Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 15, 2016
Title: Spondylarthropathies Psoriatic Arthritis – Pathogenesis, Etiology - Poster II
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: The spondyloarthritides (SpA) are a group of chronic inflammatory disorders involving the axial spine and the peripheral joints. Genetic, functional and clinical trial evidences suggest an important role for IL17A within the context of type 17 immunity. This study aims to understand the different components of the type 17 immune axis in patients with SpA compared to healthy controls.
Methods: Peripheral blood was obtained (with ethical approval and informed consent) from 38 patients with SpA, 17 age and sex matched healthy donors, and 14 patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) matched for CRP. Mononuclear cells were analyzed by flow cytometry using a multicolor antibody panel staining surface phenotypic markers and intracellular cytokines.
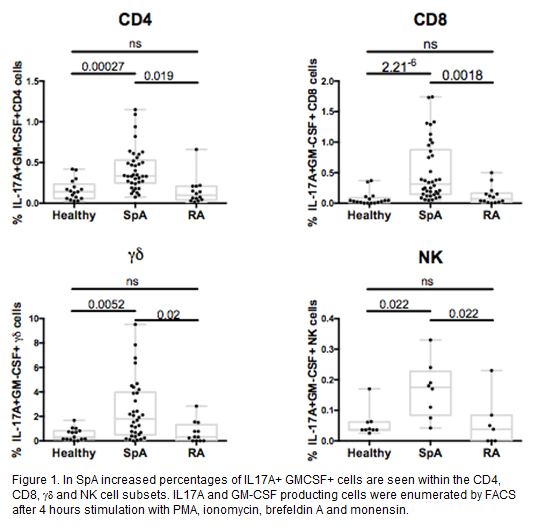
Results: Patients with SpA had a higher percentage of CD4 Th17 cells than healthy controls (mean±SD) (1.27±0.69 vs 0.67±0.41%; p<0.001). The production of IL17A in the CD8 (1.30±1.01 vs 0.40±0.45%; p<0.001) and in the γδ T cell compartment (4.86±7.04 vs 1.01±0.85%; p<0.001) was also higher in SpA than controls. Within the type 17 axis, polyfunctional cells coexpressing IL17A and GM-CSF were increased in the CD4, CD8, γδ and NK compartment in SpA, compared to healthy controls and Rheumatoid Arthritis patients (Figure 1). Analysis of the regulatory T cell pool showed a similar frequency of Tregs in the peripheral blood of SpA patients compared to healthy controls (SpA: 5.4±2.5% vs 4.7±1.9%; p=0.22), although in patients, Tregs appeared enriched in the synovial fluid compared to the peripheral blood (mean of difference±SEM: 8.8±1.3%, p<0.01).
Conclusion: Immunophenotypic analysis of the peripheral blood of SpA patients shows increased levels of type 17 immunity across multiple lymphocyte compartments, with a specific increase of polyfunctional cells coexpressing IL17A and GM-CSF. This broad skewing towards type 17 immune response in SpA supports an important role in disease.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Simone D, Al Mossawi H, Ridley A, De Wit J, Sekine T, Ansar N, Doig K, Bowness P. Type 17 Immunity in Spondyloarthritis Is Expanded Across Multiple Lymphocyte Subsets [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/type-17-immunity-in-spondyloarthritis-is-expanded-across-multiple-lymphocyte-subsets/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/type-17-immunity-in-spondyloarthritis-is-expanded-across-multiple-lymphocyte-subsets/