: 0.5 mg/dl (0.9-3.8), ESR: 16.5 mm/hr (8-56), Wbcs: 10*10^9/L) (7.6-14.7) Hb: 11.6 g/dl (10.9-12.7), Plt: 310 *10^9/L) (268-401), IL-18: 24,336 pg/mL (4,147- 49,275).
Conclusion: The CARRA SJIA-LD cohort represents a broad spectrum of clinical features which commonly includes clubbing, cough, tachypnea, dyspnea, and PAP in all patients who underwent a biopsy. Recurrent MAS was a common clinical feature in patients who developed LD. We plan to continue enrolling patients to fully characterize the clinical features of SJIA-LD, longitudinal disease progression and trajectories, and associated immune biomarkers and cellular populations associated. This cohort will serve as an ongoing prospective cohort study for future clinical and translational research in this emerging disease.
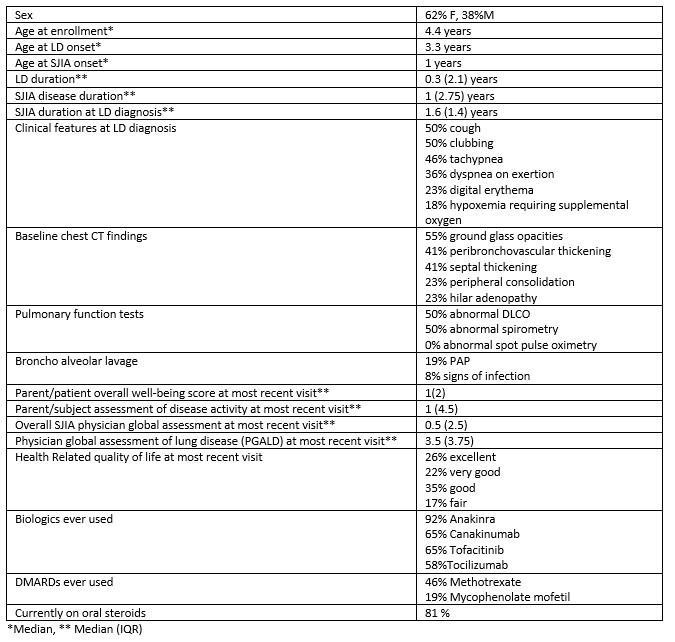 Table 1: Demographic and clinical features of patients in the SJIA-LD cohort
Table 1: Demographic and clinical features of patients in the SJIA-LD cohort
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Eloseily E, Chang M, Riordan M, Russell a, Natter M, Kimura Y, Schulert G. Update of Clinical and Laboratory Features of the Childhood Arthritis and Rheumatology Research Alliance (CARRA) Systemic Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis-Associated Lung Disease (SJIA-LD) Cohort [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 4). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/update-of-clinical-and-laboratory-features-of-the-childhood-arthritis-and-rheumatology-research-alliance-carra-systemic-juvenile-idiopathic-arthritis-associated-lung-disease-sjia-ld-cohort/. Accessed .« Back to 2023 Pediatric Rheumatology Symposium
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/update-of-clinical-and-laboratory-features-of-the-childhood-arthritis-and-rheumatology-research-alliance-carra-systemic-juvenile-idiopathic-arthritis-associated-lung-disease-sjia-ld-cohort/
